Navigating the complexities of aphasia, discerning its various types, and deciphering the most effective treatment options can be daunting. You’re not alone in this journey, though.
With the recent advancements in neurobiological research, various promising therapies are emerging that could revolutionize how we approach aphasia treatment. But how exactly do these treatments work? And, more importantly, how effective are they in real-world applications? [1]
Understanding the Etiology of Aphasia
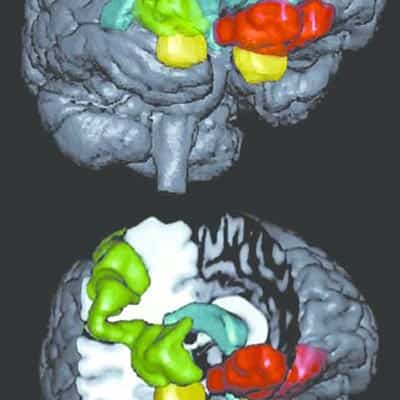 To truly grasp the treatment methods for aphasia, you must first understand its root causes. Aphasia is a complex neurological disorder, often resulting from strokes, brain injuries, tumors, or infections. Understanding aphasia demographics is critical. It’s not picky about who it affects, cutting across all ages, races, and genders. But, there’s a higher prevalence in older adults, primarily due to the increased risk of stroke.
To truly grasp the treatment methods for aphasia, you must first understand its root causes. Aphasia is a complex neurological disorder, often resulting from strokes, brain injuries, tumors, or infections. Understanding aphasia demographics is critical. It’s not picky about who it affects, cutting across all ages, races, and genders. But, there’s a higher prevalence in older adults, primarily due to the increased risk of stroke.
Prevention strategies are essential. You can’t control genetics, which plays a significant role in increasing your risk for stroke and, subsequently, aphasia. But you can manage your lifestyle by maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and controlling hypertension. Educating yourself about these strategies is a great way to serve at-risk people. Aphasia rehabilitation is where the magic happens. It’s a journey, often long and strenuous, but the results are worth it. Speech-language pathologists are the heroes here, working tirelessly with patients to regain their communication abilities.[2]
Understanding neuroplasticity and aphasia is crucial. Neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections, is a beacon of hope. It’s the reason why aphasia rehabilitation works. The brain can compensate for the damaged areas, but it needs to be trained. It’s like a muscle; the more you use it, the better it becomes. Your role in encouraging and supporting this process is immeasurable.
Common Symptoms and Signs of Aphasia
Recognizing the symptoms of aphasia, which can vary significantly among individuals, is your first step in learning how to provide adequate support and care. As someone who desires to serve others, you’ll need to understand the typical manifestations of this condition.
One primary symptom is speech impairment. A person afflicted with aphasia may struggle to find the right words, speak in short or fragmented phrases, or use nonsensical words. Conversations can become challenging, but patience and understanding are key. Another tell-tale sign of aphasia is difficulty understanding speech. This may present as confusion during conversations or an inability to comprehend written words, making tasks like reading a newspaper or following a recipe difficult.
Aphasia can also affect writing abilities. Messages may become garbled, and sentences need to be completed. It’s important to offer assistance but allow the person to express themselves as independently as possible. Now, let’s talk about recovery. Language recovery is a crucial part of the journey through aphasia. This involves cognitive therapy, which targets the individual’s ability to process and understand language. You can aid in this process by engaging the person in simple conversations, reading together, or playing language-based games. Neurological rehabilitation is another essential aspect of treatment. This includes strategies to help manage the symptoms and improve communication skills. Assistive devices, like speech-generating devices and apps, can also be beneficial.[3]
In this journey with aphasia, remember, you’re not alone. Resources and support are available to help you provide the best care possible. Empathy, patience, and the right strategies can significantly improve the quality of life for those with aphasia.
Causes of Aphasia
Before exploring the complexities of aphasia, it’s crucial to understand what causes this condition in the first place. Stroke-related aphasia is one of the leading causes of this language disorder. When a stroke occurs, it can damage the areas of the brain responsible for language and communication. This damage can result in difficulty speaking, understanding, reading, and writing—collectively known as aphasia.
