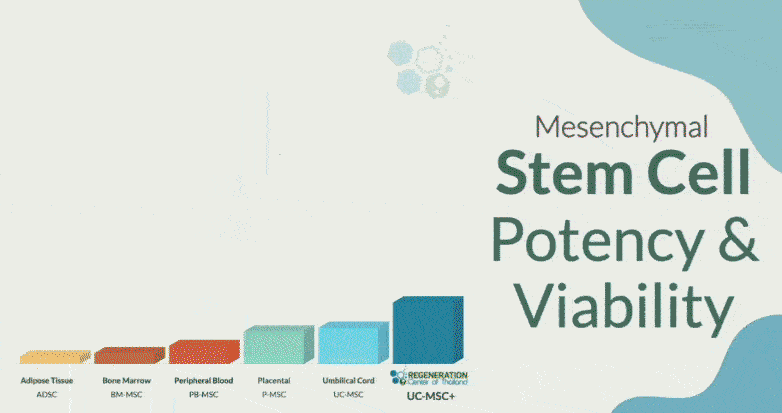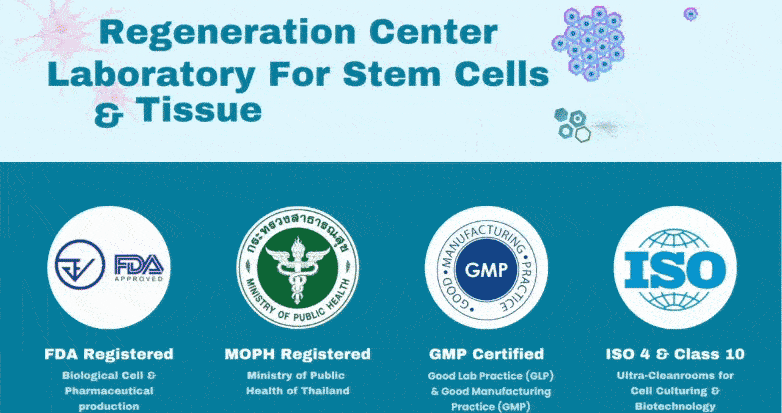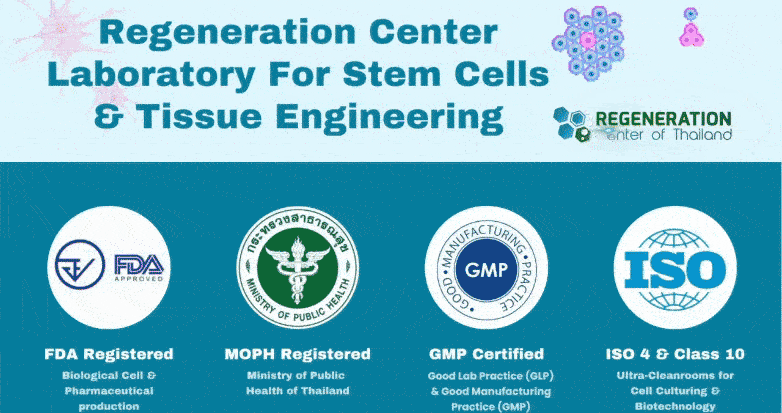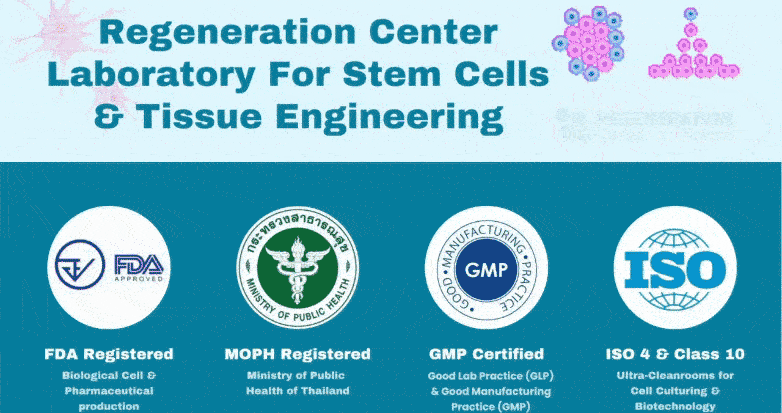
In the unfortunate event that you or perhaps a family member are coping with diabetes, you should be aware of its consequences on the body and mind. Diabetes is usually termed the “silent killer” mainly because it strikes the body slowly and without warning. Newly diagnosed diabetic patients are generally not worried about it since their symptoms are often no more severe than recurrent urination and increased thirst. Many other individuals have no symptoms at all.
