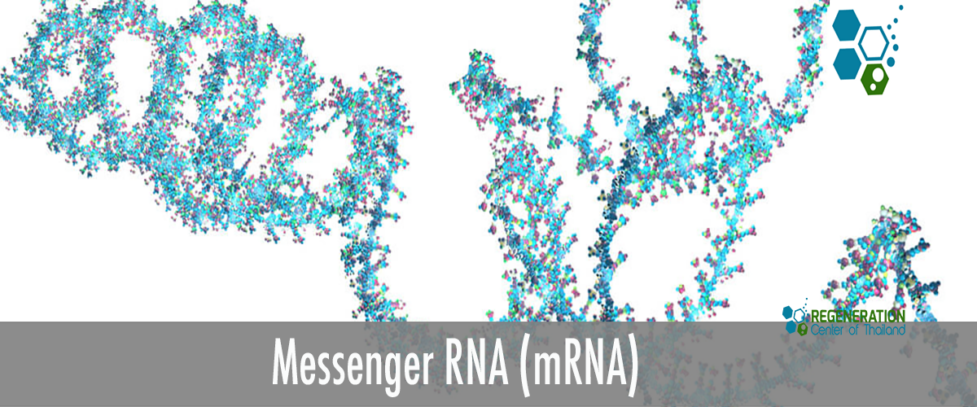
We recently experienced the powers of a ground-breaking vaccine against COVID-19 thanks to mRNA technology, but it has even more potential to democratize access to bleeding-edge medical advancements. Messenger RNA or “mRNA” is a single-stranded RNA involved in protein synthesis. Although the blueprint for proteins in living cells was discovered six decades ago, its pharmaceutical potential was long overlooked. mRNA …
Metronomic therapy
Metronomic therapy refers to the administration of low, continuous, and regular doses of certain drugs (often chemotherapeutic agents) without extended rest periods. This dosing strategy stands in contrast to the more traditional “maximum-tolerated dose” approach, where high doses of chemotherapy are given with intervening rest periods to allow for patient recovery from side effects. Features and benefits of metronomic chemotherapy: …
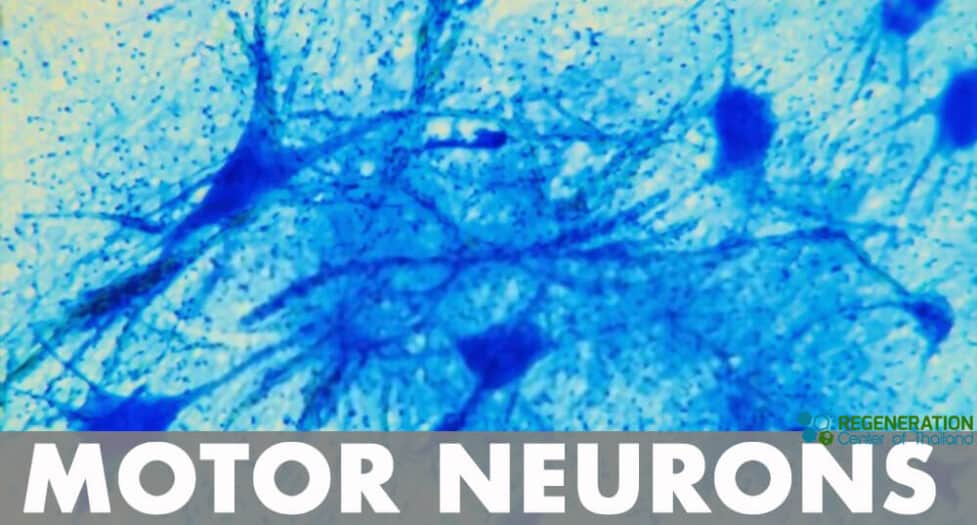
What is A Motor Neuron? Motor Nerves & Innervation
Motoneuron, also known as motor neurons, are a type of cell body located in the brainstem, motor cortex, or spinal cord. Fibers called axons project outwards to the spinal cord can indirectly or directly control muscles, organs, and glands in the body. The Somatic Motor System The somatic motor system, also known as the voluntary motor system, is responsible for …
Exosome Therapy in 2025 – Nanoparticles for Biogenesis & Delivery
