If you or someone you know struggles with rheumatoid arthritis, you’re likely searching for the newest treatment options to manage this chronic condition. For unknown causes, more women get RA than men, and the condition usually develops around middle age. For some, having a family member with RA increases the odds of developing RA later in life. Genetic screening is available to test for hereditary autoimmune diseases. In the last decade, there have been significant advancements in stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. This groundbreaking treatment has already had a substantial impact on patients suffering from this debilitating chronic disease [1].
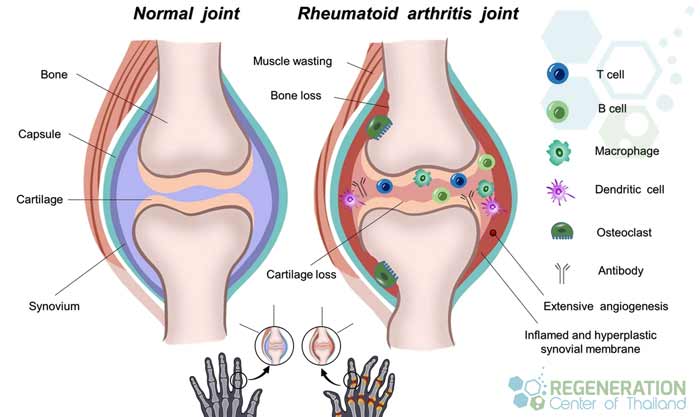
In healthy people, the immune system helps to fight invaders, such as viruses and bacteria. With autoimmune diseases like RA, the immune system mistakes their cells as foreign invaders and then releases inflammatory target chemicals to attack their cells. Tn RA attacks the synovium tissue lining around joints, which generally helps produce a fluid that keeps our joints moving smoothly. Over time, the chronically inflamed synovium gets slightly thicker, making the joint area feel painful, red, swollen, and tender. For most, moving those joints becomes difficult [2].
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation, leading to pain, swelling, stiffness, and damage. Over time, RA can also affect other organs in the body, leading to various complications. Scientists aren’t exactly sure why some people develop RA. Some research shows that these individuals might have specific genes that can be activated or triggered based on the environment. Bacterial and viral exposure and physical and emotional stress are external factors that can cause an autoimmune attack.
Treatments for Rheumatoid Arthritis in 2025
Current treatments for rheumatoid arthritis primarily focus on managing symptoms and slowing the progression of the disease. These treatments can include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Corticosteroids
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- Biologic agents
- Physical therapy and exercise
Although these treatments can provide some relief, they often come with side effects and may not be effective for everyone. This has led researchers to explore alternative treatment options, such as stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis and for treating other orthopedic joint degeneration ( sports injuries ) in the shoulders, hips, knees, lower back, neck, and spinal cord.
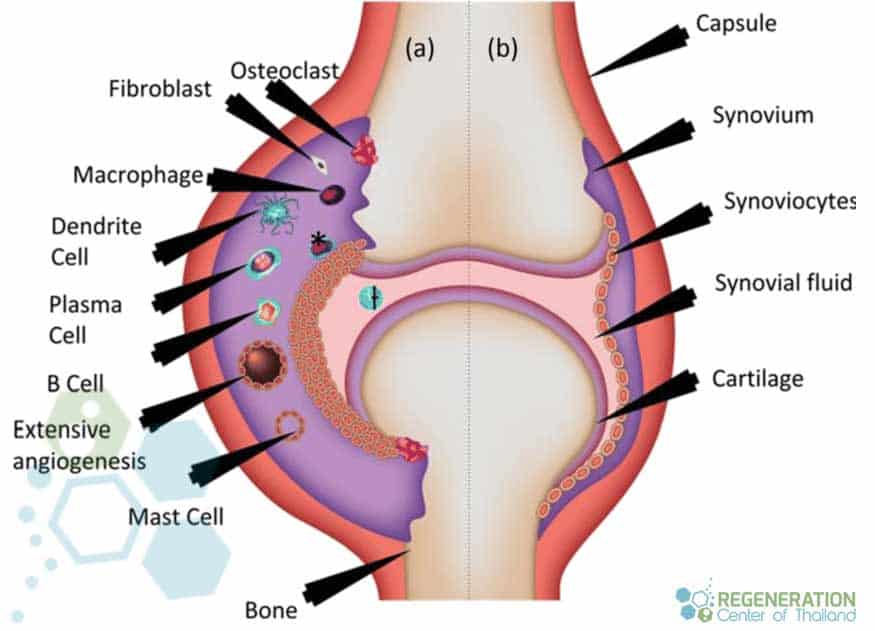
Does stem cell therapy work for rheumatoid arthritis?
