According to international statistics, chronic liver disease ranks #4 around the world as the top cause of mortality. Once a human liver incurs severe damage, it usually cannot repair itself naturally, thus posing life-threatening risks to the patient. Given this, the only possible treatment option for chronic liver disease was with a dangerous complete liver transplant. Unfortunately, there are a lot of risks to consider with liver transplant surgery. [1] The risk is mainly attributed to the tendency of rejection of transplanted organs. Sometimes, the body detects the transplanted organ as a “foreign object,” or something that has not come from its own body and should be destroyed/rejected.
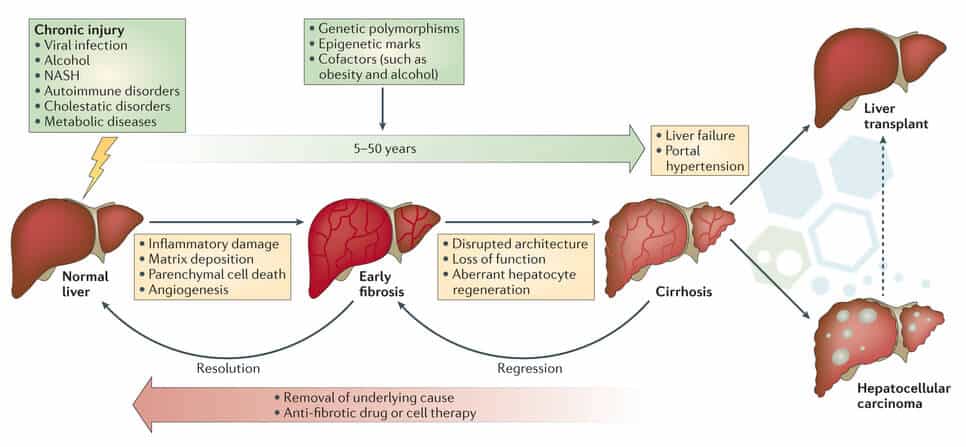
Types of Hepatic Diseases
The liver is a complex and vital organ, and there are over a hundred various classifications of liver disease. These most common types of liver disease include:
- Alagille Syndrome is a genetic disorder commonly seen in young children and infants.
- Alcohol-related liver Diseases, also known as “drug-induced” or “toxic” liver failure, this disorder is typically due to the overconsumption of alcohol or drugs or due to an immune reaction to certain medications.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency is a genetic disorder that can lead to liver disease or emphysema lung failure. Patients with Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency are often misdiagnosed with Asthma.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) is a chronic condition that occurs when a patient’s immune system attacks the liver, causing it to be inflamed continuously and unable to heal itself naturally. If left untreated autoimmune hepatitis can lead to liver cirrhosis and Hepatic failure.
- Benign Liver Tumors – Some tumors are cancerous (malignant), while others are benign (noncancerous). Noncancerous (benign) liver tumors do not spread in the body and typically do not pose any severe health threat.
- Biliary Atresia is typically a genetic disorder in newborn children that affects the production of bile and the bile ducts. Biliary atresia disease causes the bile ducts to become blocked and inflamed, allowing the bile liquid to remain in the liver and leading to scarring (cirrhosis) of the liver.
- Budd-Chiari syndrome is a rare condition caused by blockage (occlusion) of the hepatic veins. Symptoms of Budd-Chiari syndrome include ascites, abdominal pain, and liver
 enlargement.
enlargement. - Cirrhosis of the liver occurs when healthy liver tissue is replaced with non-living scar tissue. This condition is usually a symptom of several other liver diseases.
- Crigler-Najjar Syndrome (CNS) occurs when there is high-level bilirubin (toxin) in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia). Bilirubin is the byproduct of breaking down red blood cells but must be removed from the body through the bile and intestines. High levels of bilirubin in the blood can lead to jaundice and can also travel to the brain and cause brain damage.
- Fascioliasis (Hepatic fascioliasis) is caused by parasitic infection of the liver by a liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica)
- Fatty liver disease or hepatic steatosis occurs when triglyceride fat rapidly accumulates in liver cells.
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a family of conditions that are usually associated with metabolic syndromes like diabetes two or obesity.
