Wharton’s Jelly, a gelatinous substance found within the umbilical cord, is a rich mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) source. These MSCs possess unique properties that make them a valuable tool in regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and immunomodulation. Lets discuss some advantages and applications of Wharton’s Jelly stem cells along with methods used for extraction and utilization in clinical applications[1].
Clinical application of Wharton’s jelly Stem Cells
The outer layer of the umbilical cord is comprised of umbilical epithelium, which shall consist of one or multiple layers of epithelial cells. These cells appear similar to the epidermal and dermal layers of human skin, indicating they are likely of amniotic origin. Umbilical epithelial cells share features with both fetal epidermis and amniotic epithelium. Although morphological differences between these epithelial types are not distinct due to their connection to the amnion and fetal skin via the umbilical cord, the umbilical epithelium has the unique ability to stratify and keratinize, setting it apart from the amniotic epithelium. Additionally, umbilical epithelial cells exhibit mesenchymal stem cells properties, such as the expression of Oct-4, Nanog, and various surface markers [2].
The stromal tissue of the umbilical cord can be divided into three zones, including the sub-amniotic zone, Wharton’s jelly, and the adventitia of blood vessels. Although the typical adventitia is not present in umbilical vessels, the stromal tissue below the umbilical cord lining to the umbilical vessels is still considered Wharton’s jelly. This stromal tissue includes sub-amniotic, clefts, intervascular, and perivascular stroma.
Advantages of Using Wharton’s Jelly Stem Cells
Compared to other sources of stem cells, Wharton’s Jelly stem cells offer several advantages:
- Adult stem cells that are easily accessible from the umbilical cord, a medical waste product, avoiding ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cell research.
- They have a higher rate of proliferation, which means they can generate a more significant number of cells for therapeutic purposes.
- They exhibit low immunogenicity, reducing the risk of immune rejection when used in transplantation [3].
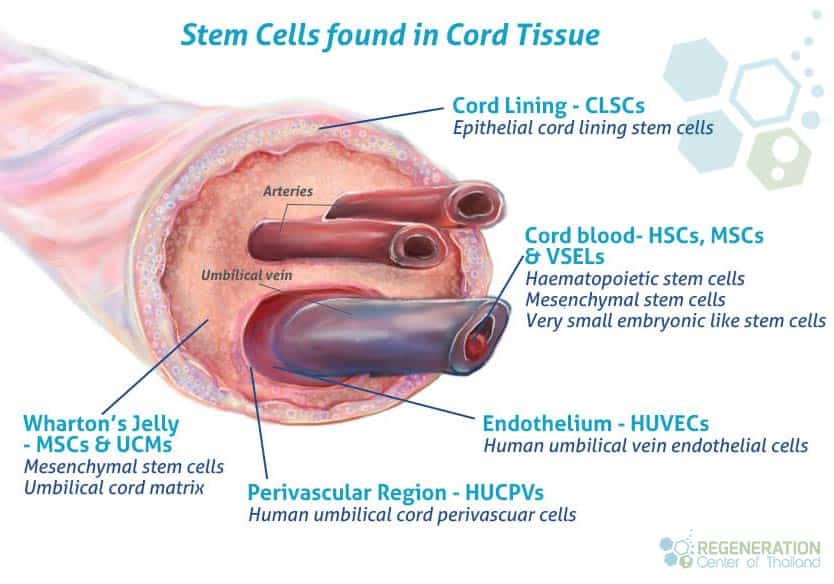
Clinical Applications of Wharton’s Jelly Stem Cells
Wharton’s Jelly stem cells are being researched for their potential applications in various fields, including:
- Regenerative Medicine: Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cells (WJ-MSCs) can differentiate into many cell types and lineages, such as bone, cartilage, and muscle cells, making them a promising candidate for treating neurological issues such as: ALS, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, MND, brain strokes along with degenerative diseases like DDD, kidney failure, liver disease, COPD, IPF, Brain Injuries, and orthopedic injuries affecting the hips, shoulders, knees and spinal cord.
- Tissue Engineering: Wharton’s Jelly stem cells can create functional, implantable tissue constructs to replace or repair damaged tissues [4].
- Immunomodulation: The immunomodulatory properties of Wharton’s Jelly stem cells can help regulate the immune system, reducing inflammation and negative autoimmune responses.
Immunomodulatory Properties of WJ-MSCs
WJ-MSCs have the potential for regenerative and immunomodulatory therapy due to their immunosuppressive and immune avoidance capabilities. They have low expression of HLA class I and an absence of HLA-DR, making them optimal for allogeneic transplantation. WJ-MSCs also induce the expansion of regulatory T cells (Treg), which can suppress the effector’s responses to alloantigens [5]. Unlike Bone Marrow-MSCs, WJ-MSCs produce high levels:
- IL-10
- TGF-β
- IL-6
- VEGF
These growth factors are essential for the immunosuppressive capability of MSC stem cells. WJ-MSCs can also inhibit the differentiation of CD14+ monocytes into mature DCs through direct contact and soluble factors. Additionally, WJ-MSCs mediate immunosuppression of B, T, and NK cells via different mechanisms, including the secretion of soluble factors like IDO, PGE2, and sHLA-G5, as well as the expansion of regulatory T-Cells.