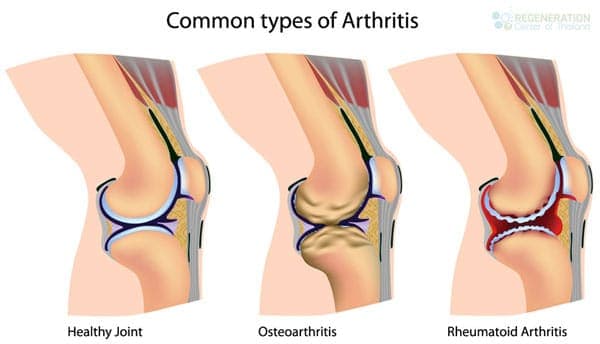
The integrity of your cartilage could slowly wear down to the point of daily mild to severe pain. Osteoarthritis may also affect the hips, knees, spinal column, and most notably, the finger articulations of your hands. Some people encounter extreme stiffness and pain, and in severe cases, the degenerative joint condition of rheumatoid arthritis can easily result in severe deformities in the affected locations. Learn more about tissue engineering and the basics of stem cell therapies.
Modulation of Immune Function
RA, or Rheumatoid arthritis, is an orthopedic disease generally occurring in men and women over 40. RA is a long-term degenerative ailment that has significant effects on the joint tissues in the hands, feet, and arms. People dealing with rheumatoid arthritis may typically live with the disease for years without even knowing they have it. Stem cell research has shown that as RA progresses, the severe destruction of your joints will undoubtedly get considerably worse. Learn more about the rheumatoid arthritis diet.
The Regeneration Center protocol for treating rheumatoid arthritis, Hashimoto’s Disease, spinal arthritis, connective tissue disease, spinal stenosis, inclusion body myositis, Ocular Myasthenia gravis MG, osteoporosis and osteoarthritis are based on evidence-based research and allows for higher success rates, higher cell viability and longer-term improvements and pain management. Our unique msc+ stem cell therapy takes a natural regenerative approach to symptom relief. It uses enhanced Mesenchymal cells (expanded) with paracrine cell signaling growth factors & chondrocyte implantation to rapidly and successfully fix the impaired cells in your body [3].
The Role of Stem Cells in Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Stem cells are unique cells in the body that can self-renew and differentiate into specialized cell types. This exceptional property makes them an attractive option for regenerative medicine and treating various diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, Sjogren’s syndrome, Type 1 diabetes, T2D, kidney disease, IBD Crohn’s Disease, pancreatitis, ALS, Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, strokes, multiple sclerosis, and cystic fibrosis.
Types of Stem Cells for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Several types of stem cells have been used in clinical trials of stem cells for rheumatoid arthritis:
- Embryonic stem cells (ESCs)
- Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
- Adult stem cells, including isolated cord tissue mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs)from peripheral blood [4].
Clinical Evidence Stem Cell Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The results of several clinical studies have shown that Isolated MSC stem cell therapy did not cause any adverse effects for patients and resulted in clinically verifiable improvements in the following areas:
- Reduction of chemokines and inflammatory cytokines
- Increase in overall percentage of Regulatory T cells that suppress immune responses ( levels measured with peripheral blood)
- Improvements in upregulation of IL-4-producing Th2 cells – Th2 cells help to mediate activation levels and maintenance of immune response against bacteria, extracellular parasites, toxins & allergens. Th2 cells also help mediate functions by producing several types of cytokines including Interleukin 4 (IL-4), Interleukin 5 (IL-5), Interleukin 6 (IL-6), Interleukin 9 (IL-9), Interleukin 13 (IL-13), Interleukin 17 (IL-17E) and Interleukin 25 (IL-25).
