Sjogren’s Syndrome (SS) is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the moisture-producing glands in the body, such as the salivary and tear glands. As a result, individuals with this condition often experience dryness in the mouth, eyes, and other areas of the body [1]. But did you know that Sjogren’s Syndrome can also lead to more severe complications if left untreated? Lets explore the ins and outs of this condition and how to manage it effectively using stem cells.
Causes and Risk Factors of Sjogren’s
Autoimmune Response – Like many common autoimmune diseases, Sjogren’s Syndrome occurs when a persons immune system mistakenly attacks its cells and tissues. In this case, the 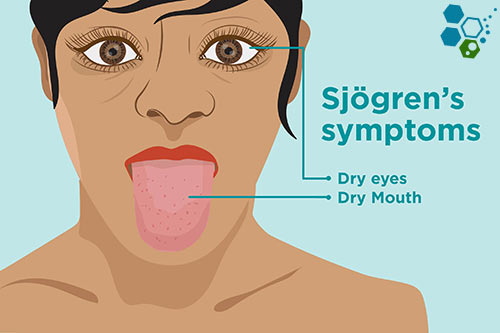 immune system targets the moisture-producing glands, causing inflammation and damage. But what exactly triggers this abnormal immune response?
immune system targets the moisture-producing glands, causing inflammation and damage. But what exactly triggers this abnormal immune response?
Genetic factors can also play a role in the development of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Certain gene variations have been associated with an increased risk of the condition, suggesting that a family history of autoimmune diseases could make you more susceptible. Learn about genetic testing for autoimmune diseases.
Environmental Factors such as viral or bacterial infections, might contribute to the development of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Some experts theorize that an infection may trigger the immune system to attack the body’s cells, leading to the onset diagnosis of the disease.
Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome (pSS)
Dry eyes are a common symptom of Primary Sjogren’s Syndrome. The lack of moisture can cause irritation, redness, and a gritty eye feeling. More severe cases can even lead to corneal damage and vision problems. Did you know that wearing sunglasses outdoors and using a humidifier indoors can help alleviate dry eye symptoms?
Dry Mouth is another hallmark symptom of Sjogren’s Syndrome and can make it difficult to chew and swallow food, speak clearly, and taste properly. Additionally, a lack of saliva can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease, so maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial for individuals with this condition[2]. In roughly 15–20% of patients who are diagnosed with pSS, there are lesions in the brain (central nervous system) that are similar to those in patients with multiple sclerosis .
Secondary Sjogren’s Syndrome
Fatigue is a common complaint among people with Sjogren’s Syndrome and FMS. It can be mentally and physically draining, making it difficult to perform daily tasks and participate in social activities. Remember to consider the impact that fatigue can have on your overall well-being [3].
Joint Pain – Those with Sjogren’s Syndrome may also experience joint pain, osteoarthritis, spinal stenosis, inflammation of spine and overall stiffness. These symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain that limits mobility especially in the lower back, neck, shoulders, knees and hips. Finding ways to manage joint pain effectively is essential, such as through orthopedic stem cells, physical therapy, or gentle exercise.
Swollen Glands – Some individuals with Sjogren’s Syndrome may notice swelling in the glands around their face and neck areas for cases of myasthenia gravis and patients with Hashimoto’s disease. This can be due to the inflammation in the moisture-producing glands, leading to discomfort and tenderness.
Complications due to Sjogren’s
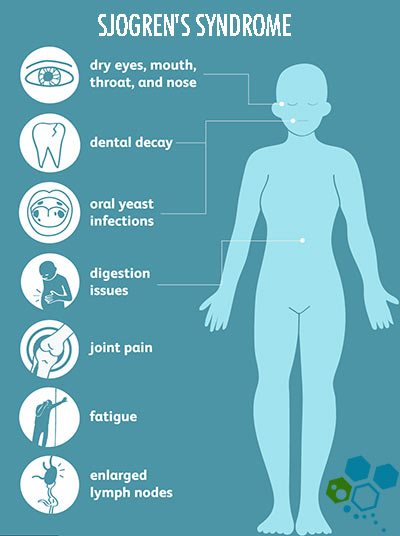 Dental Issues – As mentioned earlier, dry mouth can lead to an higher risk of tooth decay and development of gum disease. It’s crucial for individuals with Sjogren’s Syndrome to maintain good dental hygiene and have regular oral check-ups to prevent complications.
Dental Issues – As mentioned earlier, dry mouth can lead to an higher risk of tooth decay and development of gum disease. It’s crucial for individuals with Sjogren’s Syndrome to maintain good dental hygiene and have regular oral check-ups to prevent complications.
Eye Infections – The lack of eye tears can make it easier for infections to develop. It’s essential to keep your eyes clean and moist and seek medical attention if you notice signs of infection, redness, swelling, or discharge.
Lung Infections – In rare cases, Sjogren’s Syndrome can also affect the lungs, causing inflammation that lead to scarring and infections. Symptoms may include shortness of breath, persistent cough, and chest pain. Involvement of the lungs & respiratory system can cause dry airways, lung fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). These are especially common in patients who are diagnosed with primary Sjögren’s syndrome.
