The Regeneration Center would like to highlight the nine most innovative medical advances in healthcare and regenerative medicine. Last year was filled with newer, smaller, faster methods of creating genetic tests, editing genetic code, and even bloodless sensors for diabetics, children, and the elderly. New breakthroughs in drug manufacturing and delivery mechanisms were generally the fastest to market, followed by enhancement. In no particular order, these are the Top Nine Medical Advances for this year.
#1 – Gene Editing / Manipulation Using CRISPR
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats or CRISPR allow us to alter human DNA (or any organisms) in an attempt to correct defective genetic coding. What seems like science fiction from space movies is now a reality. The inexpensive gene editing technique costs as little as 700 Thai Baht or $20 USD and is quickly being adopted in genome labs around the world. The CRISPR sequence is a naturally-occurring defense mechanism found in many bacteria.
CRISPR is part of bacteria’s immune system, which stores a dangerous viral weapon that can recognize and defend the bacteria against enemy viruses the next time they try to attack. The other defense mechanism these bacteria possess is a set of enzymes known as CAS (CRISPR-associated proteins). CAS enzymes allow us to very accurately cut and replace sections of DNA or from invading viruses.
Although the practical appellations are still in their infancy, CRISPR will one day allow us to edit/repair genetic-based diseases such as Inherited Ataxia, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, Thalassemia, Sickle cell disease, and Hemochromatosis, to name a few.
#2 – Clinical Trials Based on Race/Ethnicity-Based Genetic Profiles
Some people, particularly those of Thai descent, are genetically more susceptible to certain diseases, such as Thalassemia. At the same time, many of East Asian descent are prone to getting a skin disease known as Stevens-Johnson syndrome mainly due to genetics.
Current research models are decades behind modern needs, with the participants’ epigenetic profiling being primarily of North American origin only. New genomic-based testing models being used in Asia are beginning to increase in number, bringing much-needed hope for those families suffering from usually fatal diseases. Science and regenerative medicine are only now beginning to understand genetic strongholds for some diseases so we can find new ways to develop personalized therapies based on factors such as race and ethnic background.
#3 – Non-Invasive Fetal DNA Tests – NIPD & NIPT DNA Sampling
Current options for prenatal paternity tests, such as CVS and amniocentesis, were considered invasive and carried a small but significant chance of the mother suffering a miscarriage. As a result, researchers have developed a new and non-invasive method for prenatal diagnosis using fetal cells found in maternal blood. The new NIPD and NIPT tests work by analyzing DNA profiles for specific cell markers to see if the child’s’ DNA profile matches the mother and alleged fathers (NIPT) along with samples to see if the baby might be at risk of over 100 X-linked genetic disorders including down syndrome, beta-thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, spinal muscular atrophy, fragile-X syndrome, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, myotonic dystrophy, and hemophilia. The exact same tests can also be used to determine the baby’s gender and blood type.
Studies have proven that Cell-free Fetal DNA Testing and Non-Invasive paternal testing are much more accurate than standard blood tests and ultrasound scans. This testing is available in Bangkok, Thailand, and brings more certainty to expecting parents everywhere.
#4 – Neurovascular Stent Retrievers for Strokes
Time can be a stroke patient’s best friend or worst enemy. Since time kills brain cells, restoring blood flow to the brain is critical. For optimal results, a blood clot in the brain must be removed 2-7 hours after the incident to prevent long-term brain damage, disability, or even death. Until now, brain clot-busting medications have not always been effective, leading to a new technology known as neurovascular stent retrievers. The latest technology uses a micro-sized catheter inserted through an incision in the patient’s leg and then threaded through the bloodstream. The microscopic devices are guided through the body until they reach the blood clot and quickly remove the blockage to restore normal blood flow.
.
Researchers found that victims of brain strokes whose blood clots were removed the same day via stent retriever have significantly faster recoveries and improve their chances of regaining a normal independent life. For patients who previously suffered through strokes, the chances for recovery can be improved using neural stem cells for brain strokes. The new neurovascular stent retrievers were recently approved and should be available for global use at stroke units in the 3rd quarter of 2019.
#5 – Early Detection & Screening via Protein Biomarker Analysis
Starting in 2019, a new biomarker exam will be available to offer high-risk individuals accurate screening for cancer with significantly higher chances of early detection. The new testing protocol, known as PLA or proximity ligation assays, allows clinicians to measure and visualize protein complexes. The new biomarkers will help doctors detect, diagnose, and treat patients using a special class of pharmaceuticals known as receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. The early Protein biomarker analysis primarily focuses on any structure of specific proteins circulating in the blood circulatory system.
