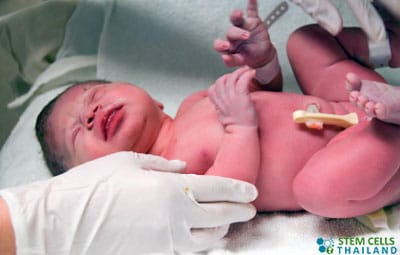
Cord blood refers to blood left in the umbilical cord after birth. Back in the day, this was generally discarded. However, because of modern advances in regenerative medical sciences, scientists have found a very useful purpose for them. The goal now is preservation or application of cord blood instead of discarding them. Why? Because it has been found to be rich in mesenchymal stem cells.
Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplants
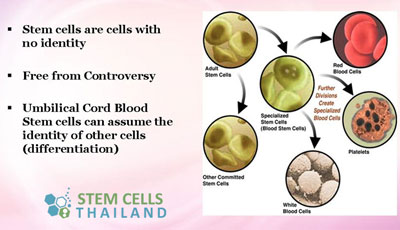
Stem cells are the essential ingredient in cell transformation, renewal and natural healing. These regenerative properties plays a pivotal role in the modern treatment of diseases. Stem Cells are natures pharmacy and they are usually found in bone marrow,adipose fat,dental pulp derived or peripheral blood of all people and are responsible for healthy cellular and tissue growth. When a stem cell undergoes division, the new cell has the option to remain the same or convert itself into another type with a different function. This process is called differentiation and it is the basis for cell therapy in Thailand.
Stem Cell Research has found cord blood to contain very high concentrations of adult stem cells that eventually develop as hematopoietic blood cells. The resultant stem cells are called hematopoietic or blood-forming stem cells as they are found to be similar to bone marrow stem cells, which has been widely used in treating a variety of genetic disorders , diseases of the blood and autoimmune diseases such as lupus, diabetes along with kidney disease, and in post cancer therapies.
Cord Tissue Collection
The collection of cord stem cells is done within minutes after delivery, specifically when the placenta has come out. The doctor drains off blood from an umbilical cord vein through needle aspiration. It only takes about 10 minutes, after which, the blood shall be sent to the laboratory for further tests to determine the presence of infection or diseases, and other necessary blood typing procedures.
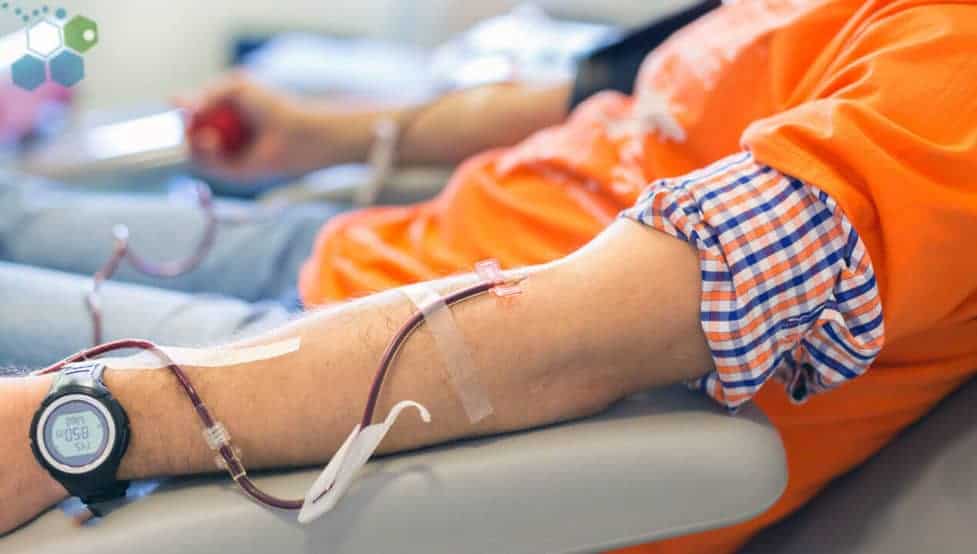
Cord blood collection actually possess lesser risks compared to having them donated. The only requirement is a pregnant mother who is about to deliver her child. There is no risk to both mother and child as the procedure occurs as a normal part of the child delivery process. Whereas with blood donations, donors will have to undergo several tests for clearance and then a series of GSF injections to stimulate release of the cells from the bone marrow into the blood. This is more painful and tedious in our treatment protocols as the donor would have to be put under anesthesia because blood is basically drawn out from the insides of the bone, which could be very painful.