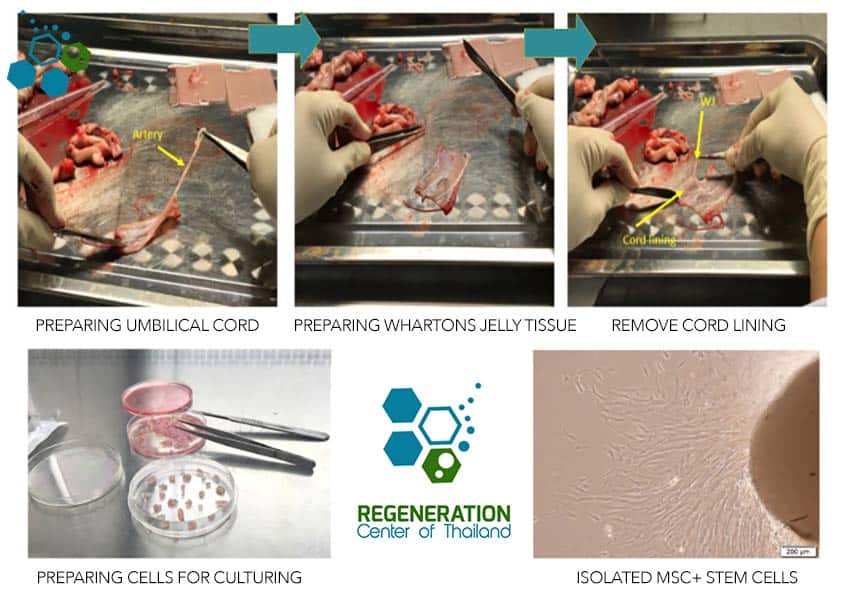
Techniques for Wharton’s Jelly Stem Cell Extraction
To harness the potential of Wharton’s Jelly stem cells, they must first be extracted using the following steps:
- Umbilical Cord Collection: After obtaining informed consent from a donor, the umbilical cord is collected following a sterile procedure during childbirth. The samples are screened for infectious diseases.
- Enzymatic Digestion: The umbilical cord tissue is minced and treated with enzymes such as collagenase and hyaluronidase to break down the extracellular matrix and release the stem cells.
- Isolation and Culture: The cord tissue is filtered, and the stem cells are isolated using centrifugation. The cells are then cultured in a suitable growth medium to expand their numbers before being utilized in research or stem cell therapies
Wharton’s Jelly stem cells hold remarkable potential for advancing regenerative medicine, tissue engineering, and immunomodulation. Their unique properties, combined with their ethical and accessible source, make them an attractive option for researchers and clinical applications of stem cell therapies at the Regeneration Center. As our understanding of these cells continues to grow, so too will their potential applications and the impact they have on improving human health.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Panta W, Imsoonthornruksa S, Yoisungnern T, Suksaweang S, Ketudat-Cairns M, Parnpai R. Enhanced Hepatogenic Differentiation of Human Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Using Three-Step Protocol.Supported by Suranaree University of Technology (SUT), the Office of the Higher Education Commission under National Research University (NRU) project of Thailand, Thailand Research Fund. Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jun 20;20(12):3016. doi: 10.3390/ijms20123016. PMID: 31226809; PMCID: PMC6627410.
[2] ^ Tanthaisong P, Imsoonthornruksa S, Ngernsoungnern A, Ngernsoungnern P, Ketudat-Cairns M, Parnpai R. Enhanced Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Umbilical Cord Wharton’s Jelly Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by GSK-3 Inhibitors.Thailand PLoS One. 2017 Jan 6;12(1):e0168059. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168059. PMID: 28060847; PMCID: PMC5217863.
[3] ^Arutyunyan I, Elchaninov A, Makarov A, Fatkhudinov T. Umbilical Cord as Prospective Source for Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:6901286. doi: 10.1155/2016/6901286. Epub 2016 Aug 29. PMID: 27651799; PMCID: PMC5019943.
[4] ^ Saleh M, Fotook Kiaei SZ, Kavianpour M. Application of Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells in patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Feb 15;13(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02746-x. PMID: 35168663; PMCID: PMC8845364.
[5] ^Günay AE, Karaman I, Guney A, Karaman ZF, Demirpolat E, Gonen ZB, Dogan S, Yerer MB. Assessment of clinical, biochemical, and radiological outcomes following intra-articular injection of Wharton jelly-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A prospective clinical study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 16;101(37):e30628. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030628. PMID: 36123928; PMCID: PMC9478323.

