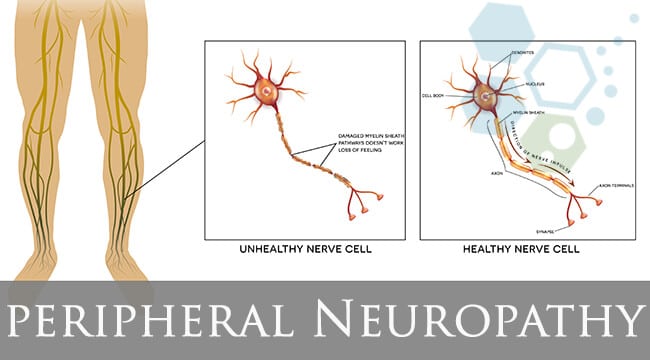
An estimated 180 million people in the world have some peripheral neuropathy or “PN” which accounts for nearly 8% of the global population. PR disease develops over time due to damage to our communication network, known as the peripheral nervous system. Neuropathy means nerve damage or disease/disorder of signals between our brain and spinal cord (central nervous system) and other parts of our bodies. Human Peripheral nerves send sensory information to our brain and spinal cord. The Peripheral nerves are also responsible for carrying movement signals from our spinal cord and brain to generate proper muscle movement. Any damage to our peripheral nervous system will interfere with these signals, similar to static in a TV or telephone signal. A patient with peripheral neuropathy cannot correctly communicate with the brain and spinal cord due to interference in the signal. [1]
Peripheral Neuropathy & Nerve Damage
Symptoms of Peripheral Nerve Damage
Symptoms of patients’ peripheral nerve damage depend entirely on which type of nerves are damaged ( motor nerves, sensory nerves, or autonomic ). As the name suggests, Motor nerves help control our voluntary responses of muscles needed in actions such as grabbing things, walking, or talking. Sensory nerves transmit the brain information about touch or pain injuries. Autonomic nerves are non-voluntary and help manage proper organ functions such as digesting food, beating the heart, or breathing. We do not have to think about breathing in and out. Our lungs manage the process automatically. Some rare cases of peripheral neuropathies can affect all two types of nerves, but most diagnoses for patients usually involve just one or two types of nerve damage.
Most diagnoses of peripheral nerve disease are categorized as one of the following: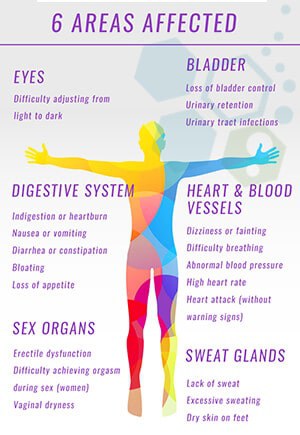
- Autonomic neuropathy
- Idiopathic Peripheral Neuropathy
- Predominantly sensory neuropathy
- Predominantly motor neuropathy
- Sensory-motor neuropathy
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Small fiber neuropathy
- Alcoholic neuropathy
- Multifocal motor neuropathy
- Optic neuropathy
- Femoral Nerve Neuropathy
- Peroneal neuropathy
Damage to the Motor nerves is commonly seen as muscle weakness. Still, it may also produce uncontrolled muscle twitches (fasciculations), painful muscle cramps, and muscle atrophy with decreased reflexes similar to patients diagnosed with Ataxia, ALS, Motor Neuron Disease, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s disease. A diagnosis of sensory nerve disease manifests itself as a variety of symptoms due to their broad range of uses/functions. Large sensory fibers in the myelin sheath identify vibrations and light touches. Any damage to the large sensory fibers will impair the sensation of touch. This type of nerve damage affects the hands and feet, causing them to feel like they are wearing gloves or stockings on the legs even though they are not wearing either. This type of damage makes men and women unable to coordinate complex muscle movements like running, fastening shirts, or maintaining proper balance when their eyes are closed.
Neuropathic Pain
Smaller sensory fibers are responsible for transmitting the sensation of temperature and pain. Patients diagnosed with damage to smaller sensory fibers may be unable to sense injury from an accident or that a wound has become infected. They also might be unable to detect the body’s signal of chest pain ( impending heart attack ). The Loss of our pain sensation is especially critical for patients with diabetic-induced neuropathy, resulting in a very high rate of limb amputations. Diabetic neuropathy is one of the most common types of peripheral nerve disease.[2]
Neuropathic-induced pain is a prevalent condition that seriously affects the emotional well-being and quality of life of a patient. Neuropathic pain also disrupts sleep, further compounding the physical burden of having sensory nerve damage. Neuropathic pain and allodynia are associated with hypersensitization of pain receptors in our skin, resulting in the feeling of severe pain from stimuli that would generally be painless. If left untreated, sensory neuropathy will lead to adverse changes in a patient’s hair, skin/joints, resulting in ligament damage, bone damage & osteoarthritis.