Similarly, aphasia isn’t exclusive to adults or older people. Pediatric aphasia, although less common, can occur in children due to brain injuries, infections, or congenital disorders. Recognizing the symptoms early is vital to provide the necessary treatment and support.
Aging increases the risk of developing aphasia, especially if the individual has suffered a stroke or brain injury. Aphasia in older adults can be particularly challenging, as it compounds the struggles often associated with aging, such as memory loss and decreased mobility. Early detection and intervention are crucial to managing the condition and improving quality of life.
Bilingual aphasia, on the other hand, affects individuals who speak more than one language. Intriguingly, one language may be more concerned in some cases. Treatment often involves language therapy in both languages.
Understanding these causes of aphasia is a step forward in preventing it. You can reduce your risk by managing risk factors for stroke and brain injuries, such as high blood pressure or diabetes. Regular screenings, especially in older people, can catch early signs of aphasia, enabling prompt treatment and potentially mitigating the severity of the condition.
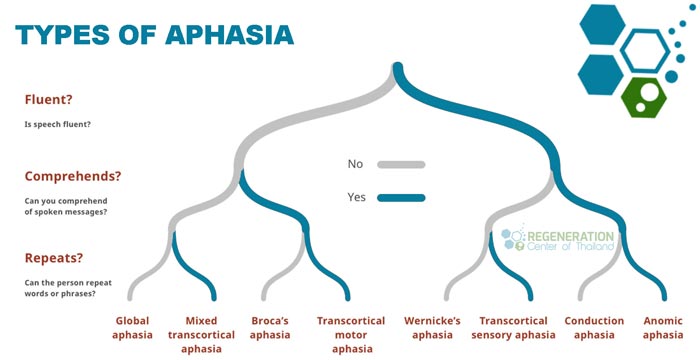
What are the three common types of Aphasia?
Now that we’ve examined the causes of aphasia, let’s explore the three main types of this language disorder: Broca’s aphasia, Wernicke’s aphasia, and global aphasia.
- Broca’s aphasia often results in difficulty speaking and writing, yet comprehension remains relatively unscathed. Aphasia’s societal impact is visible mainly here, as it can impede a person’s communication ability, affecting their relationships and careers. However, you’ll find hope in speech therapy advancements, which can significantly improve the patient’s ability to express themselves.
- Wernicke’s aphasia, on the other hand, affects comprehension. Patients can speak fluently, but their words may need to be clarified or incoherent. This can be frustrating and impacts the patient’s emotional well-being, making them feel isolated. Technology’s role in recovery is crucial here, as innovative tools can improve understanding and communication.
- Global aphasia is the most severe form, impacting both speech and comprehension. Caregivers must learn effective coping strategies to support the patient. Enhancing the quality of life for someone with global aphasia is possible with patience, love, and the right resources.
Dysphasia vs. Aphasia: What’s the Difference?
While you may hear the terms dysphasia and aphasia used interchangeably, they refer to distinct conditions in language disorders. With dysphasia, the prevalence is significant, making it a common challenge many individuals face. It’s a condition that affects one’s ability to produce or understand language. It might lead to difficulties in speaking, reading, writing, or understanding spoken words, significantly impacting communication.
Conversely, aphasia is typically the result of damage to the brain, often from a stroke or injury. The progression of aphasia can vary widely. Some people may experience a sudden onset following a brain injury, while others may gradually decline in language abilities due to ongoing brain changes. This deterioration can profoundly impact communication, making it difficult for the person to express and understand language.[4]
Both dysphasia and aphasia can have serious complications, affecting a person’s ability to interact and engage with others. Miscommunication can lead to frustration and social isolation, so language rehabilitation is crucial. It’s all about helping those affected to regain their communication skills, whether through speech therapy, assistive devices, or other strategies.
How Is Aphasia Diagnosed?