Understanding Hyperglycemia
As time goes by, however, the effects of both kinds of diabetes become increasingly severe and may lead to death. These symptoms include heart disease, eye issues, kidney failure, nerve damage, and erectile dysfunction, to name a few. Hypoglycemia (acute low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high level of blood sugar) are the key contributors to the effects of diabetes. According to recent research, some oral diabetes medications can also contribute to heart malfunction.[1] That is precisely why it’s vital that women and men who are clinically diagnosed as “diabetic” immediately seek treatment to relieve hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. These conditions often trigger more harmful, degenerative ailments. The regeneration center can help treat DM with our innovative, enriched, and expanded Mesenchymal cell treatment for Diabetes safely and without artificial medicines or the need for regular insulin dependency.[2]
Damage to Insulin Producing Beta-Cells
Stem Cell treatments for diabetes and functional medicine look to fight the disease at its origins in the pancreas, decreasing hyperglycemia and associated complications (see above).
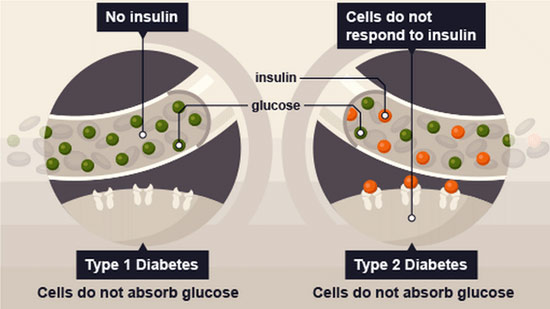
According to recent research, it can also relieve hypoglycemia or low levels of blood sugar, which consequently can lead to fatality if it is not treated immediately. Diabetic patients are treated by introducing enhanced UC-MSC+ cells to the pancreatic area via IV or directly (severe cases). Diabetes is a metabolic disease with a significant inflammatory component, wherein the individual has an elevated blood sugar level because the human body cannot generate enough insulin or because the cells are no longer responding to the insulin produced naturally by the body. The high blood sugar levels instigate signs of polyuria or recurrent peeing, Polydipsia or an abnormal increase in thirst, polyphagia, pancreatic cancer, pancreatitis or the state of increased hunger, and, in severe cases, lupus disease.[3]
3 Types of Diabetes Mellitus:
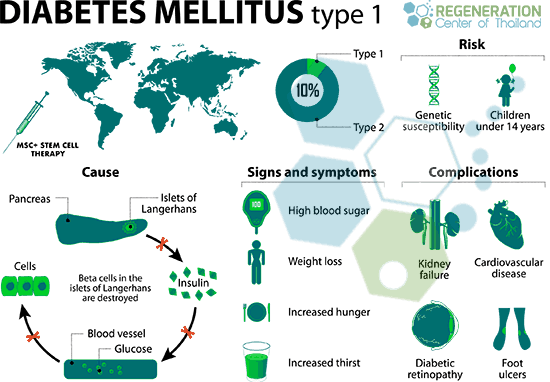 Type 1 diabetes results from your body’s failure to generate insulin and currently requires the individual to inject insulin. (Likewise known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, IDDM for short, and juvenile diabetes)- Stem Cell therapy to stop autoimmune attacks from destroying insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells and insulin-producing beta cells. The usual symptoms that are associated with Type 1 diabetes can include Polydipsia (constant thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (constant hunger), weight loss, dry mouth pSS, and fatigue. A Type 1 diagnosis is caused by destroying functional beta cells in the patient’s pancreas. Learn more about stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes. Other known complications for uncontrolled blood sugar levels and type 1 diabetes include heart disease, Hashimoto’s disease, diabetic retinopathy, inclusion body myopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and renal disease. Type 1 diabetes is especially dangerous for women, who have a 42% higher risk of mortality compared to men. The average life expectancy for type 1 diabetics is less than 11 years for men and less than 13 years for females.[4]
Type 1 diabetes results from your body’s failure to generate insulin and currently requires the individual to inject insulin. (Likewise known as insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, IDDM for short, and juvenile diabetes)- Stem Cell therapy to stop autoimmune attacks from destroying insulin-producing pancreatic islet cells and insulin-producing beta cells. The usual symptoms that are associated with Type 1 diabetes can include Polydipsia (constant thirst), polyuria (excessive urination), polyphagia (constant hunger), weight loss, dry mouth pSS, and fatigue. A Type 1 diagnosis is caused by destroying functional beta cells in the patient’s pancreas. Learn more about stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes. Other known complications for uncontrolled blood sugar levels and type 1 diabetes include heart disease, Hashimoto’s disease, diabetic retinopathy, inclusion body myopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and renal disease. Type 1 diabetes is especially dangerous for women, who have a 42% higher risk of mortality compared to men. The average life expectancy for type 1 diabetics is less than 11 years for men and less than 13 years for females.[4]
