Still considered one of the most lethal cancers in the world, Pancreatic cancer is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world, with an average survival rate of less than 8%, making it the only known cancer type with pancreatic cancer life expectancy and survival rates below 10%. Pancreas cancer typically forms in the pancreas (lower part of the stomach), where its primary job is to slowly release enzymes to help aid in digestion and release hormones that help humans manage blood sugar levels. Once it takes hold, Pancreatic cancer usually spreads reasonably rapidly to surrounding organs and is rarely detected in the early stages. Early detection is beneficial, and patients with pancreatic cysts or hereditary components of pancreatic cancer should schedule regular screenings to detect any problems early on.
Biological Immunotherapy for the Pancreas
High-Risk Factors for Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Patients who are considered high risk for developing pancreatic cancer include:
- Patients with Diabetes
- Previous or Current Smokers
- Patients with Chronic Pancreatitis (Inflammation)
- Hereditary (DNA)Disposition for pancreatic cancer
- Genetic Disposition for Lynch syndrome, BRCA2 gene mutation & FAMMM syndrome (mole-malignant melanoma)
Obesity – Learn about genetic testing for Hereditary Pancreatic Cancer - Elderly ( Over 65 )
Signs & Symptoms Advanced Pancreatic Cancer
One of the early symptoms of pancreatic cancer is diabetes mellitus. Other early warnings of pancreatic cancer include:
- Radiating pain in the back or upper abdomen area
- Rapid and Unintended weight loss
- Sudden Loss of appetite
- Onset of diabetes
- Previous diagnosis of liver cancer
- Diagnosis of renal cancer
- Blood clots
- Pancreatitis
- Frequent Fatigue
- Jaundice ( Yellowing of skin and whites of the eyes)
- Depression
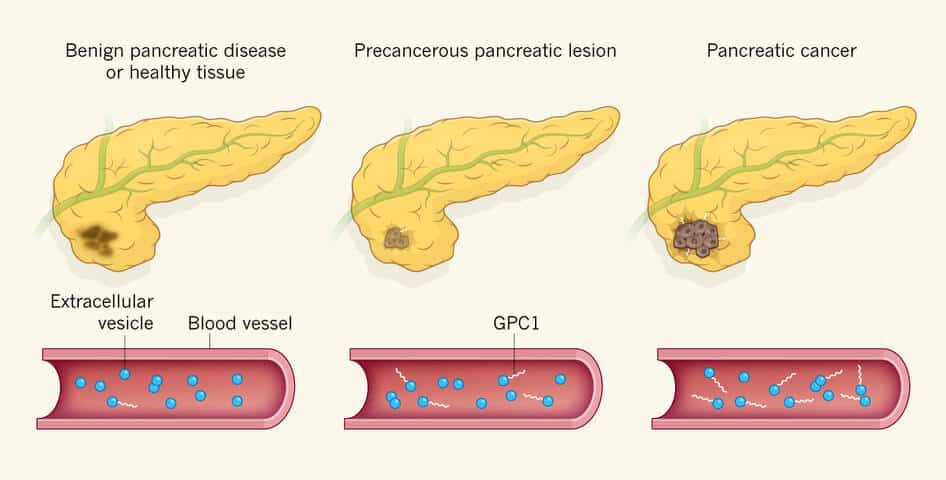
Four Stages of Pancreatic Cancer
- Confirmation of the Cancer is sometimes treatable using radiotherapy surgery
- The tumors have spread to nearby organs/tissues and possibly to lymph nodes
- The Cancer has spread well beyond the pancreas to major blood vessels and lymph nodes
- Cancerous mass spreads to distant areas, causing lung cancer, liver disease, stomach and the peritoneum lining (mesothelioma), and renal failure.
Causes of Exocrine Cancers
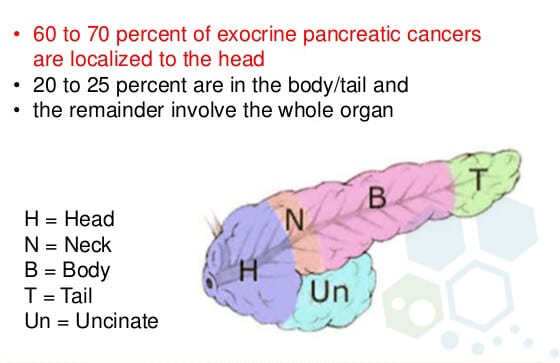
Cancer in the pancreas results from mutations in the DNA. These DNA mutations cause human cells to grow/divide uncontrollably and accumulate in masses. These accumulating mass of cells form a tumor in the duct lining of the pancreas.[1] This form of pancreas cancer is known as pancreatic exocrine cancer or pancreatic adenocarcinoma. In some rare cases, cancer can also form in neuroendocrine cells of the pancreas, which is irresponsible for the production of hormones. Cancer stem cells that attack this function are pancreatic endocrine cancers, islet cell tumors, and pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
Traditional Treatments for Pancreas Cancer
Functional medicine for cancer and clinical trials with gene therapies are available to patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, depending entirely on the type of cancer they are diagnosed with, the stage of cancer, and the location/spread of the disease.
The primary goal is usually to try to altogether remove the underlying cancer tumor along with any other cancerous masses in the body. For some cases, a complete surgical resection, Whipple procedure, laparoscopy, or distal pancreatectomy is an option; however, it requires very early detection and is only viable to less than 18% of the patients who are diagnosed with pancreatic cancer.