- Over 65% of patients showed significant disease remission based on ACR criteria & = DAS28 scores six months after treatment.
- The results also show that MSC stem cells can have long-term beneficial effects up to 36 months after therapy.
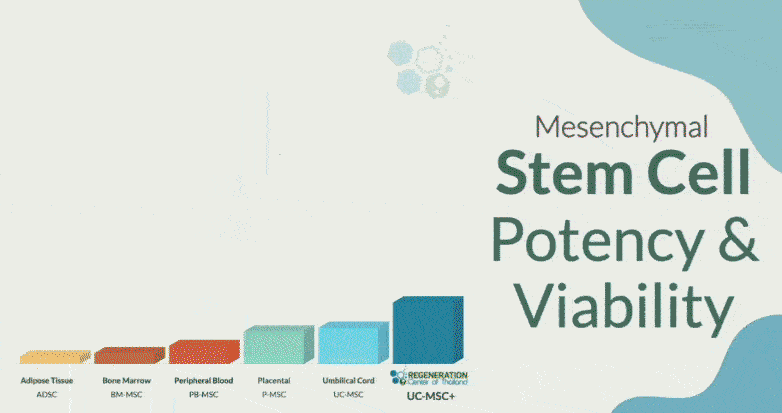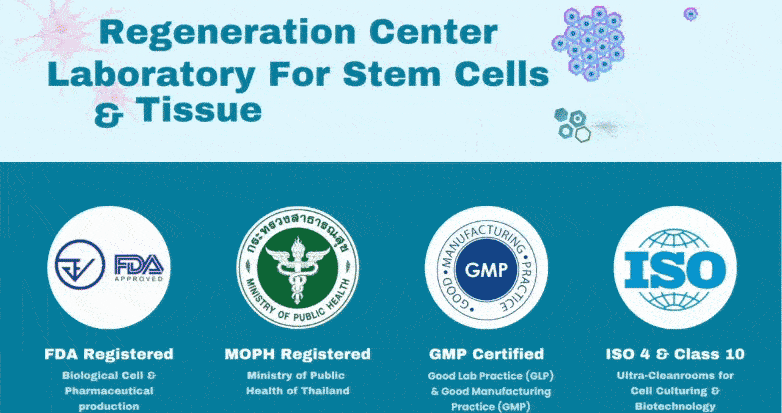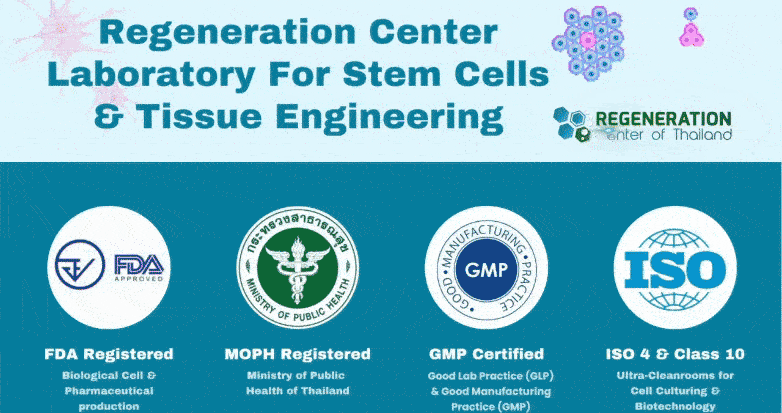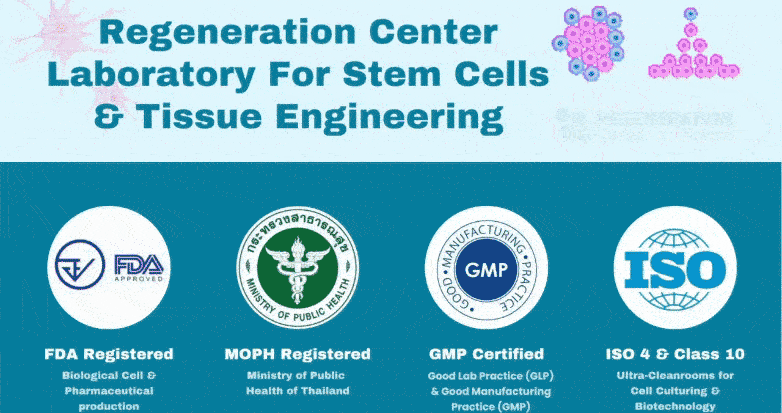
UC-MSC+ stem cells have gained significant attention in recent years due to their anti-inflammatory, cell signaling, and immunomodulatory properties, making them a promising option for treating rheumatoid arthritis. The Regeneration center protocol for RA uses proprietary methods that allow for a 25X increase in the immunomodulatory effects of Isolated MSC Stem cells for RA utilizing a combination of tissue-specific growth factors, priming by pro-inflammatory cytokines, autophagy, and hypoxia over a 2-week protocol[5].