Cord Blood Banking
If you are a parent and you wish to donate cord blood, you may be able to do so by contacting blood cell banks and making the necessary arrangements about six weeks prior to your due date. You have the choice to store your newborn’s cord blood at a private cord blood bank for family use in case your baby or a relative needs it. It can also be stored in public blood banks for anybody to have access to it as long as it is their genetic match.
UCB Stem Cells for Treatments
In Thailand today,Umbilical Cord Blood or UCB stems cells are currently being used in treatment of over 105 diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancers, hereditary/genetic diseases as well as blood disorders such as sickle cell anemia. Our allogenic Cord blood stem cell transplant program uses only the highest quality stem cells that are infused into the bloodstream and injected locally into areas of distress where they help jumpstart the natural healing and repairing process for any type of tissue or cells in the body.More frequently asked questions
Diseases Treatable with UCB Cord Tissue Stem Cells Today:
Treatable Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes
- Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
- Juvenile dermatomyositis
- Shwachman syndrome
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia
- Cyclic neutropenia
- Congenital sideroblastic anemia
- Kostmann’s syndrome
- Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
- Red cell aplasia
- Thrombocytopenia with absent radius (TAR syndrome)
- Glanzmann’s disease
- Fanconi anemia
- Dyskeratosis congenita
- Severe aplastic anemia
- Autoimmune neutropenia (severe)
- Evan’s syndrome
Cancers Treatable with UCB Stem Cells
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML)
- Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- Burkitt’s lymphoma
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
- Juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia (JMML)
- Lymphomatoid granulomatosis
- Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
Blood Disorders Treatable with UCB Stem Cells
- α-thalassemia major (hydrops fetalis)
- Sickle βo Thalassemia
- E-βo thalassemia
- HbSC disease
- E-β+ thalassemia
- β-thalassemia major (Cooley’s anemia)
- Sickle-cell anemia (hemoglobin SS)
- β-thalassemia intermedia
Metabolic Disorders Treatable with UCB Stem Cells
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Sandhoff Syndrome
- Hurler syndrome
- Metachromatic leukodystrophy
- Lesch-Nyhan disease
- X-linked lymphoproliferative disease
- Immunodeficiencies
- Krabbe disease (globoid cell leukodystrophy)
- Niemann Pick Syndrome, type A and B
- Alpha mannosidosis
- Tay-Sachs Disease
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- DiGeorge syndrome
- X-linked Mucolipidosis, Type II
- Adenosine deaminase deficiency
- Omenn’s syndrome
- Gunther disease
- Adrenoleukodystrophy Gaucher’s disease (infantile)
- Hurler-Scheie syndrome
- Sanfilippo syndrome
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome
- Immune dysregulation polyendocrineopathy
- Batten disease (inherited neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis)
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia
- Hunter syndrome
- Myelokathexis X-linked immunodeficiency
- Thymic dysplasia
- Chronic granulomatous disease
- Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome
- IKK gamma deficiency
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
- Reticular dysplasia
- Mucolipidosis Type II, III
Cord Blood Stem Cell Transplants
Treatable Immunodeficiencies
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency
- X-linked agammaglobulinemia
- X-linked lymphoproliferative disease
- X-linked Mucolipidosis, Type II
- Adenosine deaminase deficiency
- Myelokathexis X-linked immunodeficiency
- IKK gamma deficiency
- Thymic dysplasia
- DiGeorge syndrome
- Chronic granulomatous disease
- Omenn’s syndrome
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Reticular dysplasia
- Immune dysregulation polyendocrineopathy
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Autism

Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes
- Dyskeratosis congenita
- Congenital sideroblastic anemia
- Amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia
- Evan’s syndrome
- Glanzmann’s disease
- Fanconi anemia
- Autoimmune neutropenia (severe)
- Kostmann’s syndrome
- Cyclic neutropenia
- Thrombocytopenia with absent radius (TAR syndrome)
- Shwachman syndrome
- Red cell aplasia
- Severe aplastic anemia
- Congenital dyserythropoietic anemia
- Juvenile dermatomyositis
- Diamond-Blackfan anemia
The Basics of Cord Tissue Stem Cells
Other Treatable Diseases With UCB
- Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- Osteopetrosis
- Spondyloarthritides diseases
- COPD
- Gout
- Spinal Cord Injuries
- Arthritis
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis
- Cardiac Diseases
- Diabetic Neuropthy
- Degenerative Disc Disease DDD
To learn more about cord blood banking or cord blood stem cell treatments please contact us today.