Sarcopenia, the gradual loss of muscle mass and strength associated with aging, presents a significant challenge to maintaining quality of life in older adults. This condition, which affects millions worldwide, can lead to an increased risk of falls, fractures due to osteoporosis, and loss of independence. While traditional approaches such as exercise and nutrition have long been the cornerstone of management, emerging stem cell therapies offer a promising new frontier in combating sarcopenia. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring these innovative treatment options can provide valuable insights into addressing this age-related decline and potentially transforming how we approach healthy aging.[1]
What Is Sarcopenia?
With age, many individuals experience a progressive loss of muscle mass, strength, and function, known as sarcopenia. This condition is characterized by a gradual decline in skeletal muscle tissue, typically beginning around 30 and accelerating after 65. Sarcopenia is a complex, multifactorial disorder that significantly impacts an individual’s quality of life, mobility, and independence.
The primary factors contributing to sarcopenia include decreased physical activity, nutritional deficiencies, and hormonal changes associated with aging. As muscle mass diminishes, individuals may experience reduced strength, impaired balance, and increased risk of falls and fractures. This decline in muscle function can lead to a cycle of decreased physical activity, further exacerbating muscle loss. Diagnosing sarcopenia involves evaluating muscle mass, strength, and physical performance through various methods, including dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), and grip strength tests. Early detection is essential for implementing effective rehabilitation strategies and preventing further decline.
Management of sarcopenia typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining resistance training, aerobic exercise, and nutritional interventions. Resistance training, in particular, has shown considerable benefits in preserving and even increasing muscle mass and strength in older adults. Proper nutrition, including adequate protein intake and vitamin D supplementation, supports muscle health and function.
Causes of Age-Related Muscle Loss
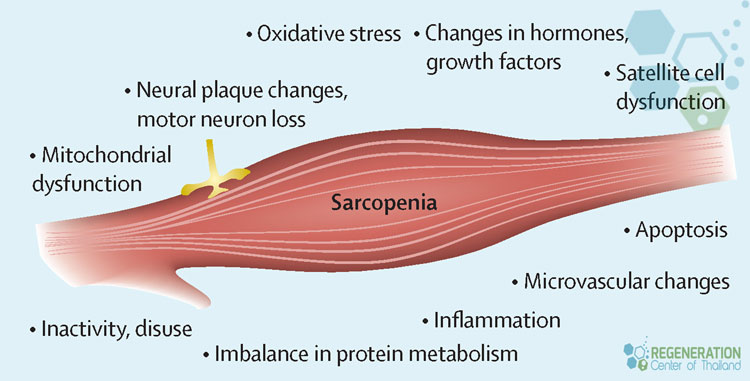
The causes of age-related muscle loss are multifaceted and complex. As we age, various physiological changes contribute to the gradual decline in muscle mass and function, known as sarcopenia. Understanding these underlying factors is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
One primary cause of sarcopenia is the alteration in muscle metabolism that occurs with aging. The body’s ability to synthesize proteins decreases, reducing muscle fiber size and number. Additionally, hormonal changes play a significant role in age-related muscle loss. Declining growth hormone, testosterone, and estrogen levels contribute to decreased muscle mass and strength. Physical inactivity is another major factor in the development of sarcopenia. As individuals age, they become less active, leading to muscle disuse and atrophy. This sedentary lifestyle can accelerate the loss of muscle mass and function, creating a vicious cycle of decreased mobility and further inactivity [2].
Nutritional deficiencies also contribute to age-related muscle loss. Inadequate protein intake and insufficient consumption of essential vitamins and minerals can impair muscle protein synthesis and maintenance. Ensuring proper nutrition becomes increasingly important as we age to support muscle health.
Genetic factors play a role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to sarcopenia. Some people may be genetically predisposed to faster muscle loss or have a reduced capacity for muscle regeneration. Understanding these genetic influences can help identify those at higher risk and guide personalized interventions.
Recognizing Sarcopenia Symptoms
Recognizing the symptoms of sarcopenia is essential for early intervention and effective management of this age-related condition. As muscle mass and strength decline, individuals may experience various symptoms that can significantly impact their quality of life and overall health.
The primary indicator of sarcopenia is muscle weakness, which manifests as a decreased ability to perform tasks requiring strength. This weakness can lead to mobility issues, such as difficulty climbing stairs, rising from a seated position, or maintaining balance while walking. Individuals may notice a gradual decline in their physical capabilities, often attributing these changes to normal aging rather than a specific condition.
