Arthritis consists of over 128 unique conditions and auto-immune diseases that can trigger severe joint irritation and discomfort. Stem Cell transplants for arthritis can help manage and eliminate the arthritic condition permanently, safely, and effectively using enhanced UC-MSC+ stem cells.
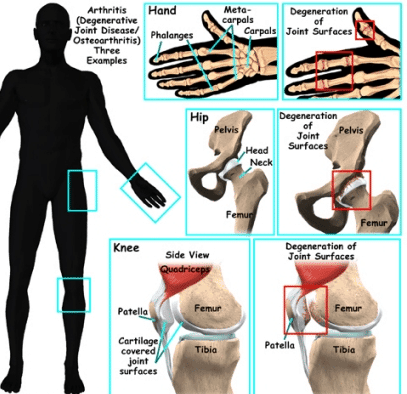
Arthritis is not a single condition; it is a family of over 100 types of conditions referring to joint disease or joint pain. The two common forms of arthritis are osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The disease affects people of all genders, ages, and racial backgrounds and is considered one of the leading causes of disabilities in the world. A diagnosis of arthritis can occur as we begin to age.
Common symptoms of arthritis include:
- Severe Pain in joints
- Swelling of joints
- Stiffness or decreased range of motion
- Redness
Rheumatoid Arthritis Vs. Osteoarthritis Treatment
Signs often come and go, ranging from mild, moderate, to even severe. Patients frequently ignore the symptoms for years but usually find that the disease degenerates even further over time, causing severe chronic pain and the inability to do typical day-to-day activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or exercising. If left untreated, Arthritis will cause permanent and visible joint damage, such as knobby/knotted finger joints. An MRI or X-ray is needed to evaluate treatment options thoroughly for those who do not display symptoms. Some types of severe arthritis will also affect the patient’s heart function, vision/eyes, impaired kidney function, skin, lungs, and circulatory system.
Risk factors for Acquiring a Diagnosis of Arthritis include:
- Genetics or Family history – Arthritis can run in families, so patients who have parents or siblings with the disorder will likely develop arthritis. Genes can also make us more susceptible to external/environmental factors that trigger the onset of arthritis. Testing for genetic arthritis is now available.
- Gender – Women are much more likely to develop rheumatoid arthritis than men, while most patients who get diagnosed with gout ( another type of arthritis) are men.
- Patients with a previous joint injury – People who have injured and surgically treated hip or knee joints are at a much higher risk of developing arthritis in that joint. An alternative to knee surgery or reduce the risk of knee osteoarthritis, Hip Surgery, or shoulder surgery is recommended.
- Obesity/Body Weight—Excess weight can damage joints and put extra stress on joints such as knees, spine (spinal stenosis), or hips. Therefore, overweight people have a much higher risk of developing arthritis as they age.
- Age – The risk of acquiring many types of arthritis increases as we age.
There are numerous well-known types of joint arthritis in the world today. The two main types of joint arthritis are osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis. RA, or Rheumatoid joint inflammation, is a constant ailment. RA starts with irritation, tiredness, joint discomfort, and or stiffness. As this problem worsens, you will experience frequent flu-like symptoms and muscle pains. Osteoarthritis, on the other hand, is a “wear & tear” problem. Osteoarthritis is a lot more familiar with age and is now manageable with Stem Cell treatment for Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis begins with stiffness and joint discomforts and is treatable with stem cell treatment for osteoarthritis.
Ankylosing Spondylitis & Spinal Arthritis
UC-MSC+ Stem Cells for Autoimmune Arthritis
Additional types of joint inflammations that are treatable in a short trip to Thailand consist of:
- Stem Cell Treatment for Lupus

- Cell Transplants for Fibromyalgia
- Stem cell therapy for Gout
- Therapy for Septic Arthritis
- Stem Cell Treatment for Sarcopenia
- Stem Cell Treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Stem Cells for Hip Arthritis
- Treatment for Psoriatic Joint inflammation
- Stem Cell Treatment for Knee Osteoarthritis
- Treating Arthritis in Feet and Hands
- Stem Cell Therapy for Shoulder Arthritis
The types of stem cells needed for treatment depend on the autoinflammatory vs autoimmune disease the patient is diagnosed with. However, (UC-MSC+) mesenchymal stem cells offer a viable alternative to invasive knee replacement surgery or hip replacement surgery. The Regeneration Center provides a safe and effective cell-based treatment for degenerative Arthritis that can quickly help relieve pain, problems, and unnecessary physical suffering. Usually, most adult females and men between 40 and 65 establish some cartilage and joint issues that result in osteoarthritis. These conditions can safely be treated today using UC-MSC+ Cells for Joint inflammation and Arthritis.
