Mesenchymal (MSC) derived stem cells are the bodies own restoration system. Nature allows MSC cells to deliver a homing signal that helps recruit other stem cells in the body to mobilize and “fix” an injured area. Researchers at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine have recently reported that MSC Mesenchymal stem cells are much better prepared to begin the bodies natural recovery process. Much more than even the self-repair done by the damaged tissues themselves.
Types of MSCs Stem Cells
Doctors have been extracting MSC cells for the use of stem cell treatments in Thailand for over 10 years now. The MSC cells are typically drawn out from bone marrow,blood,adipose tissue or dental pulp and then processed and expanded in close system stem cells labs in Bangkok. The MSC+ stem cells are then grafted or delivered via IV drips to the patient to begin the regeneration process. After years of successful treatment the doctors have developed a distinct protocol that promotes rapid signaling and healing with cell populations in the patients body. Evidence has clearly shown that patients receiving MSC derived cells recover much more quickly than those patients who had not received treatments in Thailand through direct MSC enriched stem cell grafts.
What Are Mesenchymal Stem Cells?
The key to regenerative medicine and healing today should not hinge on the location of the grafted MSC+ stem cells. The human physique, already has a natural delivery system that can be used to promote a faster healing process. Researchers have also looked into the overall habits of MSC+ stem cells in a wide array of before and after stem cell treatments including patients with Diabetes,Crohn’s disease, congestive heart failure, bone defects,cerebral palsy and arthritis or joint/ ligament damage repair. Although MSC+ Stem cells have been known as the magic behind stem cells in the use of regenerative medicine and tissue repair,up until now long term studies had not been completed so doctors and researchers had not been able to discuss exactly how MSC+ stem cells function along with other Multipotent cell lines including neural stem cells,hematopoietic stem cells, pancreatic stem cells, cardiac stem cells and neural progenitor adult stem cell activators.
Our stem cell doctors are finding even uses of the signaling or “homing” powers of MSC+ cells that will hopefully eliminate the need for eternal injections of stem cells for a truly cell-free treatment protocol that only uses the bodies own hospital. We home to establish new and innovative treatments by utilizing cellular molecules as medication as an alternative to costly and inefficient pharmaceutical treatments of today.
Mesenchymal stem cells typically refers to adult stem cells that are derived from several types of tissues in the human body such as adipose tissue. However, there is still confusion as to whether different tissues carry the same type of mesenchymal stem cells from from autologous transplants or allogeneic transplants.
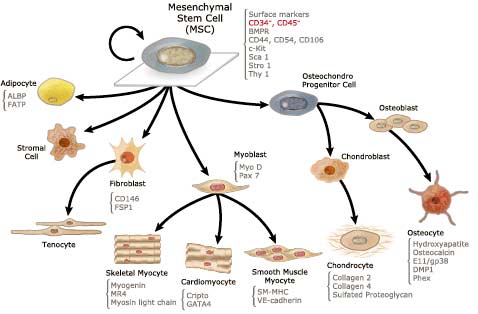
MSC cells are short for “Mesenchymal Stromal Cells” and are considered to be multipotent cells that can naturally differentiate themselves into a variety of vital stem cell types with the added feature or “immortality.” Both Muse Cells and MSC cells have the amazing capacity to keep self renewing.
Several Types of MSC Stem Cell Lineages
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells have been clinically proven to be able to differentiate in vitro [1] (in the lab) or in vivo (in people) into cell types such as:
- Adipocytes [2]
- Osteoblasts [3]
- Blood Cells and Hepatocytes
- Chondrocytes [4]
- Myocytes
- Brain Cells and Neurons
- Pancreatic islet cells for the treatment in Diabetes Type 1 and Diabetes Type 2
Regeneration center of Thailand offers a unique protocol using MSC stem cells from cord blood, Dental Pulp, Amniotic Membrane, Peripheral Blood and placenta derived MSC stem cells in most of our regenerative medicine programs.
To learn more about MSC+ Stem Cells or to inquire about a specific treatments we offer please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Bhonde, Ramesh R, Preethi Sheshadri, Shikha Sharma, and Anujith Kumar. 2013. Making surrogate β-cells from mesenchymal stromal cells: perspectives and future endeavors. The international journal of biochemistry & cell biology (November 22). doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.006. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24275096
[2] ^ Chen, Bei-Yu, Xi Wang, Liang-Wei Chen, and Zhuo-Jing Luo. 2012. Molecular targeting regulation of proliferation and differentiation of the bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells or mesenchymal stromal cells. Current drug targets, no. 4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22443584
[3] ^ Hanson, Summer E, Jaehyup Kim, and Peiman Hematti. 2013. Comparative analysis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells isolated from abdominal and breast tissue. Aesthetic surgery journal, no. 6 ( 1). doi:10.1177/1090820X13496115. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23908304
[4] ^ Sharma, Monika B, Lalita S Limaye, and Vaijayanti P Kale. 2011. Mimicking the functional hematopoietic stem cell niche in vitro: recapitulation of marrow physiology by hydrogel-based three-dimensional cultures of mesenchymal stromal cells. Haematologica, no. 5 (November 4). doi:10.3324/haematol.2011.050500. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22058199