Other traditional treatment options include radiation therapy & chemotherapy or a combination of the two. Still, chances of curing pancreas cancer typically depend on the tumor location and severity of spread to lymph nodes. Unlike other forms of cancers like multiple myeloma, pancreatic cancer is much more resistant to traditional chemotherapies, and most patients using traditional means ultimately relapse and succumb to the effects of the rapidly spreading disease.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Please note that not all patients are suitable candidates for treating Pancreatic Cancer with NK cells, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies. Patients with advanced-stage cancer, severe organ involvement, or other critical health conditions might not be good candidates for the estimated 3-5 week treatment.Functional Oncology for Treating Pancreatic Carcinoma
Old enemy, modern approach – The Regeneration Center oncology team takes a unique biological-based intervention for the treatment of pancreas, Colorectal cancer, and prostate cancers. The immunotherapies have shown significant advantages when combined with cellular therapies in early and advanced cases of this disease. [2]
Our integrative approach to dealing with cancers uses a variety of techniques alone or as Adjuvant immunotherapies, including:
- Immune modulation & Checkpoint inhibitors – T-cell receptors producing an antitumor immune response
- Monoclonal antibodies – mAbs
- Adoptive cell transfers or Adoptive immunotherapy
- Therapeutic Dendritic cell vaccines – Leukocytes that present Antigens to T cells
- Cytokines – Interleukin, interferon, and growth factors
- Oncolytic virus Therapy to target infects and kills cancer cells
- High-Intensity Focused Ultrasounds or HIFU
- Cyberknife and Cryosurgery
- Photodynamic Cancer Therapy
- Stem Cell Therapy
- Internal Radiation Therapy
- Electrocautery

Pancreatic Cancer Immunotherapy
Our team of cellular oncologists has over 50 years of experience dealing with cancers and the immune system. Our holistic cancer treatment protocols offer a unique bio-engineered approach without invasive surgery or dangerous side effects. Our cancer protocols provide an integrative and targeted therapy to attack the tumors, alleviate the underlying symptoms, and significantly increase the overall quality of life for any patient diagnosed with the destructive effects of the disease. [3] With or without conventional therapies, our individualized treatment programs offer patients optimal chances for success.
CAR-T cell therapy for Pancreatic cancer in 2025
Traditional cancer therapies, such as radiation therapy & chemotherapy, expose humans to significant side effects and toxicity. Over time, the conventional treatments have not changed, but the cancer cells have evolved, making them more resistant to the chemicals and rendering these traditional therapies ineffective.[4] This cellular evolution of cancer stem cells is what leads to recurrence and allows them to increase much more aggressively than before the chemo & radiation therapies began. Some new pharmaceutical medications have been developed to target and destroy cancer cells with much less toxicity effectively. Still, the payloads often don’t reach the intended destinations and are consumed by the immune system before they can get the intended targets and tumors.
Modifying Immune Cells to Fight Cancer
Stem Cell Therapy for Pancreas Cancer
Our integrated approach to the alternative treatment of pancreatic cancers, stem cell cancer treatment protocol, and NK cell therapies continue to advance year after year. With discoveries in pancreatic cancer research, clinical trials for new protocols to more effectively treat stage 1 – stage 4 pancreatic cancer. The Regen Center is a pioneer in regenerative medicine and can apply new bioengineering techniques to manage fatal conditions better and to help our patients live cancer-free lives with minimal toxicity and without fear of remission.[5]
To determine eligibility and get treatment recommendations from our immunotherapy team, we will need to better understand the patient’s needs via recent histological results, Biopsy results, blood tests, x-rays, scans, bone marrow sample results, and/or clinical diagnosis documents from your primary care oncologist.
Being diagnosed with the big “C” does not have to be the last stand. Even if traditional cancer treatment options have reached their limits, Our team can still offer options that bring you one step closer to gene therapy treatment and living a cancer-free life. We are here to help you and your family get past the disease using safe and research-based alternative treatment options for treating cancer of the pancreas. To learn more, please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Kongkam, Pradermchai, Pichit Benjasupattananun, Pongpeera Taytawat, Patpong Navicharoen, Viroj Sriuranpong, Laddawan Vajragupta, Naruemon Klaikaew, et al. Pancreatic cancer in an Thailand and Asian population. Endoscopic ultrasound, no. 1. doi:10.4103/2303-9027.151361. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25789286
[2] ^ Grierson, Patrick, Kian-Huat Lim, and Manik Amin. 2017. Immunotherapy in gastrointestinal cancers. Journal of gastrointestinal oncology, no. 3. doi:10.21037/jgo.2017.05.01. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28736635
[3] ^ Bengsch, Fee, Dawson M Knoblock, Anni Liu, Florencia McAllister, and Gregory L Beatty. 2017. CTLA-4/CD80 pathway regulates T cell infiltration into pancreatic cancer. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy : CII, no. 12 (August 30). doi:10.1007/s00262-017-2053-4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28856392
[4] ^ Chaiteerakij, Roongruedee, Gloria M Petersen, William R Bamlet, Kari G Chaffee, David B Zhen, Patrick A Burch, Emma R Leof, Lewis R Roberts, and Ann L Oberg. 2016. Metformin Use and Survival of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer: A Cautionary Lesson. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, no. 16 (April 11). doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.63.3511. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27069086
[5] ^ Sriussadaporn, Suvit, Sukanya Sriussadaporn, Rattaplee Pak-Art, Kritaya Kritayakirana, Supparerk Prichayudh, and Pasurachate Samorn. 2013. Lessons learned from 100 personal consecutive cases of pancreaticoduodenectomy at a university hospital in Thailand. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet, no. 9. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24163990