- Galactosemia is a genetic disorder that prevents patients from processing sugar galactose. Rapid accumulation of galactose in the body can result in dangerous complications such as renal failure, PKD, enlarged liver, brain damage, or cataracts in the eyes.
- Gilbert Syndrome is a genetic disorder that prevents the liver from processing bilirubin. This condition is more common in men than in women and can cause jaundice.
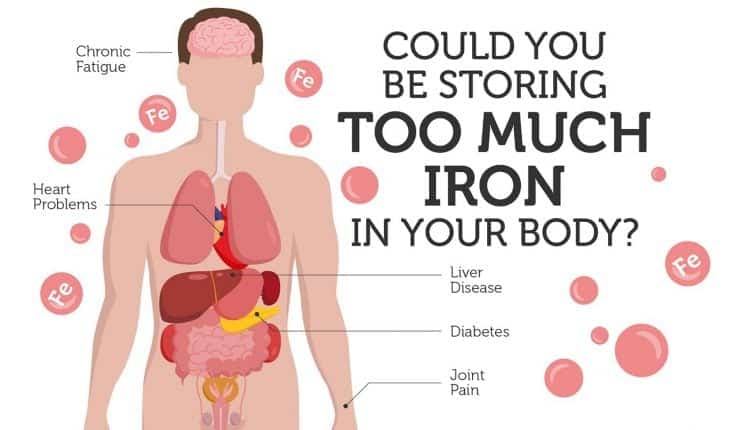
- Hemochromatosis is a common genetic disorder that causes patients to absorb and store too much iron in the body. The abundance of iron buildup can be very dangerous for several organs, especially the liver, and if left untreated, can lead to organ failure.
- Hepatic Encephalopathy, also known as portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE), is a medical condition that affects the brain function of patients with severe liver disease and the inability to remove toxins from the blood. If these toxins build up, they travel throughout the body until they reach the brain, resulting in physical and mental dysfunction.
- Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, can be caused by several factors, including viruses (viral hepatitis), liver toxins, an autoimmune response, or hereditary conditions.
- Hepatitis A liver disease is caused by the hepatitis A virus (HAV), which causes the liver to get swollen and prevents it from functioning correctly.
- Hepatitis B liver disease is usually preventable and caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). A Hepatitis B diagnosis can cause the liver to enlarge and prevent proper function. Hepatitis B is treatable; over 95% of adults exposed to it recover in one year or less. Chronic Hepatitis B is severe and can result in cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, or liver cancer.
- Hepatitis C liver disease is caused by the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). It can be autoimmune and causes severe inflammation in the liver, which leads to scarring and liver fibrosis. The cellular death of liver cells triggers the body to release inflammatory cells in the liver, leading to hepatomegaly (enlargement of the liver). It also causes the Glisson’s capsule (fibroblastic sheath) around the organ to stretch, causing pain.
- Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS) is a dangerous condition that reduces kidney function in patients with advanced liver disease. Hepatorenal Syndrome is common in patients with advanced scarring in the liver and ascites. Still, it can also happen in patients with acute liver failure, fulminant hepatic failure, or other types of liver diseases.
- Intrahepatic Cholestasis during Pregnancy (ICP) is a condition that affects the flow of bile acids in the liver, resulting in continuous itching in pregnant women. This complication usually appears in the third trimester, when hormone concentrations are highest.
- Lysosomal Acid Lipase Deficiency (LAL-D) is a progressive genetic disorder that restricts a patient’s ability to produce lysosomal acid lipase enzyme. The body needs this vital enzyme to break down lipids (fats) and cholesterol. When the lysosomal acid lipase enzyme is deficient or missing, fats accumulate in tissue and organs throughout the body, resulting in liver disease and high levels of LDL bad cholesterol linked to cardiovascular diseases.
- Liver cysts are benign but abnormal growth sacs in the liver that are filled with fluid.