Understanding Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR)
Polymyalgia rheumatica is often misunderstood, leading to unnecessary pain and suffering. PMR is a debilitating condition that causes muscle pain and stiffness, mainly in the shoulders and hips of those over 50. Effective management is essential to prevent long-term disability and improve quality of life. Recognizing the early symptoms and early detection of PMR can prevent worsening symptoms. Many people mistake early signs, like morning stiffness, for normal aging, but It’s crucial to recognize these symptoms early and consult a healthcare provider for treatment.
Getting an accurate diagnosis misdiagnosis is common in PMR cases, leading to delayed or inappropriate treatments. Diagnostic tests like ESR and CRP can help confirm PMR, differentiating it from other conditions with similar symptoms, like rheumatoid arthritis or fibromyalgia. The standard treatment for PMR is corticosteroids, but dosing needs to be individualized. Too high a dose increases side effects, while too low may not effectively control symptoms. Incorporated physical therapy can help maintain muscle strength and flexibility, preventing long-term stiffness, but many overlook this and rely solely on medications. Patients diagnosed should be monitored for complications as PMR is associated with conditions like heart failure and giant cell arteritis, which require immediate attention. Regular follow-ups and continuous monitoring for symptoms like vision changes or headaches can help prevent serious complications.
Stem Cell Therapy for Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative for managing Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR). Current treatments for PMR, like corticosteroids, can lead to significant side effects and are not always effective in the long term. Patients need to understand Stem Cell Therapy’s potential and limitations. Stem cells have unique regenerative properties that modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. This makes them suitable for conditions like PMR, where inflammation is a primary concern. Stem cell research shows that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) can effectively reduce inflammation in various autoimmune diseases.
A frequent mistake patients make is assuming stem cell therapy is a last resort. However, integrating it earlier in the treatment plan can reduce long-term reliance on steroids. Patients should consult specialists who understand conventional and emerging therapies to make informed decisions.
Stem Cells: A Potential Game-Changer for PMR
Choosing the right stem cell sources, types, and quantities is crucial because not all stem cells are created equal. MSCs derived from bone marrow or adipose tissue can help temporarily; however, umbilical cord tissue (UC-MSC) cells have shown the most promise in treating inflammatory conditions like PMR. Choosing the right stem cell source is critical to maximizing therapeutic benefits. Depending on scale and severity, the Regeneration Center might recommend combining therapies to achieve optimal results. Combining stem cell therapy with conventional treatments can sometimes enhance efficacy and minimize side effects. A multidisciplinary approach involving rheumatologists and regenerative medicine experts can offer the best outcomes. While still in its early stages, stem cell therapy will revolutionize PMR management, providing hope for those seeking alternatives to traditional treatments.