Stem cell therapy for cartilage regeneration
Cell regenerative medicine allows the replacement cells to travel throughout your body through a process known as “homing.” Homing means the cell is actively “homing” to distressed/injured areas throughout your body.[1] Autologous regeneration of joints requires harvesting the cells from autologous fat, peripheral blood, or marrow, then separating and expanding the mesenchymal cells over 2-4 weeks. [2] For older patients or those with an underlying medical condition that will not allow us to take stem mesenchymal stem cells from their body (bone marrow-derived), we can offer isolated allogeneic stem cells to begin the tissue repair process in the cartilage matrix.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Cartilage Regeneration
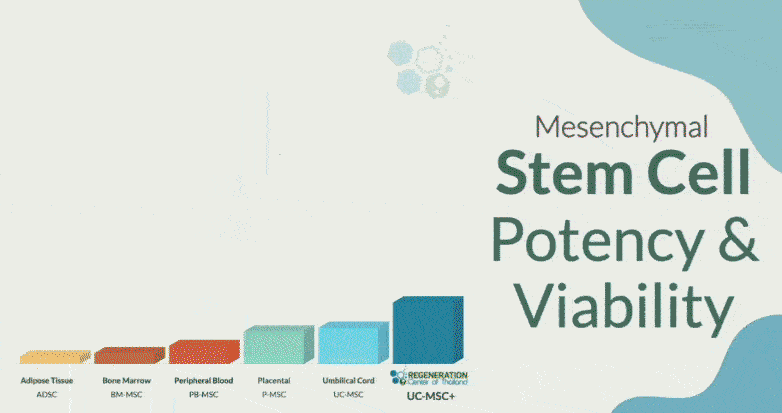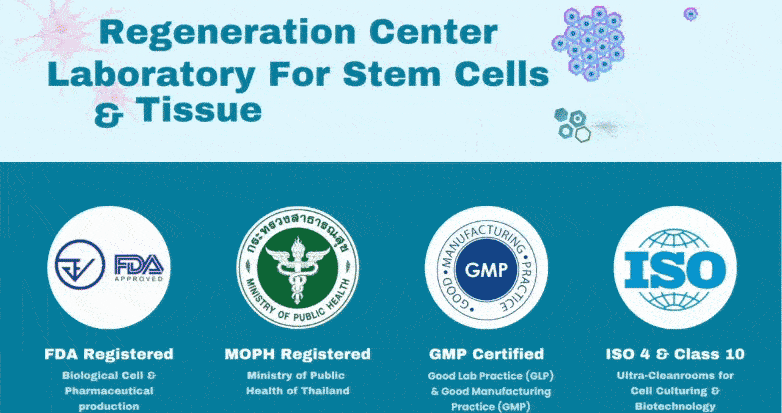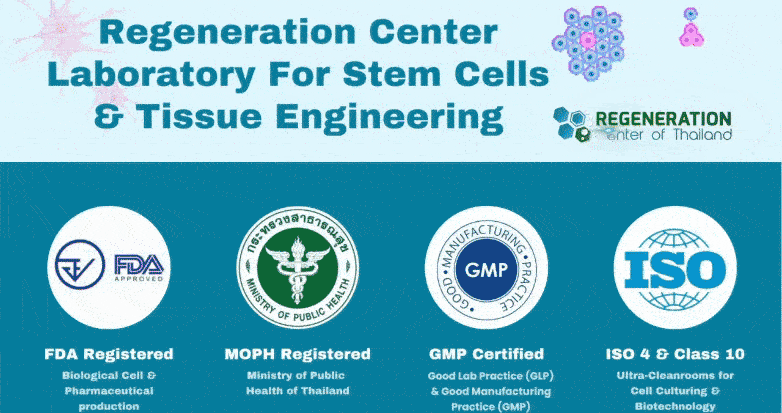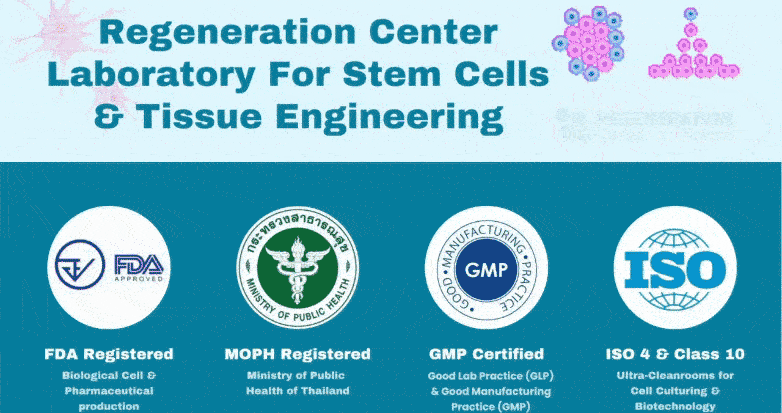
Some background information is needed to evaluate the long-term safety and efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell (UC-MSC) treatments for osteoarthritis (OA). UC-MSC cells can be easily obtained in several areas, including bone marrow, peripheral blood, cord tissue, placental tissue, and Wharton’s jelly. When properly extracted, they are considered safe and do not prevent future treatments if needed. The isolated UC-MSC stem cells are cultured for 7-10 days at our stem cell lab in Bangkok before they are injected back into the joints affected by OA. This process can be started before patient arrival so that treatment can begin on Day 1.
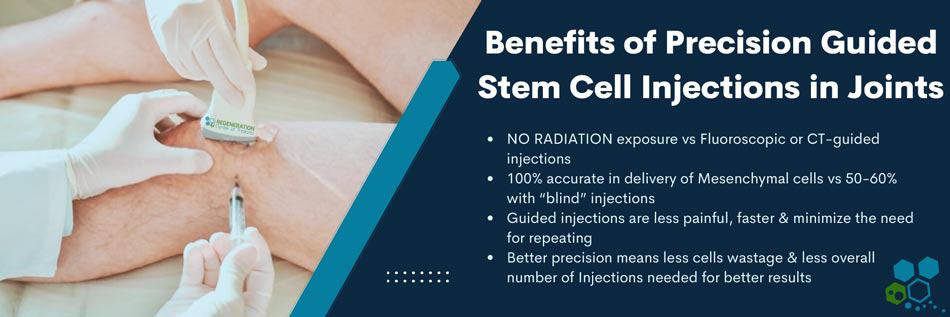
Stem Cell Delivery Methods
For patients with moderate multi-level disc degeneration, multiple sessions of clinical grade expanded UC-MSC+ Mesenchymal Cells will be used along with our proprietary mix of growth factors that can include Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β), Fibroblast Growth Factors (FGF), Platelet-Derived Growth Factors (PDGF), Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs), Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1), Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors (VEGF), Connective Tissue Growth Factors (CTGF), Epidermal Growth Factors (EGF), and Nerve Growth Factors (NGF). The isolated cells and growth factors are delivered via intravenous drips, direct local injections, intradiscal injections, intrathecal injections, fluoroscopy-guided stem cell delivery (in a hospital setting only), or a combination of different delivery methods to achieve the best results.
What are the disadvantages of using stem cells to treat Arthritis?
There are several different methods for using isolated MSC+ cells in treatment. One way involves expanding the undifferentiated stem cells in our stem cell lab to create a more uniform population of cell types needed before introducing them back to the patient over two weeks. This approach allows us precise control over the types and quantities of cells used. An alternative and less effective way is to use bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) or stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cells. This method generally does not use extensive cell manipulation and has a more straightforward regulatory pathway. However, the lack of cell culturing offers fewer MSC cells compared to expanded protocols (UC-MSC+)cells. In addition to bone marrow and adipose tissue, other sources of UC-MSC cells include isolating cells from amniotic fluid and cord membranes. Allogeneic MSC cells from these sources can be used since they have low immunogenicity and can avoid immune responses in recipients. This approach is often more beneficial for older patients or those with multiple co-morbidities whose UC-MSC cells may have reduced regenerative potential for knee OA and require total knee replacement surgery or several rounds of intra-articular injection of mesenchymal stem cells and osteoarthritis therapy.
What is the success rate of stem cell treatment for osteoarthritis?