- Liver Cancer occurs when malignant cells in the liver grow and spread. Any cancer that starts in the Liver is called liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and cholangiocarcinoma are the most common types of liver cancer, and if the disease spreads from the liver to other organs, it’s diagnosed as metastatic liver cancer. When pancreas cancer spreads, it typically affects the liver. Different rare types of liver cancer include hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma of the liver.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis or Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is a chronic autoimmune liver disease that causes damage to the intrahepatic bile ducts.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) liver disease is a chronic disease that slowly damages the bile ducts and then travels to the small intestine. Patients with PSC suffer from constant inflammation and fibrosis (scarring) of tissue that causes bile accumulation in the liver until it loses all ability to function correctly. PSC advances slowly, and liver failure can occur 8-15 years after initial diagnosis. Most patients with people with Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis will need a liver transplant, but stem cell therapy for primary sclerosing cholangitis can be helpful if applied soon after diagnosis. PSC can also result in bile duct cancer.
- Reye Syndrome can affect all organs in the body but is especially harmful to the liver and brain. It often occurs in children recovering from viral infections like chicken pox and the flu. Complications of Reye syndrome in Oliver can include abnormal liver function tests, fatty liver deposits, poor blood clotting, or total liver failure.
- Wilson Disease is a genetic disorder that causes the patient to retain excess copper deposits in the body and not release copper into bile fluid as it usually should. Copper builds up in the blood and liver, damaging the kidneys, eyes, and brain. If left untreated, Wilson’s disease can result in severe brain damage, spondyloarthropathy induced hepatic steatosis, kidney failure, liver failure, and death.
Diagnosis & Genetic Testing for Liver Diseases
Blood Tests and radiology scans used to diagnose liver failure include:
Liver Panels & Liver Function Test (LFT), Complete Blood Count Comprehensive Metabolic Panel (CMP), Alpha-1 Antitrypsin, Bilirubin, DCP, AFP Tumor Markers, Albumin, Total Protein, GGT, PT, AMA, AST, ALP, ALT, Copper Test (hepatic copper concentration), Ethanol tests, Overdose Drug Testing, Iron Tests, Hepatitis A Test, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Tests.
The regeneration center and its functional medicine department offer a comprehensive list of DNA testing options to test for inheritable liver & glycogen storage diseases, including the following panels:
ATP7B, SPG70, JAG1, NOTCH2, ILLD, METRS, MRS, FBP1, SLC5A1, SLC2A2, PHKA2 G6PC, GBE1,SLC37A4, PYGL GYS2, PHKB, PHKG2,FBP, FBPase 1 & RpL17
To help reduce the risk of developing liver disease, consider changing your diet (learn about good fats vs fad fats) and exercise regularly.
Early Symptoms of Liver Disease
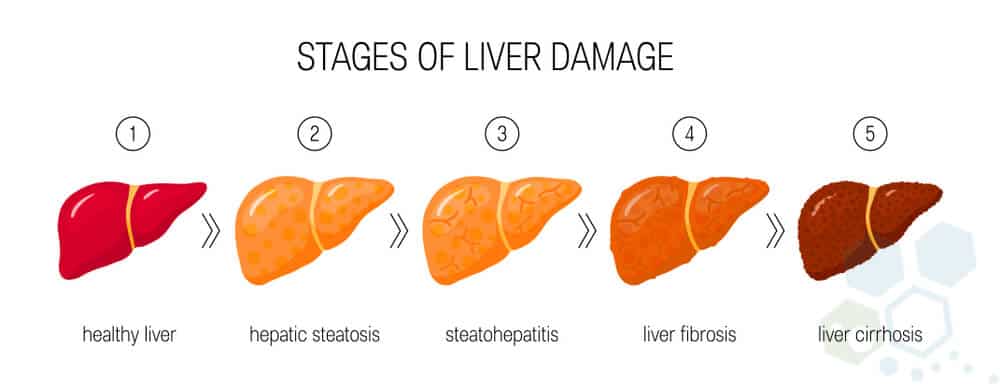
Common Causes of Liver Disease
It is widely accepted that most of the common causes of chronic liver disease are modifiable before they become an issue by altering your eating and health habits. The best treatment plans always start with prevention. Healthy living practices will be crucial after treatment to avoid relapse and chronic liver disease. The Liver is the largest organ in the human body and is fully capable of regenerating itself under normal conditions. Since the Liver has many responsibilities, such as detoxifying the blood, fighting infections, and aiding in the digestion of foods, it can severely impact a person’s overall health if it becomes diseased.