To diagnose aphasia, your healthcare provider will typically thoroughly evaluate your language skills and abilities. This initial diagnosis process includes an in-depth look at your ability to 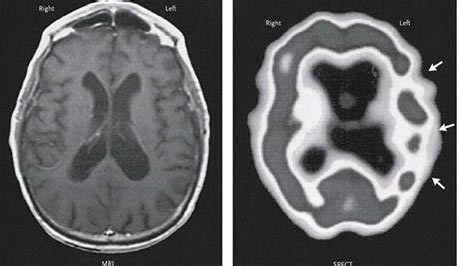 understand, speak, read, and write. It’s not just about finding the problem but also determining the severity levels of aphasia, which range from mild to severe.
understand, speak, read, and write. It’s not just about finding the problem but also determining the severity levels of aphasia, which range from mild to severe.
Neuroimaging also plays a crucial role in the diagnosis process. Radiology scans from MRI or CT can help your healthcare provider pinpoint where the damage in your brain is located, which can subsequently inform the type of aphasia you have. It’s through these scans that the underlying cause of your language difficulties can be identified, whether it’s due to a stroke, brain tumor, or another neurological condition such as Dementia, Spinal Cord Injuries, and transverse myelitis. Once you’ve been diagnosed, the next step is often speech therapy. The effectiveness of this treatment depends on the severity of your aphasia and your determination to improve. You’ll develop strategies to enhance your communication and language skills in therapy. It might be challenging, but it’s an essential part of your journey towards recovery.
But it’s not just about treatment—it’s also about long-term management. Aphasia can be emotionally taxing, and patient coping strategies are an integral part of managing the condition. This might involve joining a support group, learning new communication methods, or focusing on stress reduction techniques. Diagnosing and managing aphasia can be a complex process, but with the right help and support, you can navigate this journey.
Can autoimmune disease cause Aphasia?
Autoimmune diseases can potentially cause aphasia, although this is relatively rare and typically occurs as part of a broader spectrum of neurological symptoms. Aphasia, which is a disorder affecting speech and language skills, is most commonly associated with brain damage from strokes, head injuries, or tumors. However, certain autoimmune conditions can affect the brain or nervous system in a way that impacts language functions. Some autoimmune conditions that could potentially lead to aphasia:
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): MS can cause lesions in the brain, which may affect areas responsible for language. While aphasia is more uncommon in MS compared to other neurological symptoms, it can occur in some cases.
- Lupus (Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, SLE): Lupus can affect the nervous system and brain, leading to a condition known as neuropsychiatric SLE. In some cases, this may include symptoms affecting speech and language.
- Vasculitis: This condition involves inflammation of the blood vessels and can affect any organ in the body, including the brain. When blood vessels in the brain are involved, it can lead to neurological symptoms, including aphasia, in rare instances.
- Sjögren’s Syndrome: Though primarily affecting moisture-producing glands, Sjögren’s syndrome, Hashimoto’s, and FMS can have neurological complications that might, in rare circumstances, impact cognitive functions, including language.
- Autoimmune Encephalitis: This group of conditions involves a direct autoimmune attack on the brain, leading to various neurological symptoms. Depending on the areas of the brain affected, speech and language capabilities can be impaired.
It’s important to note that when aphasia occurs in the context of an autoimmune disease such as rheumatoid arthritis or connective tissue disease, it is usually part of a broader set of neurological symptoms. Diagnosis and treatment would typically focus on managing the underlying autoimmune disorder, which may help alleviate the aphasia or prevent further progression. If someone is experiencing new or worsening language difficulties, it’s crucial to seek medical evaluation to determine the cause and appropriate treatment.
Traditional Aphasia Treatments
After the diagnosis, it’s crucial to explore various traditional aphasia treatments that can help enhance communication skills and improve quality of life. Here are some options that patients might consider include:
- Speech therapies are often the first step in treating aphasia. They involve working with a speech-language pathologist to relearn or adapt speech. This can include exercises to improve your ability to produce language, such as naming objects, practicing conversational skills, or learning new communication methods like gestures or writing.
- Language retraining is another critical component of traditional aphasia treatment. It involves re-teaching the brain how to understand and use language. This method can be very effective, especially when started early.