UC-MSCs mainly describe various stromal cell populations that are expanded outside the body. For over 40 years, UC-MSC cells have been used in musculoskeletal treatments because of their ability to become tissue-specific cells like osteoblasts, chondrocytes, and tenocytes. However, about a decade ago, The Regeneration Center started isolating MSC cells to enhance their ability to sense their environment and release bioactive molecules, such as cytokines, antioxidants, and trophic growth factors. These molecules and growth factors are used with UC-MSC+ stem cells to re-establish tissue balance after an injury. Thus, our combination protocol using UC-MSC+ cells offers significantly higher success rates thanks to adding the medicinal signaling cells and tissue-specific growth factors. Clinical trials have shown that expanded UC-MSC cells can help repair tissues by reducing inflammation, limiting stress response, and recruiting immune and reparative cells. Regeneration Center research has also shown that a pro-inflammatory environment can help trigger the anti-inflammatory effects of UC-MSC+ cells. For example, UC-UC-MSCs exposed to synovial fluid or inflammatory cytokines show increased anti-inflammatory molecule production and inhibit T-cell proliferation. Learn about the Top 10 foods to fight osteoarthritis. While our findings don’t negate the idea that UC-MSCs can directly differentiate into tissue-specific cells, it’s difficult to achieve good results from a small sample of UC-MSC from bone marrow aspirate concentrate (BMAC) or stromal vascular fraction (SVF) injected into a joint over a short 1-3 day protocol can reach multiple damaged areas and produce new cartilage. Therefore, our treatment protocol is unique as it uses two mechanisms of UC-MSC action (paracrine and direct cell differentiation), which are not mutually exclusive. Still, their differences are crucial for understanding and setting realistic expectations for patients undergoing stem cell therapy for Arthritis.
Can stem cells reverse osteoarthritis?
Many studies have been done to assess the efficacy of regenerative treatment for osteoarthritis (OA), but there are limitations on what is realistically possible. When treating a patient with OA joints, they should expect quick symptom relief due to UC-MSC+ cells’ ability to release various molecules that help tissue repair and reduce inflammation. However, if one improperly or without tissue-specific growth factors, the duration of these effects will be limited. For a more permanent solution for OA and femoral neuropathy, a protocol must use multiple types of cells, growth factors, and delivery methods followed by proper rehab to ensure sustained long-term benefits of stem cell therapy. Our treatment goal is to improve a patient’s quality of life for longer than one year. Still, it requires several steps to be completed to achieve satisfactory results, especially for those who have been suffering for a long time and have been using daily painkillers or anti-inflammatory drugs with known side effects. Predicting a patient’s response to the Regeneration Center treatment for Arthritis can be complex without reviewing the patient’s medical information, as each person’s symptoms, stages, and severities vary.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note that not all patients are suitable candidates for stem cell therapy for Osteoarthritis or Gouty Arthritis. Patients with advanced joint damage, severe deformities, multiple joint involvement, or other significant health issues may not be good candidates for treatment.Expanded UC-MSC+ Stem Cells for Osteoarthritis
Stem cell research for arthritis has helped us create a unique protocol focused on safety and efficacy. Our stem cell treatments for arthritis combine an affordable method of managing arthritic degenerative conditions that can assist your body in healing faster, eliminating pain stiffness, and improving function by removing the pain. The protocol for treating Arthritis in 2 phases using Mesenchymal Cells combined with growth factors to create a higher percentage of blood platelets. Cellular therapy for Arthritis and Osteogenic cartilage cells & growth factors are combined to help expedite the recovery process in the damaged tissues and knee cartilage. Stem cell research has shown UC-MSC cells are the gold standard alternative therapy to repair tissue via essential anti-inflammatory elements and growth factors needed for the cell-homing process and instruct the cells of the body that it’s time to commence the natural healing process.