Fatigue levels may increase as sarcopenia progresses, with individuals experiencing exhaustion more quickly during physical activities. This fatigue can contribute to a reduced desire for exercise and social engagement, potentially exacerbating the condition’s effects. Nutrient deficiencies can both contribute to and result from sarcopenia. Inadequate protein intake, in particular, can accelerate muscle loss and hinder the body’s ability to maintain existing muscle tissue. Regular blood tests can help identify these deficiencies and guide appropriate dietary interventions.
Physical therapy plays a vital role in both diagnosing and managing sarcopenia. Trained professionals can assess muscle strength, flexibility, and functional capacity through standardized tests. These assessments help confirm the presence of sarcopenia and provide a baseline for monitoring progress and tailoring treatment plans to individual needs.
Regenerative decline of stem cells in sarcopenia
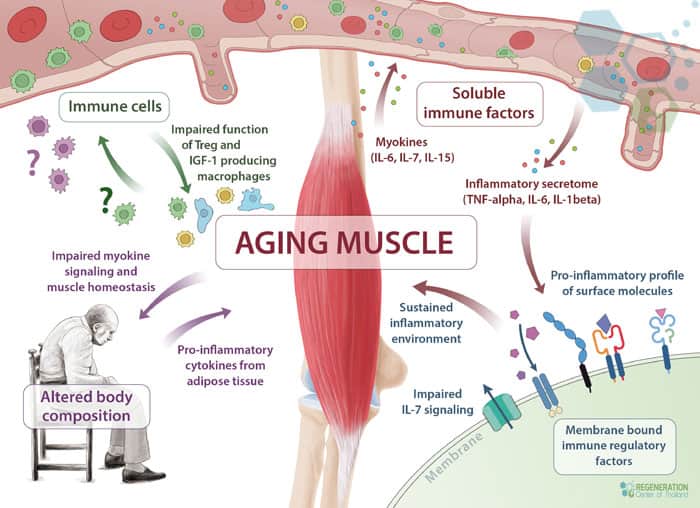
Underlying the visible symptoms of sarcopenia lies a complex biological process involving the decline of muscle stem cells, also known as satellite cells. These cells are essential in muscle tissue regeneration and maintenance throughout life. However, as the aging process advances, the regenerative capacity of these stem cells diminishes, contributing considerably to the onset and progression of sarcopenia.
Research in cellular therapy has shed light on the mechanisms behind this decline. Studies have shown that aging muscle stem cells exhibit reduced proliferation rates, impaired differentiation potential, and increased susceptibility to cellular senescence. These factors collectively result in a decreased ability to repair and replace damaged muscle fibers, leading to the gradual loss of muscle mass and function characteristic of sarcopenia.
Changes in the muscle tissue microenvironment further exacerbate the regenerative decline of stem cells in sarcopenia. Alterations in extracellular matrix composition, reduced blood supply, and chronic low-grade inflammation can create an unfavorable niche for stem cell activation and function. This hostile environment further impairs aging muscle stem cells’ already compromised regenerative capacity [3].
Understanding the intricacies of stem cell regeneration in the context of sarcopenia is vital for developing targeted interventions. Current research focuses on strategies to enhance stem cell function, such as modulating signaling pathways, improving the stem cell niche, and exploring the potential of exogenous stem cell transplantation. These approaches hold promise for novel therapeutic options to combat sarcopenia and enhance the quality of life for aging individuals.
Traditional Treatment Approaches
Traditional approaches to treating sarcopenia have primarily focused on lifestyle modifications and interventions aimed at mitigating muscle loss and improving physical function. These conventional methods encompass a multifaceted approach, combining exercise interventions, nutritional strategies, and physical therapy to address the complex nature of sarcopenia.
Exercise interventions, particularly resistance training, form the cornerstone of sarcopenia management. Progressive resistance exercises targeting major muscle groups have effectively stimulated protein synthesis and improved muscle strength and mass. Structured programs, typically incorporating 2-3 sessions per week, are often prescribed to optimize muscle adaptation and functional outcomes.
Nutritional strategies play a vital role in supporting muscle health and counteracting sarcopenia. Adequate protein intake, typically 1.0-1.2 g/kg body weight per day for older adults, is essential for maintaining muscle mass. Supplementation with essential amino acids, particularly leucine, has shown promise in enhancing muscle protein synthesis. Vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids may also improve muscle function and reduce inflammation.