Type 1 vs Type 2 Diabetes
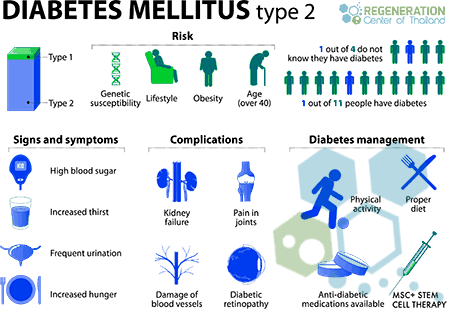
Type 2 diabetes results from insulin resistance, a condition wherein cells cannot use insulin appropriately, sometimes coupled with a complete insulin deficiency requiring insulin pumps. – Type 2 is often an acquired disease and, if caught early, is a very treatable condition at the Regeneration Center. Long-term risks of having diabetes include acute transverse myelitis, retinopathy (loss of vision), diabetic nephropathy, which leads to kidney failure, peripheral neuropathy ( foot ulcers that lead to amputations or Charcot’s joints ), and autonomic neuropathy that causes genitourinary, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular symptoms with sexual dysfunction. Patients diagnosed with diabetes also report increased occurrences of peripheral arterial disease (PAD), atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and cerebrovascular disease. Other complications include hypertension and severe abnormalities of lipoprotein metabolism. Many patients can also impair beta cell insulin secretion because of their pharmaceutical medications. These medications do not directly cause diabetes, but they may lead individuals to become insulin-resistant. Learn more about foods that fight inflammation
Gestational Diabetes is when pregnant women who’ve never had diabetes before have a high blood glucose level while being pregnant. It may precede the development of type 2 DM.- We cannot treat Gestational diabetes with stem cell therapy.
- FPG, fasting plasma glucose
- HNF, hepatocyte nuclear factor
- GAD, glutamic acid decarboxylase
- GDM, gestational diabetes
- GCT, a glucose challenge test
- IFG, impaired fasting glucose
- MODY, maturity-onset diabetes (young)
- IGT impaired glucose tolerance
Prevention of Diabetes
DNA editing is still in clinical trials, so type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented but can be identified early using DNA testing. Understanding the potential risk factors and environmental triggers are proactive measures that help delay/avoid the destruction of the friendly insulin-producing cells in the body. Several known factors can influence and expedite the development of type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle behaviors are the most influential factors. These lifestyle choices include frequent consumption of junk foods or an inactive, sedentary lifestyle. Research worldwide has already established that changing your lifestyle to include physical activities and healthy diets can prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes.
The Regeneration Center’s recommendations for a healthy diet
- Eating at least three servings of vegetables every day (including green leafy vegetables)
- Choose water, tea, or coffee over fruit juices, sodas, or other sweetened beverages
- Use whole grains for bread, rice, or pasta instead of processed white bread, rice, or pasta
- Choose natural peanut butter over chocolate spreads or jam
- Eat lean cuts of white meat, seafood, or poultry instead of red meat & processed meat
- Eat nuts, fresh fruit, or unsweetened yogurts as a snack
- Eliminate tobacco and limit alcoholic intake to a maximum of one per day
- Eating up to three servings of fresh fruit every day
Long sedentary periods, bad diets, and inactivity characterize modern lifestyles worldwide. To help prevent diabetes, The Regeneration Center recommends frequent physical activity for 15-30 minutes each time. Taking a holistic approach to disease prevention is critical for reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and its deadly complications. While these changes might be easier to implement early in life, healthy lifestyles can instantly boost quality of life with health outcomes at later stages.