Autonomic nerve disease symptoms are also very diverse because our sympathetic & parasympathetic nerves are just about every organ in the human body. Commonly associated symptoms of autonomic nerve damage “AND” include the inability to perspire/sweat, usually resulting in heat intolerance, and can be identified using modern functional medical tests. Other symptoms include:
- A loss of bladder control
- Inability to control muscles and posture leading to Knee Injuries or Degenerative Disc Herniation
- Inability to contract or expand blood vessels that regulate blood pressure.
- Irregular heartbeat
- Impaired digestion
- Loss of sweating
- Loss of sexual function and ED
- The inability to properly urinate.
- In extreme cases involving the lungs, breathing becomes difficult, leading to lung failure.
- Sciatic Nerve Injury
 Most patients with autonomic neuropathy also display gastrointestinal symptoms due to a nerve malfunction of the intestinal muscle contractions, which leads to incontinence, diarrhea, and constipation, along with problems eating or swallowing.
Most patients with autonomic neuropathy also display gastrointestinal symptoms due to a nerve malfunction of the intestinal muscle contractions, which leads to incontinence, diarrhea, and constipation, along with problems eating or swallowing.
Symptoms of peripheral nerve damage can be experienced over a few days, months, or years and classified as acute or chronic. Acute neuropathies occur when symptoms appear unexpectedly, progress rapidly, and resolve very slowly. In chronic neuropathies, symptoms usually appear subtly and progress very slowly. Some patients may show signs of relief followed by a relapse in symptoms. For others, they reach a plateau where symptoms usually stay consistently the same for months or even years. Most cases of chronic peripheral neuropathy and Ankylosing spondylitis worsen over time and become extremely painful and debilitating, with some cases becoming terminal due to compounding medical issues such as diabetes or brain strokes. [3]
The Primary Causes of neuropathy include:
- Type 2 Diabetes mellitus. The most common cause of PN, research has shown that about 45% of people with diabetes eventually develop peripheral neuropathy disease,PSC, diabetic retinopathy, or Diabetic nephropathy, which leads to Polycystic kidney disease, heart attacks, and stage 5 kidney failure.
- Toxic Exposure. The most common toxins found in alcoholic drinks (alcoholic neuropathy). Exposure to Chemotherapy and lead are also known causes of peripheral nerve damage and ataxia.
- Systemic organ failures due to hypothyroidism, vitamin deficiencies, or other diseases such as herpes or HIV infections.
- Multiple autoimmune syndromes, including Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Primary Progressive Aphasia (PPA), Guillain-Barre’ syndrome and CIPD (Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy), Type 1 diabetes and Lyme disease
- Environmental factors that occur due to repeated injuries or severe hypothermia
- Hereditary – Genetic predisposition to PND
- Idiopathic causes – Idiopathic means that the cause is unknown, and up to 20% of patients diagnosed with the disease can fall into this category.
Diagnosis of Peripheral Neuropathy
The diagnosis of Peripheral neuropathy requires multiple tests to confirm, and it has many potential causes. A patient displaying symptoms should start with a complete physical exam, including blood tests. To confirm a diagnosis, further testing is usually needed. Tests include:
- Neurological examination – To check tendon reflex, muscle strength, and the ability to feel sensations, along with checking coordination and physical posture.
- Blood tests – to check for diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, abnormal immune responses, and other indications.
- Genetic Testing for Hereditary Neuropathy
- Imaging tests. MRI or CT to look for any herniated or degenerative spinal disks, tumors, or other abnormalities that might be causing the improper nerve response.
- Nerve function tests such as “EMG” ( Electromyography ) measure electrical activity in the muscles and detect any nerve damage. An electrical probe sends signals to the nerves, and an electrode is placed along the pathway to record/measure the nerve’s response. This type of test is also known as a nerve conduction test.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note that not all patients are good candidates for treating neuropathy with stem cells or stem cell therapy for nerve damage. Patients with late-stage, severe underlying conditions, paralysis or travel restrictions may not qualify for the estimated two week treatment protocolNatural Treatment for Neuropathic Pain
Treatment options for polyneuropathy depend on the underlying causes. For patients with type 1 diabetes or vitamin deficiencies, treatment often entails directly treating the underlying cause of their peripheral neuropathy diagnosis. Other measures, such as removing toxins or unfavorable environmental factors, can be used to treat mild conditions. Patients diagnosed with autoimmune neuropathy usually require much more aggressive therapies, including:
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin therapy
- Glucocorticoid therapy (High dose steroids)
- Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE)
Current medications such as carbamazepine, Gabapentin, topiramate, Tricyclic antidepressant medications ( amitriptyline desipramine), Pain medications like ibuprofen or tramadol are used to mask the symptoms but do not do much as far as treatment of the underlying causes.
