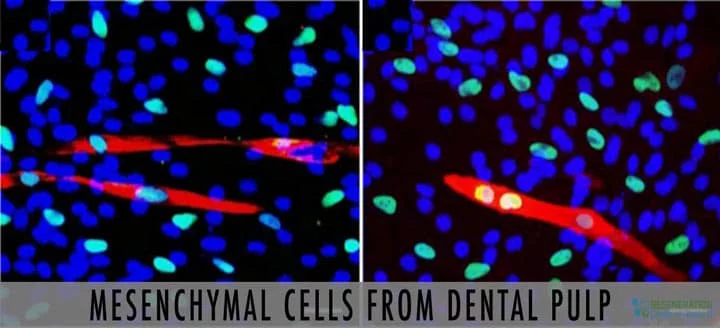
Dental pulp stem cells derived (DPSCs) represents a new and exciting alternative source of adult stem cells for use in regenerative medicine. The DPSCs are considered very unique because the cells are relatively easy acquire in an extremely safe and low invasive procedures. During our early development, dental pulp is the main source of nutrition of our jaw,brain and developing teeth due to them containing potent quantities of mesenchymal stem cells. DPSCs are a variant of adult stem cells and are typically found in baby wisdom and are usually discarded when the teeth fall out naturally.
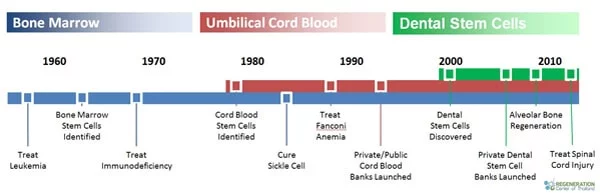
Adult stem cells used in our treatments can be identified in many tissue and organs in the human body, including peripheral blood,brain,bone marrow,blood vessels, skin, skeletal tissue, teeth, guts,livers, heart,testis and ovarian epithelium tissue.[1]
Clinical trials and research done by our doctors have clearly established the ability of enriched multi-potent dental pulp stem cells to transform into:
- Bone – Osteoclasts and Osteoblasts
- Muscle cells – myocytes
- Cartilage cells – Chondrocytes
- Adipocytes – Fat tissue [2]
- Neural Cells to generate glial cells, astrocytes, nerves and brain tissue
- Myocardiocytes for repairing/replace damaged cardiac cells/tissue after heart attack [3]
Safeguarding Future Health with Dental Pulp Cell Banking
Stem Cells from Dental Pulp also present a unique opportunities for parents to take advantage of stem cell banking as an biological insurance policy for themselves and their family, especially if they did not store their children’s cord blood cells or placenta derived cells. The advent of this advanced bioengineering technology has paved the way for dental pulp Mesenchymal stem cells to provide patients an immediate solution in case of injury, disease or accidents. Cryogenically saved cells can be immediately prepared and expanded for use in treatment as little as 48 hours after injury/request by our patients ( In Thailand only. We cannot send stored cells abroad due to shipping restrictions ) The promise and potential for such personalized medicine is great and has immense potential for the treatment of several types of degenerative diseases.[4]

What Can DPSC’s be used for?
Stem cells taken Dental Pulp can be used to treat the following areas:
- Dental/Tooth reconstruction
- Corneal reconstruction
- Heart disease , Myocardial infarction and Congestive heart failure
- Spinal cord injuries
- Strokes and Traumatic Brain Injuries
- Muscle repair for Sports injuries
- Liver repair & regeneration
- Cardiovascular Diseases
- Peripheral nerve repair
- Diabetes Type 2
- Wounds and Burn healing
- Bone & tissue engineering
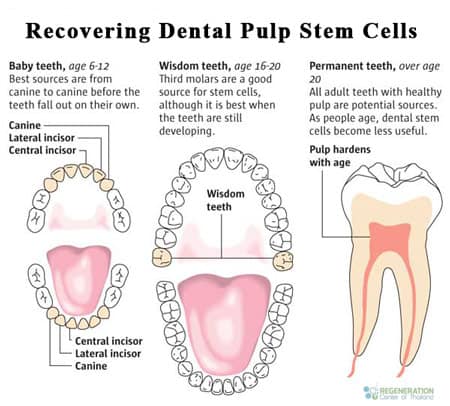
Extracting and Preserving Tooth Stem Cells
When a child’s deciduous teeth (wisdom teeth) come out naturally (ages of 6 and 12) They can be temporarily placed in a sealed container of milk and shipped to our stem cell lab in Bangkok. For optimal results, the fallen teeth should be less than 3 days old. Once our lab has received the package, dental pulp stem cells are isolated, cleaned,processed and cryogenically preserve the stem cells for up to 20 years. The cells can then be used for the child donor or other family members to treat future health conditions. The Regeneration Center of Thailand and BioEden Labs have developed the unique technology and expertise to preserve your children’s dental pulp cells ready for use in case they are ever needed.
All these properties and findings show that dental pulp stem cells offer tremendous utility for regenerative cellular therapies for both neurodegenerative diseases and traumatic injuries such as those to our central nervous system along with spinal cord injuries.
To learn more about regenerative medical therapies using dental pulp stem cells please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Osathanon, T, C Sawangmake, N Nowwarote, and P Pavasant. 2013. Neurogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells using different induction protocols. Oral diseases, no. 4 (May 7). doi:10.1111/odi.12119. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23651465
[2] ^ Osathanon, Thanaphum, Nunthawan Nowwarote, and Prasit Pavasant. 2011. Basic fibroblast growth factor inhibits mineralization but induces neuronal differentiation by human dental pulp stem cells through a FGFR and PLCγ signaling pathway. Journal of cellular biochemistry, no. 7. doi:10.1002/jcb.23097. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21381082
[3] ^ Sawangmake, Chenphop, Nunthawan Nowwarote, Prasit Pavasant, Piyarat Chansiripornchai, and Thanaphum Osathanon. 2014. A feasibility study of an in vitro differentiation potential toward insulin-producing cells by dental tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, no. 3 (August 30). doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.08.121. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25181343
[4] ^ Sukarawan, Waleerat, Nunthawan Nowwarote, Piyarat Kerdpon, Prasit Pavasant, and Thanaphum Osathanon. 2013. Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on pluripotent marker expression and colony forming unit capacity of stem cells isolated from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Odontology, no. 2 (July 20). doi:10.1007/s10266-013-0124-3. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23872868