Stem Cell therapy for Osteoarthritis
Isolated and enhanced UC-MSC+ stem cells are introduced to multiple points near the joints or tissue bordering the troublesome areas. [3] Utilizing only the latest techniques to treat arthritis, these repair stem cells modify and mend the damaged tissues and instruct the broken cells to repair themselves, resulting in pain relief.[4] We are the leading treatment provider center of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Mesenchymal and Autologous Stem Cell Therapy from adipose tissue, peripheral blood, bone, & Stem cell treatment for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Other cell-based therapies we offer include treatment of spinal trauma, treatment for heart disease, peripheral neuropathy, treatment for diabetics, treatment for Autism, treatment of knee osteoarthritis, reduced knee pain, and stem cell treatment for kidney failure. [5]
Before After Stem Cell Therapy for Arthritis
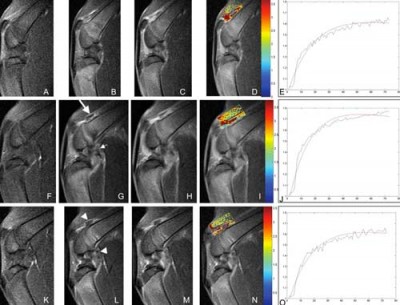
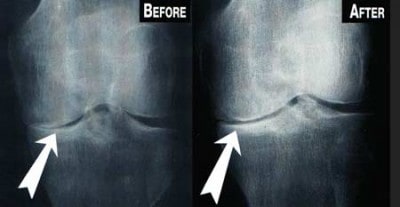
Avoid Joint Replacement Surgery With Stem Cell Therapy in Knee
Total Number of Adult Stem Cell Injections: The total number of Endogenous Mesenchymal Stem cells, cartilage cells exosomes, and regenerative growth factors to repair tissue will vary based on patient needs, locations of knee pain, and severity of cartilage defects. Eligibility criteria depend on the injury requirements needed; the treatment infusions can be done via a guided radiograph through Intravenous Infusions, Direct injection, intra-articular injections, or Intrathecally using different cell types.[6]
Rehabilitation Post Treatment: Physical Rehabilitation and weight loss programs are optional but highly recommended. Complete physical rehab services after regenerative therapy can be provided upon request for 2-3 hours per day and up to 5 days per week.
The Total Time Required To Treat the Hip and Knee is estimated to be around two weeks (depending on the type and seriousness of the condition). Medical and travel visas for extended accommodations at a hotel or apartment for the patient and family can also be provided upon request.
Treating Osteoarthritis with Stem Cells
Cost of Stem Cell Treatment for Osteoarthritis in 2025
UC-MSC+ Stem Cell treatment for arthritis and osteoarthritis cell therapy will require an estimated 10-14 days. Due to the varying degrees of severity, our orthopedic team will need to evaluate potential patients to establish an appropriate protocol. Upon completion of the medical review, a detailed treatment plan will be provided that will include the specifics, such as the exact total number of nights required, along with the total medical-related costs. To begin the evaluation process for our multi-stage arthritis treatment protocol w/ intra articular injections, please prepare your recent medical records, such as radiology scans w/ Blood tests, and contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Hauser, Ross A, and Amos Orlofsky. 2013. Regenerative injection therapy with whole bone marrow aspirate for degenerative joint disease: a case series. Clinical medicine insights. Arthritis and musculoskeletal disorders (September 4). doi:10.4137/CMAMD.S10951. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24046512
[2] ^ Kheansaard, Wasinee, Sumana Mas-Oo-di, Surasak Nilganuwong, and Dalina I Tanyong. 2012. Interferon-gamma induced nitric oxide-mediated apoptosis of anemia of chronic disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology international, no. 1 (January 19). doi:10.1007/s00296-011-2307-y. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22258456
[3] ^ Oshita, Koichi, Kunihiro Yamaoka, and Yoshiya Tanaka. 2013. [Regulation of osteoclastogenesis by human mesenchymal stem cells leading to application of a novel treatment for rheumatoid arthritis]. Journal of UOEH, no. 1 ( 1). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23475022
[4] ^ Roelofs, A J, J P J Rocke, and C De Bari. 2013. Cell-based approaches to joint surface repair: a research perspective. Osteoarthritis and cartilage, no. 7 (April 15). doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.04.008. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23598176
[5] ^ Turajane, Thana, Ukrit Chaweewannakorn, Viroj Larbpaiboonpong, Jongjate Aojanepong, Thakoon Thitiset, Sittisak Honsawek, Juthatip Fongsarun, and Konstantinos I Papadopoulos. 2013. Combination of intra-articular autologous activated peripheral blood adult stem cells with growth factor addition/ preservation and hyaluronic acid in conjunction with arthroscopic microdrilling mesenchymal cell stimulation Improves quality of life and regenerates articular cartilage in early osteoarthritic knee disease. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet, no. 5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23745314
[6] ^ Zhen, Gehua, Chunyi Wen, Xiaofeng Jia, Yu Li, Janet L Crane, Simon C Mears, Frederic B Askin, et al. 2013. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nature medicine, no. 6 (May 19). doi:10.1038/nm.3143. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23685840