Exomes are the portions of an organism’s genome containing protein-coding genes. They comprise a small part of the total DNA, usually around 1-2%, but are responsible for most known genetic functions. Exomes contain sequences called exons, which are the coding regions within genes. These exons are transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins, which perform various functions within the …
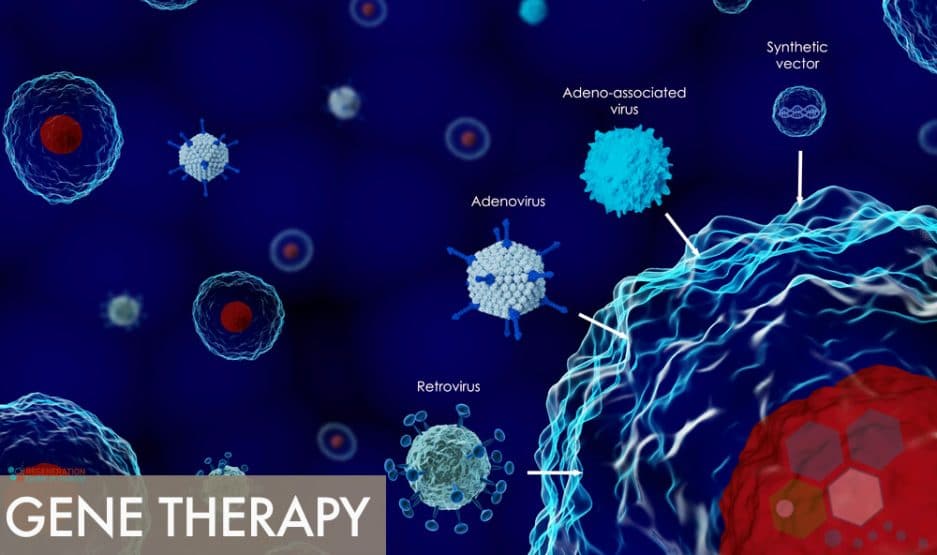
Gene Therapy and the Future of Precision Medicine
Most traditional treatments today are designed using a one-size-fits-all to cover the “average” patient. But advances in biotechnology and Artificial intelligence (AI) medical researchers are now equipped with vast amounts of personalized datasets at their disposal, and can analyze unique situations based on our genetic profiles, family medical histories and other relevant medical conditions to better understand what types of …
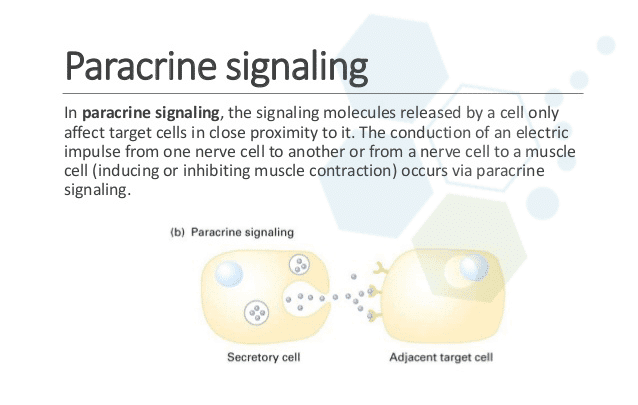
Auto Paracrine Signaling Mechanism & Stem Cell Communication
What is Paracrine Communication? Paracrine signaling also known as Paracrine communication is a natural method of communication between cells that causes desired changes in surrounding cells and chemically altering the behavior surrounding cells. Why is paracrine signaling important? The paracrine communication system, exosomes and cytokines are critical for the success of functional medicine, regenerative medicine, and stem cell therapies. The …