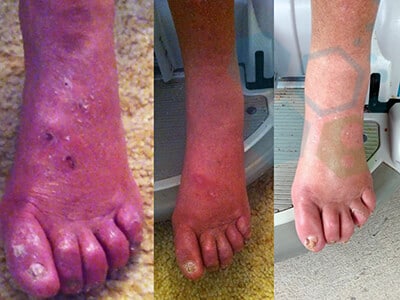
Stem Cells for Neuropathy in Legs and Feet
Expanded UC-MSC+ Stem cell therapy offers a promising avenue for addressing neuropathy in the legs and feet and provides the potential to reduce patient discomfort significantly. This condition, often characterized by pain, numbness, and impaired mobility due to nerve damage, can be effectively managed by harnessing the regenerative potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) or other advanced cell types. The treatment aims to repair damaged nerve tissues, reduce inflammation, and restore nerve function. Stem cells can be administered through targeted injections or intravenous delivery, where they release growth factors and signaling molecules to promote healing and regeneration. Clinical studies have shown that stem cell therapy can improve sensation, reduce discomfort, and enhance overall quality of life for patients with peripheral neuropathy caused by diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or injury. As research advances, stem cell treatments provide hope for those seeking innovative solutions to chronic nerve-related conditions.
Stem Cell Therapy for Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic-induced neuropathy, or diabetic neuropathy, is a type of nerve damage that occurs as a complication of diabetes. High blood sugar levels over prolonged periods can injure nerves throughout the body, but diabetic neuropathy most often damages nerves in the legs and feet. The condition can manifest in various forms, including peripheral neuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, proximal neuropathy, and focal neuropathy, each affecting different body parts in distinct ways. Stem cell therapy offers a promising approach to treating diabetic neuropathy. This condition severely impacts the quality of life and urgently needs effective solutions. There are several types of diabetic neuropathy we can target, including:
- Peripheral Neuropathy: The most common type, affecting the feet and legs first, followed by the hands and arms. Symptoms may include tingling, burning, numbness, or pain ranging from mild to severe.
- Autonomic Neuropathy affects the nerves that control involuntary functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and bladder function. It can lead to urinary issues, digestive problems (e.g., gastroparesis), and sexual dysfunction.
- Proximal Neuropathy (Diabetic Amyotrophy): A rare type that affects nerves in the thighs, hips, buttocks, or legs, leading to muscle weakness and pain. It usually affects one side of the body and can cause significant disability.
- Focal Neuropathy (Mononeuropathy): Involves damage to a specific nerve, often in the hand, head, torso, or leg. It can cause sudden pain or weakness and affect the eyes, leading to double vision or pain behind one eye.