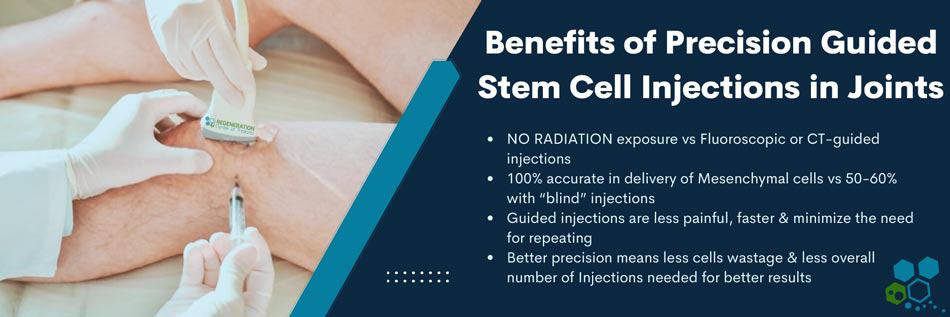
How Does Stem Cell Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Work?
Stem cell treatment for rheumatoid arthritis primarily focuses on utilizing isolated and expanded UC-MSCs cells + cell-specific growth factors to target inflammation and promote tissue repair. The process generally involves: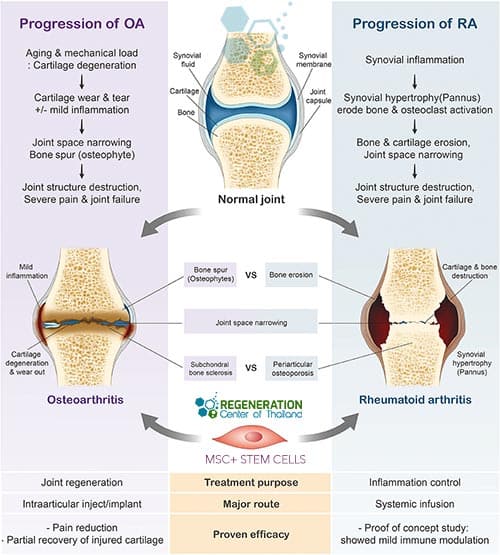
- Harvesting MSCs from the patient’s bone marrow, adipose tissue, or donated umbilical cord tissue
- Processing and expanding the types and quantities of stem cells in a certified stem cell laboratory
- Depending on the patient’s medical needs, the isolated & expanded stem cells are introduced back into the patient’s affected joints or through combinations of intramuscular injections and intravenous infusions
Once inside the body, the isolated MSC cells are growth factors that help to:
- Modulate the adverse immune response and reduce inflammation
- Releasing growth factors and cytokines to promote tissue repair and regeneration
- Inhibiting the formation of scar tissue and promoting the growth of healthy cartilage
Stem cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis has the potential to offer a more comprehensive solution for patients with this chronic condition by addressing both inflammation and joint damage.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note that not all patients are good candidates for treating Rheumatoid Arthritis with stem cells. Patients with severe complications such as advanced joint deformities, significant organ involvement (e.g., interstitial lung disease, rheumatoid vasculitis), or severe cardiovascular disease may not qualify for the estimated treatment protocol.Challenges & Considerations when using Stem Cells for RA
While stem cell therapy holds great promise for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, several challenges and considerations must be addressed and understood:
- Stem cells are not appropriate or effective in all cases. Patients with idiopathic diagnosis, multiple comorbidities, and severe and debilitating chronic pain might not respond well.
- Optimal stem cell source: Determining the best source of isolated UC-MSC Stem cells needed for therapy remains vital for each case. The Regeneration Center offers both autologous and allogeneic stem cell therapies for RA, and each source (bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord tissue) has advantages and drawbacks.
- Standardization of procedures: As the stage and severity of rheumatoid arthritis vary for each patient, there is no standard protocol for using stem cells. The Regeneration Center stem cell protocol can differ depending on the source for harvesting, processing/culturing, and administering the stem cells.
- Cost and accessibility: Isolating and expanding specific types of cells for use in RA treatment can be expensive, and insurance coverage varies widely depending on where patients live. Ensuring accessibility and affordability for patients is essential, and the cost of treating rheumatoid arthritis with stem cells at the Regeneration Center will be provided in detail upon completion of the medical evaluation.