Organ donors are very limited, and the prices for liver transplants are very high. The surgery itself involves many risks. Thankfully, our internationally trained stem cell regeneration doctors created a more modern approach to healing. Adult stem cell therapies help induce the rapid production of hepatocytes in a patient with chronic liver disease or Cirrhosis of the Liver.
Liver Disease Treatment with Stem Cells
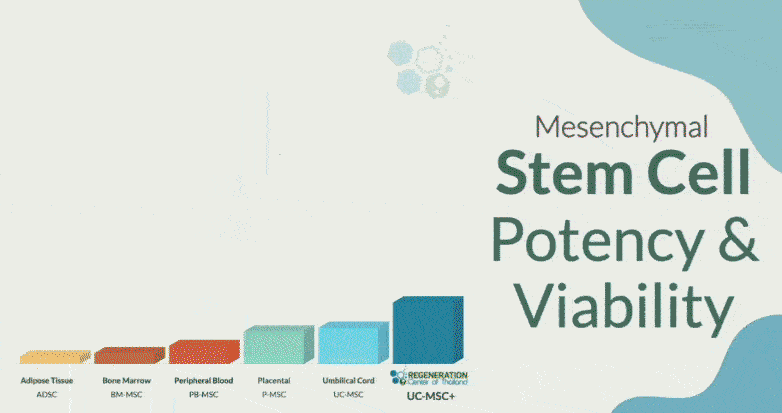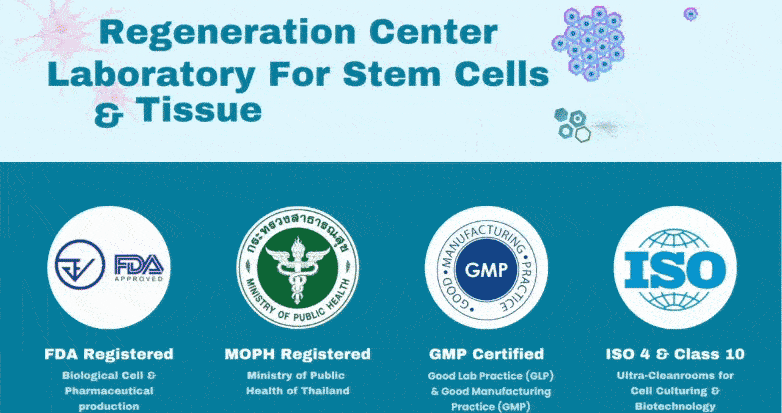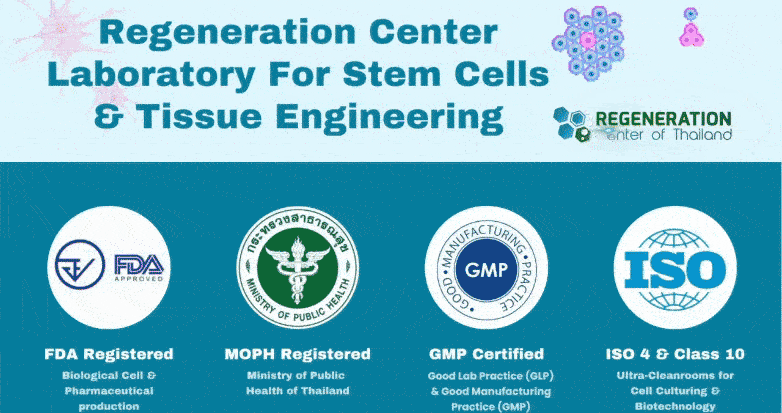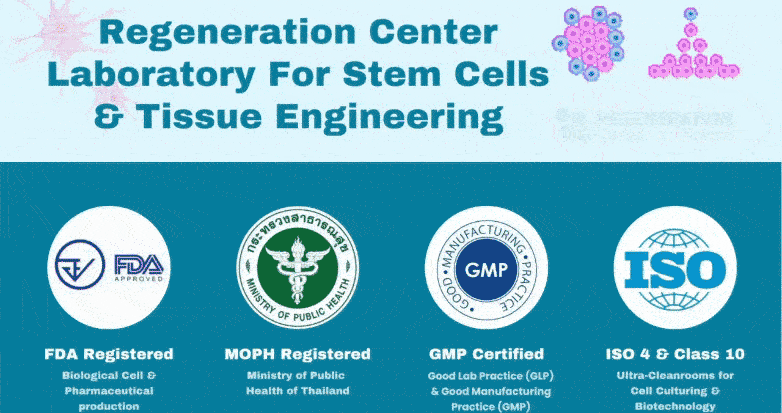
Enhanced mesenchymal stem cells (MSC+) offer an attractive therapeutic solution to reverse hepatic cirrhosis and liver diseases based on many factors, including: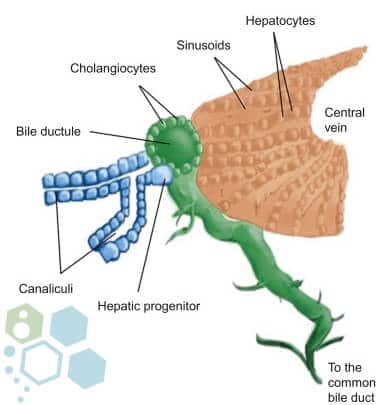
- Immunomodulatory properties [2]
- Ability to differentiate into hepatocytes, biliary epithelial cells, and liver progenitor cells
- Natural replacement of damaged hepatocyte cells
- Reduction of pro-inflammatory cytokines
- Reversing hepatocellular damage and repair hepatic ducts & hepatic plates
- Promote persistent hepatocyte regeneration [3]
- Capacity to inhibit cell activation
- Stop Fatigue. Jaundice. Constant Itching.
- Increases rate of apoptosis (a paracrine mechanism )
- Increase in Anti-Fibrotic Properties
- Regeneration of Liver Tissue via hepatocytes (liver cells)
- Improve overall liver function and enhanced quality of life
Hepatocyte Cells to Reverse Liver Scarring
With recent advancements in regenerative medicine for failed kidneys, heart attacks, and diabetic nephropathy, there is finally an effective alternative liver regeneration treatment to repair fatty liver & chronic liver disease using targeted protocol of liver cells and growth factors. Liver stem cell therapy can help reduce inflammation and liver fibrosis through paracrine regeneration and immunomodulation functions on liver cells & CD4+ T cells. These combined effects are expected to play a favorable role in restoring liver homeostasis. Chronic parkinsonism is also known to be associated with liver cirrhosis.[4]