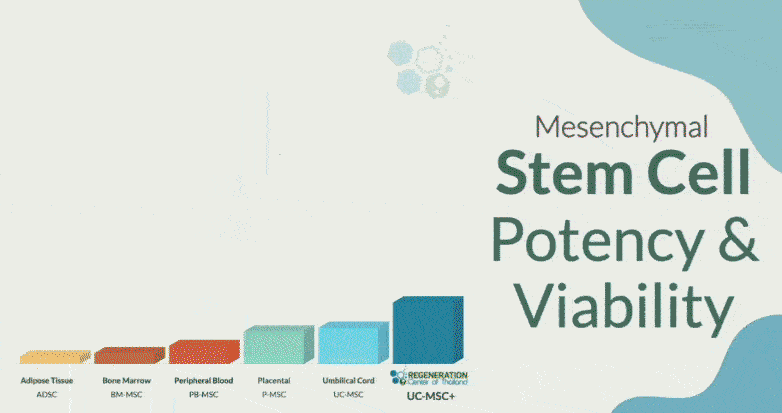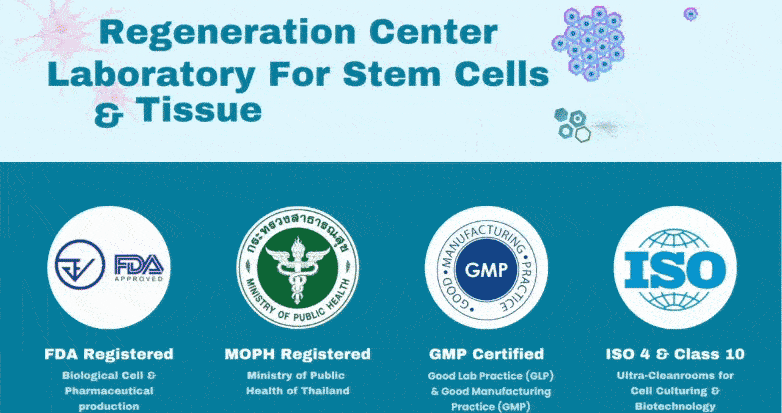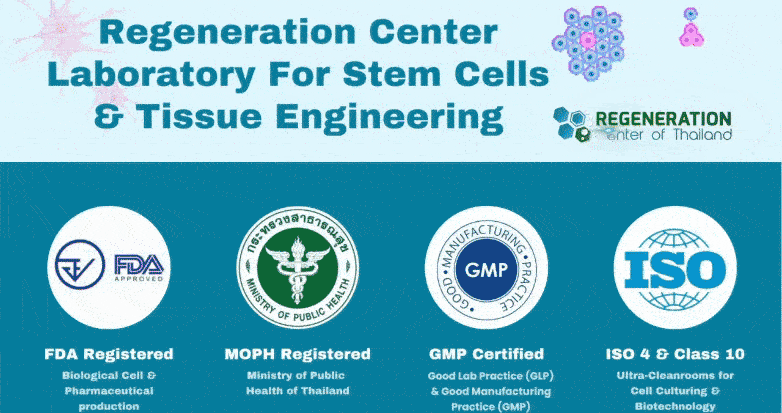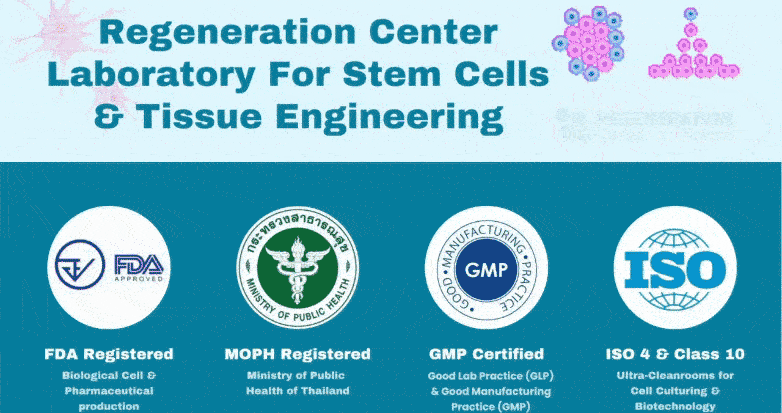
Some benefits of isolated and expanded UC-MSC+ stem cell treatment include:
- Regenerating Damaged Nerves – Stem cells have the potential to regenerate damaged nerves. Diabetic neuropathy results from prolonged high blood sugar levels damaging the nerves, leading to pain and loss of sensation. Research shows that stem cells can differentiate into various cell types, including nerve cells, and help repair damage, offering a pathway to relief that traditional medications cannot provide.
- Reducing Inflammation – Inflammation exacerbates nerve damage in diabetic patients. One mistake people make is relying solely on painkillers, which do not address the underlying inflammation. Stem cell therapy has anti-inflammatory properties that could reduce nerve inflammation and slow the progression of neuropathy, making it a dual-action treatment.
- Promoting Blood Vessel Formation – Poor blood circulation is a significant issue in diabetic neuropathy. Stem cells can help form new blood vessels, improving blood flow to affected areas. Angiogenesis is crucial because enhanced circulation supports nerve health and function. Studies have shown significant improvements in patients’ symptoms when blood flow is restored.
- Limited Side Effects Compared to Traditional Treatments
Unlike many medications with a host of side effects, isolated stem cell therapy offers a natural alternative with a lower risk profile. Patients can avoid complications like liver damage or addiction, often associated with long-term medication use, while still targeting the root cause of their neuropathy.