Stem Cell Treatment for T2 Diabetes
UC-MSC+ Beta Stem Cells for Type 2
At this stage, cures for Type 1 diabetes or gestational diabetes are very, very low probability. A genetic component of the disease will require gene therapy to reprogram the cells to prevent them from reverting to their compromised states; however, these solutions are just in the clinical trials stage and have not been approved for clinical applications. According to the international diabetes federation,
New research has also shown that some patients with myasthenia gravis (MG) also had type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) before the onset of MG, which suggests that the onset diagnosis of Myasthenia gravis may correlate with the history of Type 2 Diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is usually treatable and reversible if caught early before it affects the body’s immune system and other organs/systems. Often, patients ignore the disease and try to manage the symptoms using traditional diabetes medication (Metformin, Thiazolidinediones, DPP-4 inhibitors, Meglitinides), change of diet, and regular insulin therapy to manage blood glucose levels. If metabolic diseases are left untreated, complications often occur and can include:
- Foot Complications / Ulcers
- SpA Spondyloarthritides Disorders
- Kidney Failure (Nephropathy) and PKD
- Ketones & DKA (Ketoacidosis)
- ARLD
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis and Gout
- Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease – IBD
- High Blood Pressure & Hypertension ( leads to heart disease, eye problems )
- Brain Strokes
- HHNS – Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome
- Pancreas Cancer
- Damage to insulin-producing cells requiring insulin pumps
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Gastroparesis
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note patients with multiple comorbidities or immune system dysregulation may have travel restrictions in travel to Thailand. All potential candidates seeking stem cells for diabetes must be approved in advance using current medical records and recent blood panels that include HbA1C, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), blood pressure, and lipid profiles.Treat Diabetes with Functioning Beta Cell Transplants
Cell lineages and quantities will depend on the patient’s medical needs; Diabetics are most often treated by isolated and expanded UC-MSC+ Cells along with ductal epithelial cells, β-cells & pancreatic islet-like cells. Older patients or severe cases with multiple underlying conditions will require enhanced allogeneic stem cells (Cord tissue derived w/ anti-HLA antibodies) that are differentiated into glucose-sensing, insulin-producing beta cells.[5]
Diabetes Stem Cell Treatment Guidelines – 2025
The total number of stem cell infusions will depend on the patient’s medical needs but include UC-MSC+ Mesenchymal stem cells, pancreatic progenitor cells, and β-cells of the pancreas (insulin-producing beta cells).
Types of Cells and Delivery Methods: A combination of isolated and expanded mesenchymal stem cells, Pancreatic endocrine cells are differentiated into beta cells and delivered along with pancreatic progenitor cells are delivered to the patient via IV, Intrapancreatic Injections, Intraperitoneal Injections, or Intra-Arterial Injections, depending on patient needs.
Rehabilitation Treatment (Optional): Rehabilitation therapy (2 hours per day and five days per week) , medical visas, and accommodations for an extended stay can also be included at an additional cost.
Treating T2DM With Stem Cells
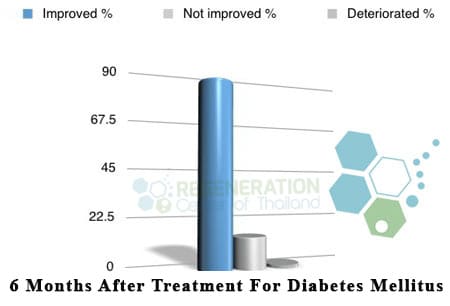
The cellular treatment for Diabetics and neogenesis of β-cells & pancreatic islets will require a minimum of 10-14 days in Bangkok. The costs for treating Type 2 Diabetes with UC-MSC+ cells will depend on many factors, including current health and other underlying medical conditions. To better prepare, our medical team will need to review patients’ relevant medical information, genetic tests for risk variants found in diabetes (if available), and recent blood tests. Upon completion of the evaluation, our recommendations and treatment plan will be provided, including all medical-related costs, including stem cell extractions and cell delivery stages. Stem cell therapy for diabetes success rates depend on stage and severity. To learn more about the treatment of Onset DM using Adult stem cells, please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1]^ Kao, Der-I, and Shuibing Chen. 2012. Pluripotent stem cell-derived pancreatic β-cells: potential for regenerative medicine in diabetes. Regenerative medicine, no. 4. doi:10.2217/rme.12.27. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22817630
[2]^ Sacks, Frank M, Michel P Hermans, Paola Fioretto, Paul Valensi, Timothy Davis, Edward Horton, Christoph Wanner, et al. 2013. Association between plasma triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and microvascular kidney disease and retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a global case-control study in 13 countries. Circulation, no. 9 (December 18). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002529. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24352521
[3]^ Sacks, Frank M, Michel P Hermans, Paola Fioretto, Paul Valensi, Timothy Davis, Edward Horton, Christoph Wanner, et al. 2013. Association between plasma triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and microvascular kidney disease and retinopathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a global case-control study in 13 countries. Circulation, no. 9 (December 18). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.002529. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24352521
[4]^ Sukpat, Supakanda, Nipan Isarasena, Jutamas Wongphoom, and Suthiluk Patumraj. 2013. Vasculoprotective effects of combined endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic wound care: their potential role in decreasing wound-oxidative stress. BioMed research international (June 17). doi:10.1155/2013/459196. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23844362
[5]^ Zhao, Yong, Zhaoshun Jiang, Tingbao Zhao, Mingliang Ye, Chengjin Hu, Huimin Zhou, Zhaohui Yin, et al. 2013. Targeting insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes via immune modulation of cord blood-derived multipotent stem cells (CB-SCs) in stem cell educator therapy: phase I/II clinical trial. BMC medicine (July 9). doi:10.1186/1741-7015-11-160. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23837842