Physical therapy interventions focus on improving balance, flexibility, and overall mobility. These programs are tailored to individual needs and may include gait training, balance exercises, and functional movement patterns to enhance daily living activities and reduce fall risk. Lifestyle modifications, such as smoking cessation and moderate alcohol consumption, complement these interventions. Healthcare professionals often emphasize the importance of maintaining an active lifestyle and regular physical activity to preserve muscle mass and function throughout aging.
TREATMENT RISKS & PRECAUTIONS
Not all patients are suitable candidates for treating sarcopenia with stem cells. Patients with severe muscle deterioration, advanced sarcopenia, or other significant health conditions might not be good candidates for treatment.Stem Cell Therapy for Sarcopenia
While conventional approaches have shown efficacy in managing sarcopenia, emerging research has spotlighted stem cell therapy as a promising avenue for treatment. This innovative approach utilizes stem cells’ regenerative potential to address the underlying causes of muscle loss and weakness associated with sarcopenia [4].
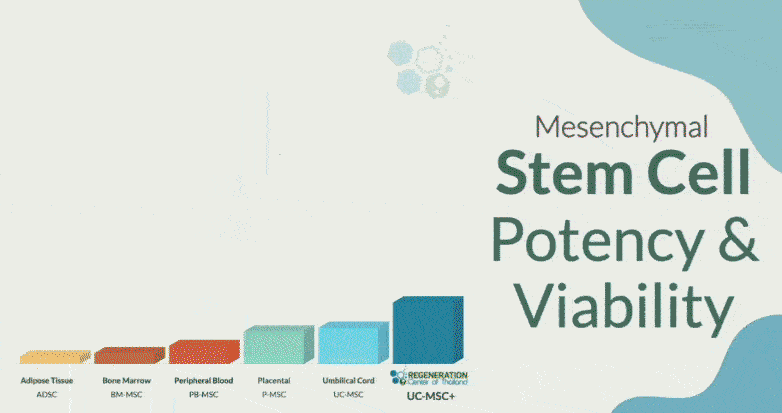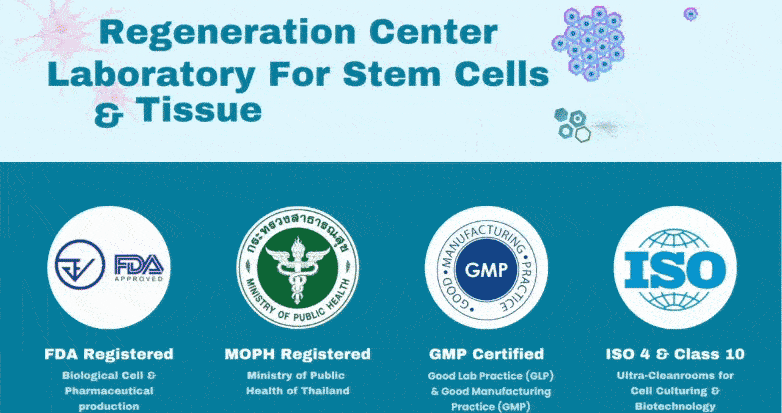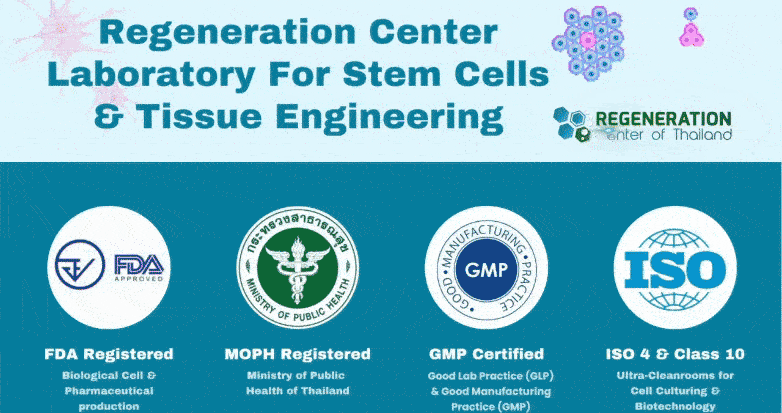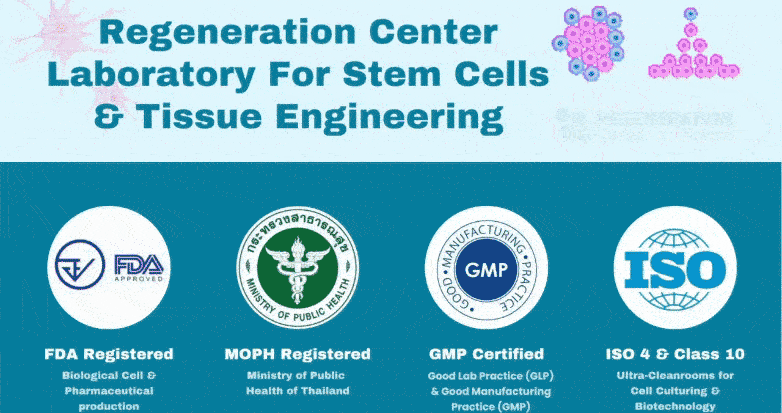
Stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), have demonstrated the ability to promote muscle regeneration and repair. When introduced into affected muscle tissue, these cells can differentiate into muscle fibers and stimulate the production of growth factors that support muscle health. Early clinical trials have shown encouraging results, with improved muscle mass, strength, and function observed in sarcopenia patients receiving stem cell treatments.