1 Year After Stem Cells for Nerve Damage (Foot Drop)
Stem Cell Therapy for Neuropathy in 2025
Mesenchymal Stem cell therapy (UC-MSC+) and paracrine signaling offer a unique and effective modern treatment option for patients suffering from neuropathy nerve damage and neuropathic pain. Unlike traditional treatments that respond poorly to opioid and OTC analgesics, our UC-MSC+ enhanced cell therapy uses a multi-layer combination therapy consisting of MSC+ hematopoietic 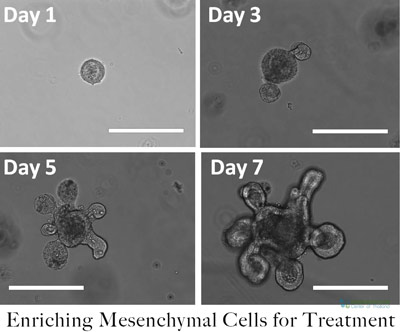 stem cells, leukocytes, red blood cells, CD90 positive cells, CD31 positive cells, CD45 cells, and endothelial cells to precisely repairing the damage on the tissue nerve level and recover lost functions. UC-MSC Stem cell treatments focus on the root of the underlying issue (nerve damage), not just temporarily mask the symptoms with painkillers.
stem cells, leukocytes, red blood cells, CD90 positive cells, CD31 positive cells, CD45 cells, and endothelial cells to precisely repairing the damage on the tissue nerve level and recover lost functions. UC-MSC Stem cell treatments focus on the root of the underlying issue (nerve damage), not just temporarily mask the symptoms with painkillers.
We treat neuropathic pain and create anti-inflammatory zones by releasing cytokines vital to nerve regeneration. Our cell injection protocol has been clinically proven to decrease proinflammatory (IL)-1β interleukin cytokine while increasing the anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines in the lesioned nerve, along with a significant reduction in mechanical allodynia & thermal hyperalgesia. The consensus among our patients who had stem cell therapy for pain reduction was overwhelmingly beneficial and positive after the 1-2 week stem cell therapy. Our treatment is safe, with minimal side effects like drowsiness and weight gain.[4]
The cells used in the treatment are multipotent hematopoietic & undifferentiated cells taken from adult sources depending on the patient’s needs. The harvested cells are non-immunogenic and 100% matched to the patient.[5]
Neuropathy Treatment Evaluation, Guidelines & Costs
Get safe and permanent treatment for neuropathy at the Regeneration Centre. If you or a loved one are suffering from neuropathic pain or neuropathy. In that case, you/they are probably in unnecessary physical agony and should try to get out of the painful situation as early as possible. A clear diagnosis with recent test results is important in treating the condition with stem cells. Our request for a medical review can be made online. It will enable our medical team to better understand your needs before suggesting an effective protocol that will be used to treat this condition. Please note that the treatment requires travel to our stem cell hospital in Thailand for the estimated 2-week therapy course. Our pain management solutions help solve the root of the pain issues to improve the quality of life for our patients safely. If your daily activities are being affected by neuropathy, please get in touch with us today. Our medical professionals are experienced and trained in several pain conditions to ensure your condition improves as quickly as possible so you can get back to everyday life completely free of any discomfort or pain that comes with peripheral neuropathy.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Gerawarapong, Chinapat. 2015. Association of Peripheral Autonomic Neuropathy and Sympathetic Skin Response in the Patients with Diabetic Polyneuropathy: A Pilot Study in Thailand. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet, no. 12. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27004308
[2] ^ Han, Ji Woong, Dabin Choi, Min Young Lee, Yang Hoon Huh, and Young-sup Yoon. 2015. Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Diabetic Neuropathy by Direct Modulation of Both Angiogenesis and Myelination in Peripheral Nerves. Cell transplantation, no. 2 (May 13). doi:10.3727/096368915X688209. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25975801
[3] ^ Kosachunhanun, Natapong, Siam Tongprasert, and Kittipan Rerkasem. 2012. Diabetic foot problems in tertiary care diabetic clinic in Thailand. The international journal of lower extremity wounds, no. 2 (May 2). doi:10.1177/1534734612446967. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22553278
[4] ^ Nayagam, Bryony Ariya. 2012. Human stem cells ameliorate auditory evoked responses in a model of neuropathy. Stem cell research & therapy, no. 6 (November 8). doi:10.1186/scrt135. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23134736
[5] ^ Puataweepong, Putipun, Mantana Dhanachai, Ake Hansasuta, Somjai Dangprasert, Chomporn Sitathanee, Thiti Swangsilpa, Patamintita Vitoonpanich, and Pornpan Yongvithisatid. 2015. Outcomes for Pituitary Adenoma Patients Treated with Linac- Based Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Radiotherapy: a Long Term Experience in Thailand. Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention : APJCP, no. 13. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26225666