- Music therapy is a more novel approach that’s shown promising results. Music can stimulate areas of the brain involved in language, and singing can help regain speech rhythm and intonation. Don’t worry, you don’t have to be a great singer to benefit from this.
- Computer-based interactive treatments are becoming increasingly popular. They offer interactive exercises you can do at your own pace and tailored to your needs and abilities.
Biological-Based Treatments for Aphasia
In addition to traditional methods, you might also consider biological-based treatments for aphasia, which focus on restoring or improving brain function. These treatments leverage the neuroplasticity role – the brain’s ability to rewire and create new connections – to help with recovery.[5]
One critical method in this approach is brain stimulation. This can include transcranial magnetic stimulation, which uses magnetic fields to stimulate nerve cells in the brain, potentially improving language capabilities. However, it’s vital to understand that this isn’t a one-size-fits-all treatment, as everyone’s brain is unique.
Another aspect to consider is the immune system’s impact on recovery. Some evidence suggests that a robust immune system may aid in neural repair and neuroplasticity. Maintaining overall health is an integral part of the treatment plan.
Hormone therapy, particularly with substances like progesterone and estrogen, has shown some promise in aiding recovery from brain injury. These hormones may enhance the brain’s capacity to reorganize and form new connections after damage. Lastly, it’s crucial not to overlook genetic influences on aphasia treatment. Everyone’s genetic makeup is different, affecting how well specific therapies work. For example, some people may respond better to certain medications due to their genetic makeup.
Stem Cell Therapy for Aphasia
Stem cell therapy is a promising approach to exploring new frontiers in neurodegenerative diseases such as aphasia, ALS, MND, and Parkinson’s. Stem cell sourcing is an essential part of this innovative treatment. It involves obtaining stem cells from various sources, such as the bone marrow or adipose tissues. These cells are then introduced into the patient’s body, where they can rejuvenate damaged brain cells.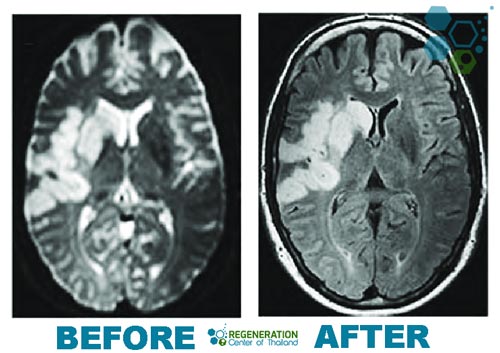
Next, let’s discuss therapy duration. This can vary significantly based on your case. Some patients may need a single session, while others might need multiple sessions over several weeks or months. It’s important to understand that stem cells for treating Aphasia aren’t a quick fix but a process that requires patience and commitment.
Patient eligibility is another crucial factor. Stem cell therapies are not appropriate or effective in all cases, and some patients with aphasia are not suitable candidates for them. However, stem cells can be a good option for those not responding to conventional treatments. Pre-existing health conditions, age, and the severity of aphasia can all influence eligibility.
The Regeneration Center Difference
Total Number of MSC+ Cell Infusions for Global Aphasia: For most patients, we will need multiple Infusions of isolated and expanded mesenchymal cells, which can be cultured from autologous sources of bone marrow (BMMSC) or allogeneic sources of cells (UC-MSC). These cells can be combined with neural progenitor cells, fibroblast growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines to allow for higher survival rates of transplanted cells per treatment stage.
Delivery Methods of MSC+ Cells: The goal of treatment is to help reduce systemic neuroinflammation and promote faster recovery of any lost function through neurogenesis. The cells can be administered via Stereotactic-guided delivery, inhalation therapy via micro-nebulized mesenchymal cells Intravenously, Intrathecally, or fluoroscopic guided delivery (hospital setting) is sometimes needed to bypass the blood-brain barrier. A board-certified neurosurgeon performs our intrathecal cell deliveries.
Rehabilitation Post Treatment: Physical Rehabilitation in Bangkok is optional but highly recommended. Complete physical rehab services post-therapy can be provided upon request for 2-3 hours per day and up to 5 days per week.