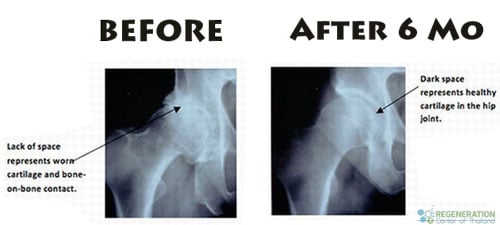
The treatment efficacy of stem cell therapy for sarcopenia is still being evaluated through ongoing clinical trials. The Regeneration Center has investigated various stem cell sources (autologous and allogeneic), delivery methods, and dosing regimens to optimize patient outcomes. Preliminary data suggest that stem cell therapy may offer longer-lasting benefits compared to traditional treatments, potentially slowing or even reversing the progression of sarcopenia in some cases.
As with any emerging treatment, careful consideration of the potential risks and benefits of immunomodulation biological treatments is essential. While stem cell therapies offer short-term benefits, more extensive long-term case studies will be needed to establish their long-term safety and efficacy. Patients considering this treatment option should consult with healthcare professionals like the Regeneration Center, experienced in functional healthcare and regenerative medicine, to guarantee proper monitoring and care.
Number of Stem Cell Infusions for Sarcopenia: 2-8 directed infusions of expanded Mesenchymal “UC-MSC+” Stem Cells delivered with tissue-specific growth factors for increasing fibrocartilage fibers, growth factors & differentiated scaffold formation.
Types of Stem Cells and Delivery Methods: The Regeneration Center offers customized UC-MSC+ Mesenchymal Cell Therapy protocols, depending on patient needs and the underlying injury and degeneration severity. Our outpatient procedures do not require invasive surgeries and are done over 10-14 days. The delivery of the cells is made via radio guidance (when necessary) or, more commonly, through the combination of Intravenous Drip, direct Local injections, Intra-articular Injections, Intraosseous Injections, Intrathecal Injections (if experiencing neuropathy), Ultrasound-guided (in office) or fluoroscopy-guided stem cell delivery (in a hospital setting only).
Benefits of Stem Cell Treatment
Stem cell therapy for sarcopenia offers several potential benefits that make it an attractive treatment option. Our innovative approach to treating age-related muscle loss holds promise for 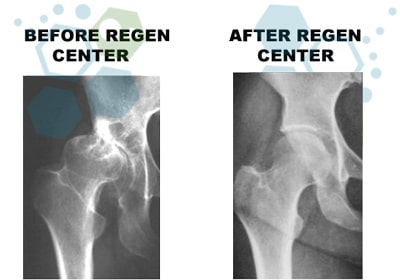 enhancing muscle regeneration and improving the overall quality of life for affected individuals. By utilizing isolated and expanded stem cells’ regenerative capabilities, our cellular therapy aims to counteract the detrimental effects of aging on muscle tissue.
enhancing muscle regeneration and improving the overall quality of life for affected individuals. By utilizing isolated and expanded stem cells’ regenerative capabilities, our cellular therapy aims to counteract the detrimental effects of aging on muscle tissue.
One of the primary advantages of stem cell treatment for sarcopenia is its potential to stimulate the growth of new nerve and muscle fibers. We have developed a process to help restore lost muscle mass and strength, improving our patient’s mobility and independence. Additionally, UC-MSC+ stem cell therapy can help enhance the body’s natural repair mechanisms, promoting faster recovery from muscle injuries and reducing the risk of falls in older adults[5].