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Treatment for hereditary conditions using gene therapies is not available at the Regeneration Center. Patients with severe thrombocytopenia and coagulopathy limiting travel may not be candidates for the estimated 2-week treatment protocol.Can stem cells cure liver cirrhosis?
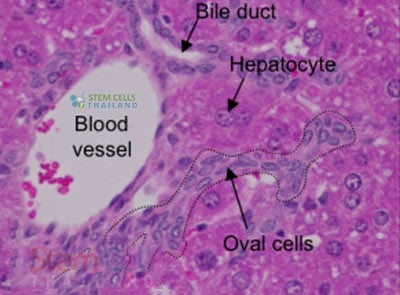 The liver is generally made up of cells called hepatocytes [5]. The enhanced liver cells can replicate so that new hepatocytes will replace old hepatocytes naturally after 200 to 300 days of use. If a patient’s liver is severely damaged, the hepatocytes cannot do the natural replicating process. This is where oval cells come to the rescue. It is believed that oval cells can also produce new hepatocytes should the need arise. Combo treatment for Liver failure is done as an outpatient procedure. It looks to introduce therapeutic levels of hepatocytes, liver cells, or Hepatic oval cells using the paracrine mechanism to initiate the healing of damaged tissues and cells forcefully.[6]
The liver is generally made up of cells called hepatocytes [5]. The enhanced liver cells can replicate so that new hepatocytes will replace old hepatocytes naturally after 200 to 300 days of use. If a patient’s liver is severely damaged, the hepatocytes cannot do the natural replicating process. This is where oval cells come to the rescue. It is believed that oval cells can also produce new hepatocytes should the need arise. Combo treatment for Liver failure is done as an outpatient procedure. It looks to introduce therapeutic levels of hepatocytes, liver cells, or Hepatic oval cells using the paracrine mechanism to initiate the healing of damaged tissues and cells forcefully.[6]
A combination UC-MSC+ Hepatic Cell treatment protocol can expand adult multipotent stem cells and hepatic growth factors. Multipotent stem cells can differentiate into different kinds of cells, including hepatocytes (liver cells).[7]
After Treatment of the Liver with Stem Cells
Oval Cell Therapy for Liver Cirrhosis Stages
Computed Tomography Angiography, or CTA, is often used to deliver stem cells using an exact method of hepatocyte or oval cell delivery using a catheter. The femoral catheter used can be

guided to appropriate areas of damage [8]. The damaged tissues/livers being treated require multiple treatment steps over two weeks.
