Also referred to as “somatic stem cells,” adult stem cells are known as undifferentiated or “blank” cells present in the body. In spite of its name, adult stem cells are present in both adults and the young. Their primary purpose is to compensate for the degenerative cells by replacing them through multiplication, and the eventual repair of damaged tissue.
The Basics of Stem Cells Science
Sources of Adult Stem cells

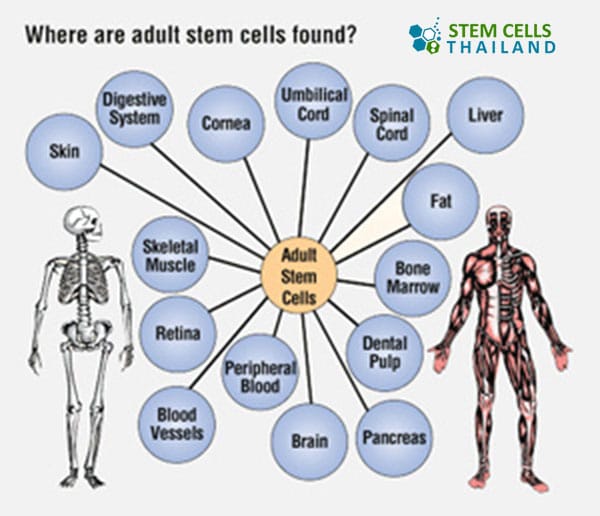
- Bone Marrow: One of the most known sources of adult stem cells. They can differentiate into several cell types, including those that make up blood and bone.
- Adipose Tissue (Fat): These stem cells are used in regenerative therapies, as they can be turned into various cell types.
- Peripheral Blood: Stem cells can also be extracted from circulating blood.
- Brain: Even though it was once believed that the adult brain couldn’t generate new cells, it’s now known that it does produce new neurons. Neural stem cells in the brain can give rise to its three major cell types: nerve cells (neurons) and two categories of non-neuronal cells—astrocytes and oligodendrocytes.
- Skin and Hair Follicles: Stem cells in the skin can give rise to new skin cells, and certain cells in hair follicles can produce new hair.
- Liver: Under certain conditions, the liver can regenerate with stem cells playing a role in this process.
Applications of Adult Stem cells:
- Regenerative Medicine: Adult stem cells are used to replace cells that are damaged or lost due to injury or diseases. For example, bone marrow transplants use stem cells to replace cells damaged by chemotherapy or radiation.
- Drug Testing: Adult stem cells can be used for testing the effectiveness and safety of new drugs.
- Modeling Diseases: They can be used to produce cells that have the same genetic makeup as a patient, providing a human model to understand the disease and find potential treatments.
Advantages of using Adult Stem cells:
- Ethical Considerations: Unlike embryonic stem cells, the use of adult stem cells doesn’t raise ethical issues as they’re sourced from the individual, avoiding the controversies surrounding embryo destruction.
- Lower Rejection Risks: When patients receive stem cells derived from their own tissues, there’s a reduced risk of immune rejection compared to cells from other sources.
Challenges with Adult Stem Cells:
- Limited Potency: Adult stem cells don’t have the same potential as embryonic stem cells to become any cell type in the body, which limits their therapeutic applications.
- Extraction Difficulties: Obtaining adult stem cells can sometimes be challenging and invasive, like in the case of bone marrow extraction.