The term Regenerative medicine pertains to a medical field focusing on treatments utilizing adult stem cells and embryonic stem cells. These are used to stimulate the process of differentiation into a particular cell variant deemed necessary for cell and tissue repair.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on regenerative medicine, a revolutionary approach to healthcare that’s set to change how we treat diseases and injuries. By diving into the basics of regenerative healthcare, we’ll uncover how this advanced field employs tissue engineering and stem cell therapies.
The Basics of Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative medicine is not just a buzzword; it’s a rapidly growing field that offers the promise of repairing damaged tissues and organs in the body. Unlike traditional medicine, which mainly focuses on treating symptoms, regenerative healthcare aims to tackle the root causes of ailments. Utilizing groundbreaking techniques in tissue engineering, and stem cell therapies, this form of medicine opens up new pathways for treating debilitating conditions.
Tissue Engineering and Stem Cell Therapies
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering, a cornerstone of regenerative medicine, deals with the fabrication of artificial organs and tissues that can be used for transplantation. These bioengineered tissues not only offer the potential for limitless donor organs but also reduce the risk of rejection by the body.
Stem Cell Therapies
Another pivotal aspect is stem cell therapies. Stem cells are unique in that they have the ability to become many different types of cells. With proper manipulation, these cells can be guided to repair tissues or replace damaged organs, offering a wide range of treatment possibilities.
Applications in Healthcare
From orthopedic surgeries to treating chronic diseases, regenerative healthcare has numerous applications. Ongoing research aims to tackle complex conditions like Alzheimer’s, type 1 diabetes, and even spinal cord injuries. The spectrum of its application in regenerative healthcare is incredibly vast.
- Orthopedic Treatments: Bone and cartilage repair
- Cardiovascular Diseases: Heart tissue repair
- Neurological Conditions: Treatment of degenerative nerve diseases
Future Prospects of Regenerative Medicine
Considering the exponential growth and scientific advancements, the future for regenerative stem cell treatments is immensely promising. With continued investment in research, we can expect revolutionary treatments that could even eliminate the need for organ transplantation in the foreseeable future.
Regulatory Considerations and Ethical Implications
While the possibilities are thrilling, it’s important to consider the regulatory and ethical aspects. Governing bodies like the FDA are putting stringent measures in place to ensure the safety and efficacy of treatments.
The Transformative Power of Regenerative Medicine
Regenerative healthcare and functional medicine is more than just a promising field; it’s a transformative approach to healthcare. With its potential applications in tissue engineering and stem cell therapies, it’s set to redefine how we perceive medicine and treatment. The potential for curing previously untreatable conditions makes this a realm of science worth watching closely.
Regenerative healthcare refers many biomedical uses in clinical therapies we offer that involve the use of stem cells. Examples include upper motor neuron cells, progenitor cells that are obtained by differentiation and culturing along with the induction of biologically active molecules that are injected alone to increase stem cells naturally or are secreted by the enriched / infused cells in a process known as immunomodulation therapy. The transplantation lab grown organs and also for tissue engineering.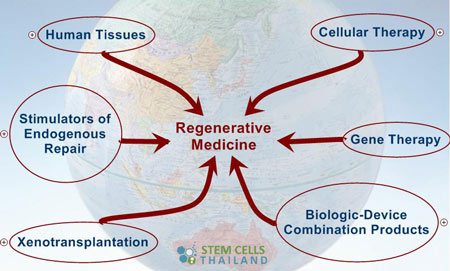
The Regeneration center is the leading proponent of safe and effective regenerative medicine to eliminate disease and suffering for all humans. The term regenerative medicine was first used in the human genome projected when scientists isolated human embryonic stem cells along with embryonic germ cells. These freshly-isolated cell lines essentially opened the gates and mysteries of cell biology for the first time in human history. Those early findings lead to more research which ultimately lead to the use and manufacturing of nearly all cell types in the human body for use in clinical regenerative therapies.

