Ataxia occurs when a disruption in body equilibrium, neurotransmitters, and cell signaling capacity occurs, primarily through a lesion in the frontal lobe. It refers to a lack of muscle control or coordination of voluntary movements, such as walking or picking up objects. It may be due to various underlying neurological disorders that affect the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls muscle coordination.
What is Ataxia?
Friedreich’s ataxia sclerosis is another type of Ataxia, but Friedreich’s is hereditary. Lesions similar to those found in Aphasia, Multiple Sclerosis, and strokes can be found in the lateral and dorsal columns of the spine. The lesions of this common movement disorder generally start during childhood and are accompanied by speech impairment, ataxia, scoliosis, peculiar movements, frequent hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and even paralysis.[1]
Motor ataxia is the inability to manage muscle coordination. Sensory ataxia is called such because the proprioceptive area between the peripheral nerves and the motor cortex is lost. This loss results in uncoordinated movements, which become more apparent when an individual’s eyes are closed.
Ataxia-telangiectasia is a severe progressive form of cerebellar ataxia related to abnormal eye movements, oculocutaneous telangiectasia, immunodeficiency, and sinopulmonary disease.[2]
Stem Cell Therapy for Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Neural Cell Treatment for Ataxia and Autoimmune cerebellar ataxia offers a promising treatment for those who can repair/reverse loss of motor neuron related brain damage. Stem cells are essentially un-specialized cells that can be differentiated into any cell or tissue in the human body, including neural cells, astrocytes & oligodendrocytes. Stem cells are unique since they can reproduce themselves and divide indefinitely.[3] Adult stem cells can also create specialized cells such as:
The ability to make new cells and tissues in the body indicates that adult stem cells can be used to replace diseased and damaged body tissues, organs, and lesions for treating Ataxia with Stem Cells. Learn more about stem cells. Ataxia therapy with stem cells is non-invasive (No Surgery) and can bypass the blood-brain barrier using intrathecal infusions or fluoroscopic guided delivery (hospital setting).[4]
Our Ataxia protocol seeks to repair damaged and/or diseased tissues caused by injuries or hereditary conditions, such as Spinal muscular atrophy.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note that not all patients are suitable candidates for treating Ataxia with stem cells. Patients with advanced neurodegeneration and severe motor dysfunction,Learn about brain-healthy foods here. Patients with late-stage, severe supplement brain fog or other significant health conditions might not be good candidates for treatment.Treating Sporadic Spinocerebellar Ataxia
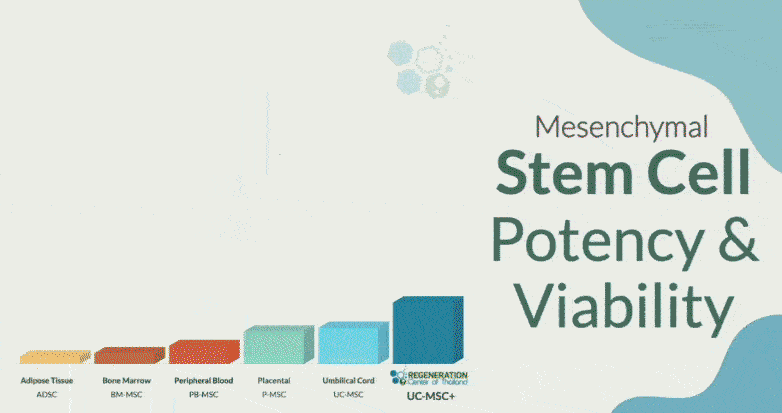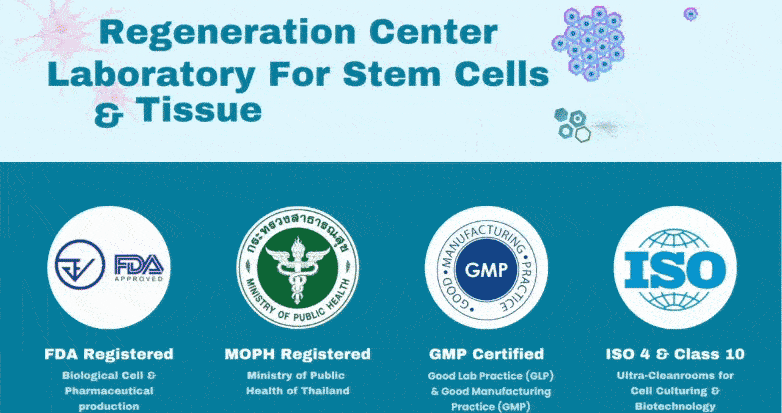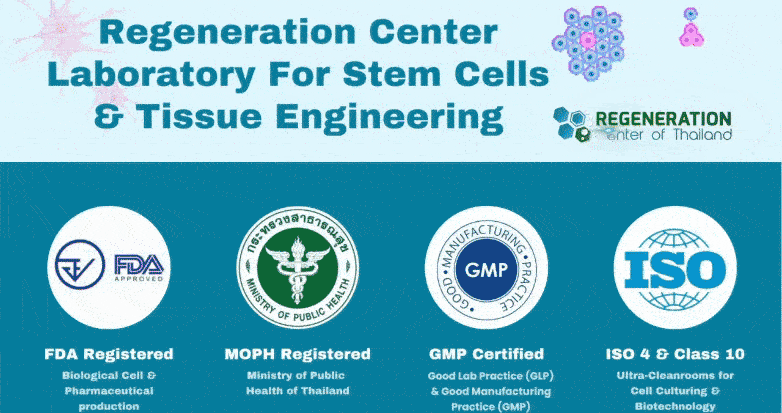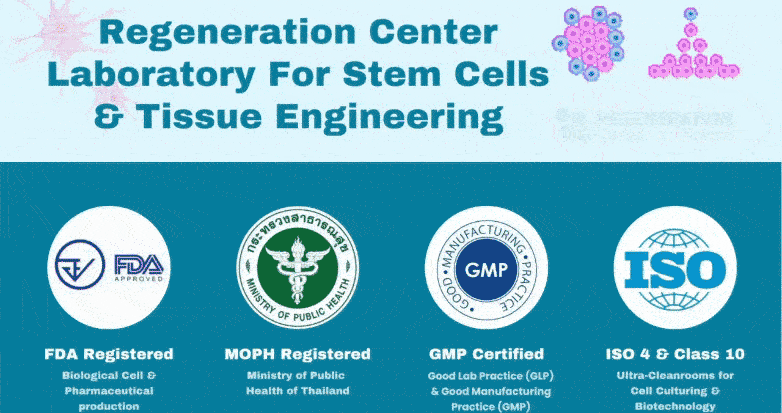