Total Treatment Time Required is estimated to be around two weeks (depending on the type and seriousness of the condition). Medical and travel visas for extended accommodations at a hotel or apartment for the patient and family can also be provided upon request.
The success rates of stem cell therapy for aphasia are encouraging but are not guaranteed. Some patients report significant improvements, while others notice only minor changes. Remember, every case is unique, and what works for one mightn’t work for another. Finally, post-therapy rehabilitation is a critical component of treatment success. This might include speech therapy, occupational therapy, and various exercises to help reinforce the new connections your brain is making. It’s not enough to receive the stem cells; you’ve got to work actively to make the most of them.
Advances in Aphasia Research
While stem cell therapy offers a promising alternative to traditional aphasia treatments, let’s not overlook the significant strides in aphasia research in areas like aphasia technology, language rehabilitation, music therapy, cognitive linguistic treatments, and aphasia support groups. Aphasia technology is leading the way with innovative solutions to improve communication. New apps and software are being developed to help individuals with aphasia relearn language and speech skills. You could be an integral part of this, assisting with using such technology in your service to others.
Interactive Language rehabilitation is another area where you can make a difference. Techniques have evolved to include more personalized and intensive therapies, leading to excellent success rates. Combine this with music therapy, and you’re providing a holistic approach to treatment. Music therapy uses melodies and rhythms to stimulate the brain’s language areas, offering a novel way to support language recovery. Then, there’s the emerging field of cognitive linguistic treatments. This approach focuses on improving cognitive processes like attention, memory, and problem-solving to enhance language skills.
Cost of Treating Aphasia with Stem Cells
- Our multi-stage treatment for Aphasia with Stem Cells will require two weeks in Bangkok, depending on the patient’s medical needs. Due to the varying degrees, areas, and sources of current damage, our medical team will need to better understand the patient’s health before accepting into the program. Upon completion of the therapy review, a detailed treatment plan will be provided, including the scope of the treatment, the treatment itinerary with the exact number of days required, and the total medical-related costs (excluding accommodations or flights).
Understanding aphasia’s causes, symptoms, and types is crucial in managing it effectively. There’s hope for improvement, from traditional to biological-based treatments and even cutting-edge stem cell therapies. Remember, aphasia doesn’t define you. Stay updated with the latest research and never stop seeking the best possible care. Your journey with aphasia is unique, and with the proper support and treatment, you can navigate challenges and enhance your communication abilities.
To begin the qualification process for our multi-stage regenerative stem cell treatment for aphasia disorders, please prepare your recent medical records and neurological test results and contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Thanprasertsuk S, Likitjaroen Y. Pattern of cortical thinning in logopenic progressive aphasia patients in Thailand. BMC Neurol. 2021 Jan 13;21(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s12883-020-02039-x. PMID: 33441094; PMCID: PMC7805202.
[2] ^ Hardy CJD, Bond RL, Jaisin K, Marshall CR, Russell LL, Dick K, Crutch SJ, Rohrer JD, Warren JD. Sensitivity of Speech Output to Delayed Auditory Feedback in Primary Progressive Aphasias. Front Neurol. 2018 Oct 29;9:894. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00894. PMID: 30420829; PMCID: PMC6216253.
[3] ^ Sheppard SM, Sebastian R. Diagnosing and managing post-stroke aphasia. Expert Rev Neurother. 2021 Feb;21(2):221-234. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2020.1855976. Epub 2020 Dec 10. PMID: 33231117; PMCID: PMC7880889.
[4] ^Crosson B, Rodriguez AD, Copland D, Fridriksson J, Krishnamurthy LC, Meinzer M, Raymer AM, Krishnamurthy V, Leff AP. Neuroplasticity and aphasia treatments: new approaches for an old problem. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2019 Oct;90(10):1147-1155. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2018-319649. Epub 2019 May 4. PMID: 31055282; PMCID: PMC8014302.
[5] ^ Liao LY, Lau BW, Sánchez-Vidaña DI, Gao Q. Exogenous neural stem cell transplantation for cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2019 Jul;14(7):1129-1137. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.251188. PMID: 30804235; PMCID: PMC6425845.