Neurological and Neurodegenerative – The presence of autoimmune disorders such as SS has been reported to increase the risk of neurodegenerative conditions like MND, ALS which suggests the possibility of shared genetic architecture between these diseases. Other clinical evidence from some observational studies has also shown that Sjögren’s syndrome (SS) can contribute to an higher risk of developing Parkinson’s disease (PD), neuropathy and dementia although it remains unknown if these associations are causal.
What other autoimmune diseases are associated with Sjogren’s syndrome?
A diagnosis of Sjögren’s is often accompanied by other autoimmune disorders such as: connective tissue disease, systemic lupus erythematosus, autoimmune thyroid disease, scleroderma, ankylosing spondylitis, sarcoidosis, UC, pancreatitis, antiphospholipid syndrome, type 1 diabetes, celiac disease, end stage inclusion body myositis and diseases that mimic rheumatoid arthritis. What are the 4 stages of rheumatoid arthritis?
Diagnosing Sjogren’s Syndrome
Medical History and Physical Examination – A diagnosis of Sjogren’s Syndrome begins with a thorough review of your medical history and a physical examination. Your primary care doctor will ask about your symptoms and look for signs of dryness in your eyes and mouth.
Biochemistry tests – Blood tests can be ordered to check for specific markers associated with Sjogren’s Syndrome, such as antibodies and inflammatory proteins. These tests can help support the diagnosis and rule out other possible conditions. Due to the many overlapping symptoms, imaging studies from MRI/CT scan/Xrays or biopsies are often needed to confirm the diagnosis of SS. These might include a salivary gland biopsy, Schirmer’s test eye exam, imaging studies from sialogram or salivary gland ultrasound.
Treatment and Management of SS
Rapid Symptom relief using artificial tears and saliva – One of the primary treatment goals for Sjogren’s Syndrome is to alleviate dryness in the eyes and mouth. Artificial tears and saliva substitutes can help provide relief and prevent complications.
Medications – Various medications can be prescribed to help manage symptoms and reduce inflammation. These include corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or medications that can stimulate saliva production.
Lifestyle Changes including Proper Diet and Nutrition – A balanced diet, rich in organic nutrients, can help support overall health and may improve symptoms of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Staying hydrated and consuming foods that are easy to chew and swallow are essential. A good diet is also a great way to reduce brain fog, increase cognative abilities and boost stem cells naturally
Exercise and Stress Management – For some people regular exercise and stress reduction techniques can help improve overall well-being and may alleviate some symptoms of Sjogren’s Syndrome. Gentle exercises like yoga, swimming, or walking can be particularly beneficial. practicing mindfulness , such as meditation or deep breathing to boost lung capacity, help manage stress and improve overall health.
Stem cell Therapy for Sjogren’s Syndrome
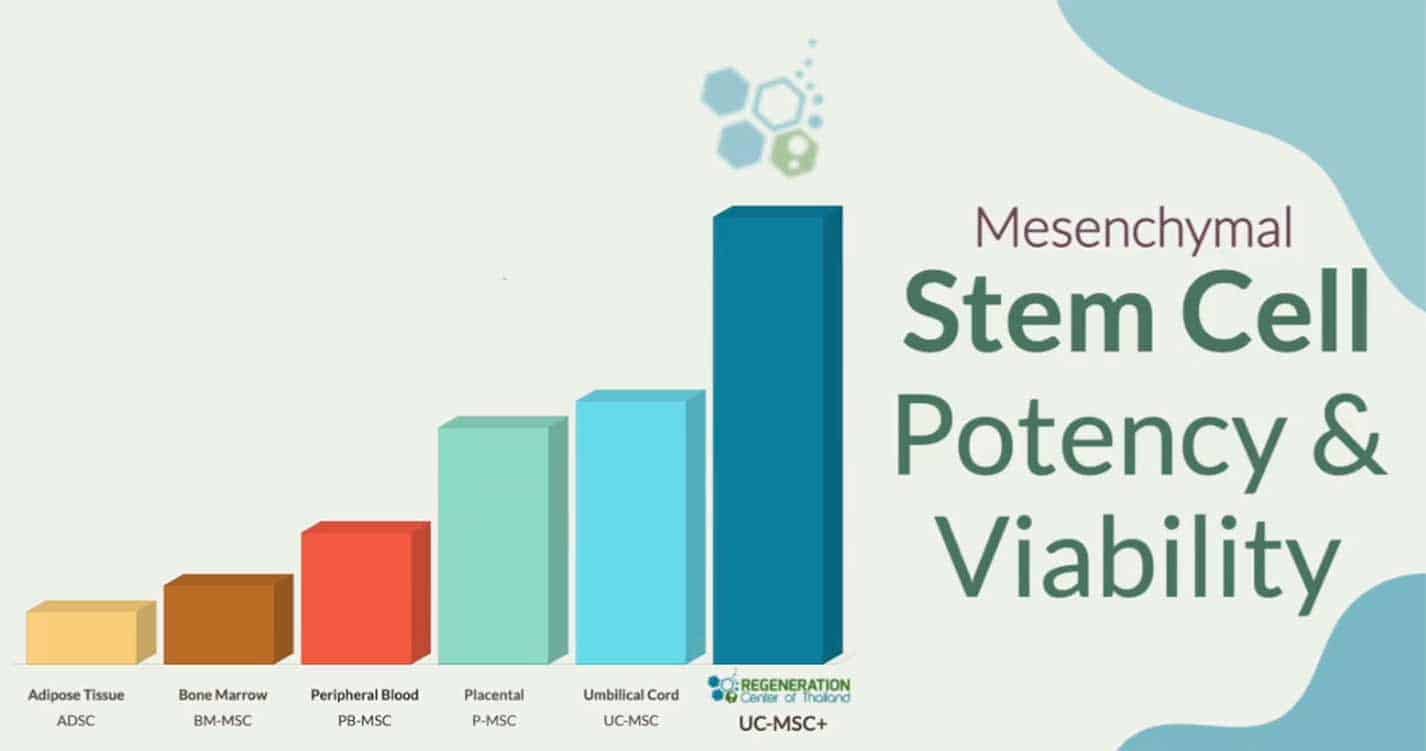