- Regulatory and ethical concerns: The use of stem cells, particularly ESCs and iPSCs, raises moral and regulatory issues that must be addressed before the widespread adoption of these treatments; however, the Regeneration Center does not use or offer Embryonic cells for any treatment.
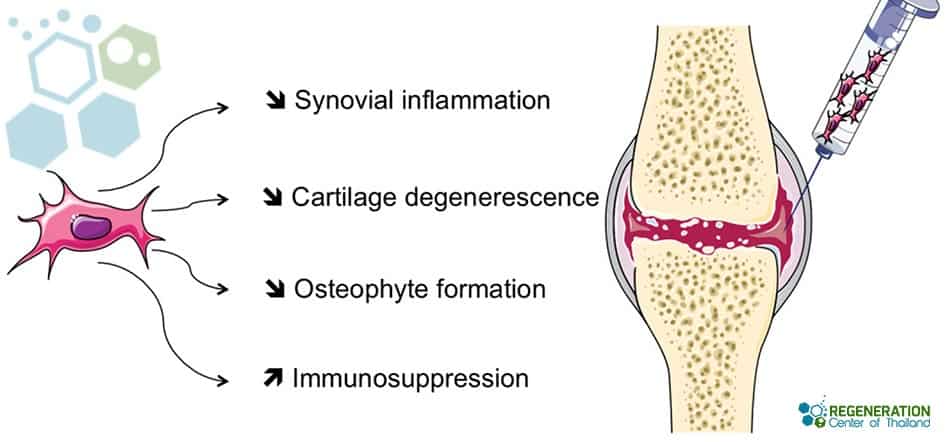
Stem cell treatment for rheumatoid arthritis represents a promising new treatment option that will revolutionize the management of this chronic and debilitating disease. Although we are still in the early stages of stem cell science, the results are encouraging, and we will only continue to get better results over time.
UC-MSC+ Stem Cell treatment for rheumatoid arthritis will require 10-14 days. Due to the varying severity, our medical team must evaluate all potential candidates to establish a current baseline and treatment recommendations. Upon completion of the medical evaluation, a detailed treatment plan will be provided that will include the specifics, such as the exact total number of nights required, along with the total medical-related costs. To begin the evaluation process for our multi-stage rheumatoid arthritis treatment using stem cells, please prepare your recent medical records, such as radiology scans and blood test results, and contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^Munchey R, Pongmesa T. Health-Related Quality of Life and Functional Ability of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Study from a Tertiary Care Hospital in Thailand. Value Health Reg Issues. 2018 May;15:76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.vhri.2017.08.012. Epub 2017 Oct 16. PMID: 29474183.
[2] ^Lau CS, Chia F, Harrison A, Hsieh TY, Jain R, Jung SM, Kishimoto M, Kumar A, Leong KP, Li Z, Lichauco JJ, Louthrenoo W, Luo SF, Nash P, Ng CT, Park SH, Suryana BP, Suwannalai P, Wijaya LK, Yamamoto K, Yang Y, Yeap SS; Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology in Thailand. APLAR rheumatoid arthritis treatment recommendations. Int J Rheum Dis. 2015 Sep;18(7):685-713. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.12754. Erratum in: Int J Rheum Dis. 2015 Nov;18(8):917. PMID: 26334449.
[3] ^Liu H, Li R, Liu T, Yang L, Yin G, Xie Q. Immunomodulatory Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 20;11:1912. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01912. PMID: 32973792; PMCID: PMC7468450.
[4] ^Sarsenova M, Issabekova A, Abisheva S, Rutskaya-Moroshan K, Ogay V, Saparov A. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 27;22(21):11592. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111592. PMID: 34769021; PMCID: PMC8584240.
[5] ^ Wang L, Huang S, Li S, Li M, Shi J, Bai W, Wang Q, Zheng L, Liu Y. Efficacy and Safety of Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: A Prospective Phase I/II Study. Thailand Ther. 2019 Dec 19;13:4331-4340. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S225613. PMID: 31908418; PMCID: PMC6930836.