Severe cases may require multiple stages to stabilize liver function. The amounts of enhanced UC-MSC+ Hepatocyte cells vary per treatment stage. Liver regeneration therapy combines hepatocyte cells, biliary epithelial cells, and liver progenitor cells.
2025 Guidelines for Treating Liver Disease
Due to the varying degrees of existing liver damage and the current stage, all potential patients must provide recent medical documents and liver radiology scans for review. It aims to offer a less invasive alternative. Isolated and enhanced liver stem cells will be administered through intravenous (IV) intrahepatic, intrasplenic, intraperitoneal, or portal vein injections (PVI), where they are transported through the blood into the liver to begin reducing severe systemic and liver inflammation, thereby restoring liver health.
Who is the right candidate for stem cell therapy for liver cirrhosis?
The Regeneration Center treatment for liver cirrhosis, hepatic fibrosis, or chronic liver disease with stem cells is an outpatient procedure that requires two weeks in Bangkok. Upon completion of treatment, a detailed medical plan will be provided, including specifics regarding the medical treatment, the exact length of stay needed, and the total expenses. To learn more about treating fatty liver, liver cirrhosis, or chronic liver disease with stem cells, please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Angulo, Paul, David E Kleiner, Sanne Dam-Larsen, Leon A Adams, Einar S Bjornsson, Phunchai Charatcharoenwitthaya, Peter R Mills, et al. 2015. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Thailand. Gastroenterology, no. 2 (April 29). doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.04.043. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25935633
[2] ^ Burkhard, Pierre R, Jacqueline Delavelle, Renaud Du Pasquier, and Laurent Spahr. Chronic parkinsonism associated with cirrhosis: a distinct subset of acquired hepatocerebral degeneration. Archives of Neurology, no. 4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12707065
[3] ^ Cantz, Tobias, Michael P Manns, and Michael Ott. Stem cells in liver regeneration and therapy. Cell and tissue research, no. 1 (September 28). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17901986
[4] ^ Esrefoglu, Mukaddes. 2013. Role of stem cells in repair of liver injury: experimental and clinical benefit of transferred stem cells on liver failure. World journal of gastroenterology, no. 40 ( 28). doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6757. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24187451
[5] ^ Shi, Ming, Zheng Zhang, Ruonan Xu, Hu Lin, Junliang Fu, Zhengsheng Zou, Aimin Zhang, et al. 2012. Human mesenchymal stem cell transfusion is safe and improves liver function in acute-on-chronic liver failure patients. Stem cells translational medicine, no. 10 (October 11). doi:10.5966/sctm.2012-0034. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23197664
[6] ^ Srivatanakul, P, D M Parkin, M Khlat, D Chenvidhya, P Chotiwan, S Insiripong, K A L’Abbé, and C P Wild. Liver cancer in Thailand. II. A case-control study of hepatocellular carcinoma. International journal of cancer, no. 3 ( 30). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1645698
[7] ^ Zimmermann, Joshua A, and Todd C McDevitt. 2013. Pre-conditioning mesenchymal stromal cell spheroids for immunomodulatory paracrine factor secretion. Cytotherapy, no. 3 (November 9). doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2013.09.004. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24219905
[8] ^ Allameh, Abdolamir, and Somaieh Kazemnejad. 2012. Safety evaluation of stem cells used for clinical cell therapy in chronic liver diseases, emphasizing biochemical markers. Clinical biochemistry, no. 6 (January 27). doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2012.01.017. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22306885


 enlargement.
enlargement.