Isolated Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC+) and stromal cells offer immunomodulatory properties that help reduce inflammation in the body. Our state of the art stem cell lab in Bangkok is able to differentiate MSC cells into many other types of cells including osteocytes, fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) & chondrocytes. By using specific tupes of cells and growth factors the immune system is altered in a safe way to reduce the negative inflammatory processes. Mesenchymal stem cells can be isolated from several sources including: bone marrow, adipose fatty tissue, umbilical cords, peripheral blood and gingiva. The secretory capacities of MSC+ stem cells give them the immunomodulatory properties that are used in cell therapies for autoimmune diseases [4].
Can Stem Cells Help With Sjögren’s Syndrome?
MSC+ cells is an effective treatment option for chronic inflammatory autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren’s Syndrome. For patients with SS that mainly affects the exocrine glands, including lacrimal and salivar glands. Results have shown good improvements in stabilizing salivary secretions and a decrease in lymphocytic infiltration (salivary glands) in patients with SS. The isolated and expanded stem cells are usually delivered via intravenous injections but can also be delivered via infra-peritoneal injections if needed. Isolated MSC +injections are done over a course of roughly 2 weeks and can lead to a reduction of inflammatory cytokines along with an increase in anti-inflammatory cytokines amd supression of serum interleukin-12 (IL-12) [5]. The overall success of stem cell treatment for Sjögren’s syndrome is measured using followup tests roughly 3-4 months post-therapy.
Cost of Treating SS with Stem Cells
Our multi-stage treatment for Primary & Secondary Sjögren’s syndrome with Stem Cells will require roughly 2 weeks in Thailand depending on the patient’s needs. Due to the varying degrees, areas, and stage of condition, our medical team will need to better understand the patient’s current health before acceptance into the program. Upon approval, a detailed treatment plan will be provided that will include the specifics including protocol overview, exact number nights required along with the total medical related costs (excluding accommodations or flights). To begin the qualification process for our multi-stage treatment for autoimmune diseases such as SS please prepare your recent medical records such as antinuclear antibody (ANA) panels, CBC, Schirmer tear test or lip biopsies and contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^Jonsson R, Brokstad KA, Jonsson MV, Delaleu N, Skarstein K. Current concepts on Sjögren’s syndrome – classification criteria and biomarkers. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018 Oct;126 Suppl 1(Suppl Suppl 1):37-48. doi: 10.1111/eos.12536. PMID: 30178554; PMCID: PMC6586012.
[2] ^Kosrirukvongs P, Ngowyutagon P, Pusuwan P, Koolvisoot A, Nilganuwong S. Prevalence of dry eye syndrome and Sjogren’s syndrome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Assoc Thailand. 2012 Apr;95 Suppl 4:S61-9. PMID: 22696854.
[3] ^Yong WC, Sanguankeo A, Upala S. Association between primary Sjogren’s syndrome, arterial stiffness, and subclinical atherosclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol. 2019 Feb;38(2):447-455. doi: 10.1007/s10067-018-4265-1. Epub 2018 Sep 3. PMID: 30178172.
[4] ^Chen W, Yu Y, Ma J, Olsen N, Lin J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: Prospective and Challenges. Stem Cells Int. 2018 Sep 16;2018:4357865. doi: 10.1155/2018/4357865. PMID: 30305818; PMCID: PMC6165618.
[5] ^Faustman DL, Davis M. Stem cells in the spleen: therapeutic potential for Sjogren’s syndrome, type I diabetes, and other disorders. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010 Oct;42(10):1576-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2010.06.012. Epub 2010 Jun 18. PMID: 20601088; PMCID: PMC4104595.