Another benefit of stem cell treatment is its potential to complement existing rehabilitation strategies. When combined with targeted physical activity and exercise programs, stem cell therapy can help accelerate muscle recovery and improve overall treatment outcomes. This synergistic approach can help patients regain strength and function more efficiently, leading to improved daily living activities and a reduced caregiver burden.
Furthermore, our unique stem cell protocols offer a promising alternative to traditional pharmacological interventions, which may have limited efficacy or unwanted side effects. By addressing the root cause of muscle loss at the cellular level, our treatment can potentially provide longer-lasting results and a more extensive solution to sarcopenia, making it an integral part of personalized treatment plans for individuals affected by age-related muscle loss.
Treatment Risks & Precautions
Looking ahead, the future of sarcopenia management appears promising, with ongoing research and technological advancements paving the way for more effective interventions. The field is rapidly evolving, focusing on developing extensive prevention strategies and innovative treatment options to address this age-related muscle loss condition.
Lifestyle interventions are expected to play a vital role in the long-term management of sarcopenia. Our research has shown the importance of tailored exercise programs that combine resistance training and aerobic activities to maintain muscle mass and function. These programs will likely be personalized based on individual needs and abilities, ensuring ideal patient outcomes across various age groups and fitness levels.
Nutritional supplements are anticipated to become more sophisticated, with targeted formulations designed to support muscle health and counteract the effects of aging. We are exploring novel compounds and combinations that may enhance protein synthesis, reduce inflammation, and improve overall muscle quality. The integration of technology in sarcopenia management is poised to transform patient care. Wearable devices and smartphone applications are being developed to monitor muscle strength, physical activity, and nutritional intake, providing real-time feedback and personalized recommendations.
Sarcopenia presents a significant challenge in aging populations, impacting quality of life and increasing morbidity. While traditional interventions like resistance training and nutritional support remain essential, emerging stem cell therapies offer promising avenues for cartilage/ligament regeneration and functional improvement. Isolated Mesenchymal stem cell treatments, in particular, demonstrate potential in addressing the underlying cellular deficits associated with sarcopenia. Integrating these novel approaches with established protocols provides more all-encompassing management of age-related muscle loss, mitigating its impact on elderly health and independence.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Sarcopenia
Please note stem cell treatments are not appropriate for all patients. Patients with underlying medical issues or severe concomitant diseases that restrict traveling should get pre-approval using our online inquiry request. To get treatment options with fixed prices, please prepare your recent lab results so we can review your needs and determine the extent of help our cell-based therapies can provide. This treatment takes place in multiple stages/days, but most standard UC-MSC+ therapies will require a minimum of 1-2 weeks at our stem cell center in Bangkok.
Upon completion of the evaluation, a detailed treatment plan will be provided, including the specifics of your treatment, such as the treatment length and the total medical-related costs (excluding accommodations or flights). To begin the qualification process for our multi-stage treatment protocol, please prepare your recent medical records with lab results and contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Bunchorntavakul C. Sarcopenia and Frailty in Cirrhosis: Assessment and Management. Med Clin North Am. 2023 May;107(3):589-604. doi: 10.1016/j.mcna.2022.12.007. Epub 2023 Feb 20. PMID: 37001955.
[2] ^Thavonlun S, Houngngam N, Kingpetch K, Numkarunarunrote N, Santisitthanon P, Buranasupkajorn P, Pongchaiyakul C, Sutcharitchan P, Wattanachanya L. Association of osteoporosis and sarcopenia with fracture risk in transfusion-dependent thalassemia. Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 29;13(1):16413. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43633-6. PMID: 37775530; PMCID: PMC10541420.
[3] ^ Vanitcharoenkul E, Unnanuntana A, Chotiyarnwong P, Laohaprasitiporn P, Adulkasem N, Asavamongkolkul A, Chandhanayingyong C. Sarcopenia in Thai community-dwelling older adults: a national, cross-sectional, epidemiological study of prevalence and risk factors. BMC Public Health. 2024 Jan 27;24(1):311. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17804-7. PMID: 38281041; PMCID: PMC10821311./p>
[4] ^ Snijders T, Parise G. Role of muscle stem cells in sarcopenia. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017 May;20(3):186-190. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000360. PMID: 28376051.
[5] ^Cai Z, Liu D, Yang Y, Xie W, He M, Yu D, Wu Y, Wang X, Xiao W, Li Y. The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal muscle in sarcopenia. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jan 24;13(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02706-5. PMID: 35073997; PMCID: PMC8785537.