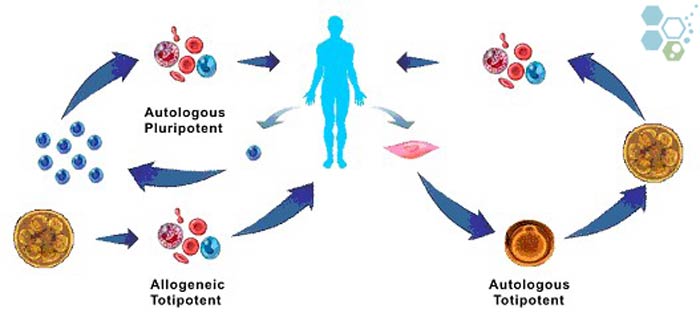
As opposed to autologous stem cells, allogeneic stem cells are isolated from donors then expanded into different cell lineages before given to patient needing a mesenchymal stem cell transplant. Unlike autologous cells allogeneic cells do not require surgical or painful extraction methods and can be safely given to replace patients own stem cells that have been destroyed by disease, injury of treatments requiring or high doses of chemotherapy. Allogeneic stem cell transplants have been used to suppress diseases and proactively treat rebuild patient immune systems for over 50 years mainly to treat blood related cancers, such as lymphoma, leukemia and other types of diseases like lung cancer, pancreatic cancer, liver cancer or auto-immune system disorders.
The Basics of Stem Cells Research
iframe src=”https://www.youtube.com/embed/i7EN6l9wqDU?rel=0&controls=0&showinfo=0″ width=”640″ height=”480″ frameborder=”0″ allowfullscreen=”allowfullscreen”>
Some sources of allogeneic stem cells include:
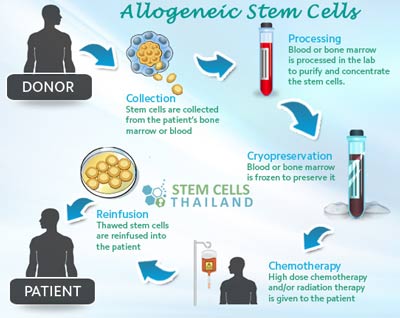
Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplants
- Cord tissue derived stem cells
- Dental pulp derived stem cells
- Peripheral blood stem cells
- Cord blood derived stem cells
- Placental (whartons jelly ) derived stem cells
- Bone Marrow derived stem cells
Stem cells are also present inside different types of human tissue including:
- The brain – Neural Stem cells
- Skeletal muscle derived stem cells
- Blood vessels
- Dental Pulp derived stem cells
- Skin Cells
- Hair Cells
- Embryonic stem cells
- Induced Pluripotent Cells
- Liver derived stem cells
However, stem cells can be difficult to extract and culture for medical use. Cells can also stay in a non-dividing / non-specific form for years until the body recruits them to repair or grow new tissue or begin the healing process after injury.