The medical term of “cytokine” is derived from a blending of two Greek words – “cyto” or cell and “kinos” which means movement.
Cytokine molecules exist in peptides, proteins and glyco-proteins (sugar attached). The cytokines cells come form a sizable family of molecules that can be classified into several different categories due to them not being part of a specific classification system.
Cytokine Chain Signaling – VIDEO
Cytokines markers range from the interferons that control the immune system’s reaction to disease and inflammation and also the biological agents known as interleukin.[1]
There’s some disagreement in the regenerative medical community whether or not molecules should be called cytokines or hormones but classic protein markers circulate in close nanomolar concentrations. Cytokinesis on the other hand circulate in picomolar concentration and might quickly differentiate in magnitude of nearly a thousand times its population as a response to an infection or inflammation.[2]
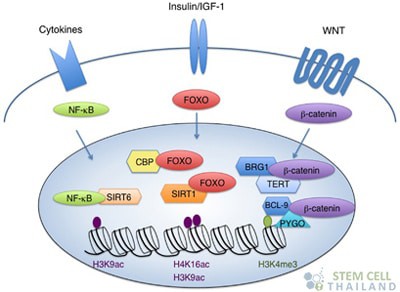
Cytokines cells have many sources with virtually all human cells having a nucleus effective at generating interleukin 1 (IL1), interleukin 6 (IL6), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha), especially the epithelial and endothelial cells along with macrophages. In contrast, classic hormones are only secreted from certain glands such as the kidney or pancreas that secretes insulin.
A cytokine’s movement patterns and activities may change into the very cell it had been secreted from. it can also work other damaged cells nearby or even “act” in a manner similar to the endocrine system to generate effects throughout the entire body, such as regulating body temperature for an example.
The most current category used to define cytokines are as “immunomodulating agents” or bio-agents that modulate the immune systems reactions. Cytokines are very important regulators of both innate and adaptive immune response system in humans.[3]
At the Regeneration Center of Thailand, Chemokines, Cytokines and other growth factors are used in most hematopoietic cord blood therapies for purposes such as:
- Self-renewal
- Quiescence
- Mobilization from the stem cell niche
- Differentiation
- Apoptosis
To learn more about cytokines or if you have any other questions please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Chuenchitra, Thippawan, Pittapun Chaitaveep, Suchitra Sukwit, Sukchai Dettrairat, Sutchana Tabprasit, Surangrat Srisurapanon, Surapol Kohreanudom, et al. 2012. Cytokine profiles in HIV-1 subtype CRF01_AE infected individuals with different rates of diseases progression: a multiplex immunoassay. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22934457
[2] ^ Kheansaard, Wasinee, Prapaporn Panichob, Suthat Fucharoen, and Dalina I Tanyong. 2011. Cytokine-induced apoptosis of beta-thalassemia/hemoglobin E erythroid progenitor cells via nitric oxide-mediated process in vitro. Acta haematologica, no. 4 (September 21). doi:10.1159/000329903. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21934298
[3] ^ Zhang, Cheng C, and Harvey F Lodish. 2008. Cytokines regulating hematopoietic stem cell function. Current opinion in hematology, no. 4. doi:10.1097/MOH.0b013e3283007db5. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18536567