Total Number of MSC+ Cell Infusions for Ataxia: For most patients with Ataxia, we will need multiple Infusions of isolated and expanded mesenchymal cells, which can be cultured from autologous bone marrow (BMMSC) or allogeneic sources of cells (UC-MSC) such as the umbilical cord, placenta, and Wharton’s jelly. These cells can be combined with neural progenitor cells, fibroblast growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines to increase transplanted cells’ survival rates per treatment stage.
Delivery Methods of MSC+ Cells for Ataxia: One of the main goals of treatment is to help reduce systemic neuroinflammation and promote faster recovery of any lost function through neurogenesis. The cells used in treatment can be administered via Stereotactic-guided delivery, inhalation therapy via micro-nebulized mesenchymal cells Intravenously, Intrathecally, or fluoroscopic guided delivery (hospital setting) is sometimes needed to bypass the blood-brain barrier. A board-certified neurosurgeon performs the intrathecal stem cell deliveries.
Rehabilitation Treatment for Ataxia: Rehabilitation therapy is optional and can be performed 2-4 hours per day up to 6 days per week. Medical visas and accommodation packages for an extended stay can also be included at an additional cost.
Ataxia Treatment Guidelines for 2025
Neural cell treatment for Ataxia will require a minimum of 2-3 Weeks in Bangkok. Due to the varying stages of the disease, our medical team will need to evaluate all potential patients before making medical recommendations. To begin the evaluation stage for our multi-stage treatment protocol, please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Boonkongchuen, Pairoj, Sunsanee Pongpakdee, Panitha Jindahra, Chutima Papsing, Powpong Peerapatmongkol, Suppachok Wetchaphanphesat, Supachai Paiboonpol, et al. 2014. Clinical analysis of adult-onset spinocerebellar ataxias in Thailand. BMC neurology (April 5). doi:10.1186/1471-2377-14-75. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24708620
[2] ^ Carlessi, Luigi, Elena Fusar Poli, and Domenico Delia. 2013. Brain and induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem cells as an in vitro model of neurodegeneration in ataxia-telangiectasia. Experimental biology and medicine (Maywood, N.J.), no. 3. doi:10.1177/1535370213480703. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23598976
[3] ^ Lolekha, Praween, and Kammant Phanthumchinda. 2009. Miller-Fisher syndrome at King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet, no. 4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19374296
[4] ^ Sutamnartpong, Panee, Sombat Muengtaweepongsa, and Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn. 2013. Wernicke’s encephalopathy and central pontine myelinolysis in hyperemesis gravidarum. Journal of neurosciences in rural practice, no. 1. doi:10.4103/0976-3147.105608. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23546346