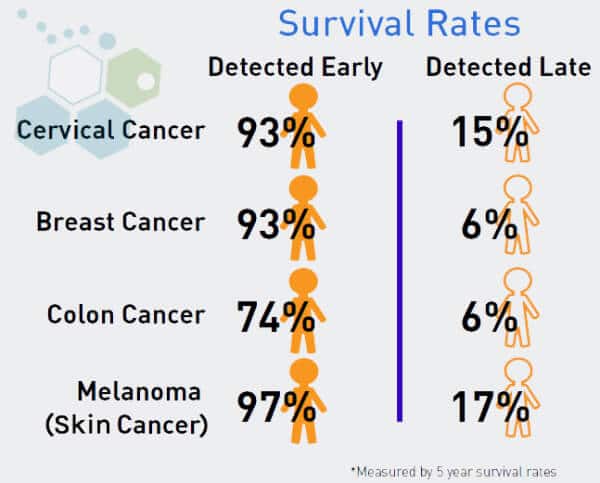
In contrast to previous exams that looked at genetic mutations after the fact, the new tests allow doctors early warnings using real-time information of any cancerous presence in the patient’s body. An estimated 2100 anticancer medications are in development or approved, but only around 29 cancer biomarkers have been approved for use in humans. Lung cancer biomarkers are especially helpful in identifying and validating diagnosis, allowing for new approaches to understanding and fighting lung diseases such as COPD.
#6 – Neuro Sensor Feedback to Control Artificial Limbs
The ability to control prosthetic limbs using neural implants has been a reality for about five years now, but in 2019, researchers found a new and significantly smoother method of controlling limbs for patients with spinal cord injuries and/or traumatic brain damage without the need for neurogenesis.
The new method uses neural cell signals associated with the movement of limbs to be decoded by a computer, allowing them to control artificial limbs with a simple thought. Sensors implanted in the brain’s motor cortex or premotor cortex can be ‘hacked’ to allow the patient total control over prosthetic arms/legs, wheelchair movement, or even full-body exoskeleton control. Researchers are now working on special brain-machine interface algorithms that are easier to control, safer, and cheaper using low-cost robotic components. Combining several techniques could make having bionic arms and legs a reality for millions of patients worldwide.
#7 – Treatment for Female Hypoactive Sexual Desire Disorder – HSDD
It is estimated that nearly 2 out of 10 women are affected by hypoactive sexual desire disorder, which often goes undiagnosed by doctors who are not sure how to adequately address the condition, leading to the under-diagnosed and under-treated condition.
While treatments for male sexual dysfunction have been around for decades, there were no treatments available for women with a loss of sexual desire. Last year, the American Food and Drug Administration approved the first medication ever to treat female hypoactive sexual desire disorder. The medication called flibanserin can boost natural stem cells, address the loss of sexual desire in premenopausal women, and help restore sexual desire for women diagnosed with HSDD. Doctors do caution that the medication is intended to treat women with diagnosed conditions only and cannot be used as an aphrodisiac.

#8 – Non-Invasive Remote Glucose Monitoring for Diabetics
The world health organization estimates that an estimated 10% of all adults in the world over 18 have diabetes. In 2022, an estimated 2.8 million deaths were directly attributed to Diabetes, and it is estimated to become the 6th leading cause of death for humans in the next 15 years. People with diabetes require constant and invasive blood samples to monitor their glucose levels. In 2020, tests requiring blood and skin penetration might finally be replaced with a non-invasive skin-top biosensor that will automatically measure insulin levels and report the results in real-time to the patient and their respective doctors.

Needle-free glucose monitoring is one of many new remote health monitoring technologies considered “frictionless” and “painless” since it requires virtually no actions from the patient. Treatment for diabetes should be the primary goal for diabetics, as uncontrolled glucose levels can cause significant health complications and even death. The new system of continuous glucose monitoring offers patients a uniquely proactive approach to preventing the condition from getting worse by making sure glucose levels stay close to the advised reference range found in people without diabetes.
#9 – Innovative Approach to Blood Clot Removal
Pulmonary embolisms (PEs) rank as the third most common cause of cardiovascular mortality in the United States, trailing only behind heart attacks and strokes. Each year, PEs lead to the hospitalization of millions of individuals and are responsible for 500,000 fatalities. Typically, these clots originate in the deep veins of the legs before migrating to the lungs, necessitating prompt and intensive treatment to avert damage to the heart and lungs.
A groundbreaking device in this treatment arsenal is the Endovascular Catheter. This device is delicately maneuvered through the bloodstream to the lungs, which deploys an expandable infusion basket directly into the clot. This mechanism creates multiple pathways for blood circulation while simultaneously dispensing a clot-busting medication directly into the clot itself.
Since its introduction in 2023, the use of Endovascular Catheters has emerged as a key option in the arsenal against pulmonary embolisms, particularly for medium-risk cases, which constitute up to 60% of PE incidences. This method represents a significant advancement in managing and treating this critical condition.
Endovascular catheters can be used for a wide range of applications, including:
- Embolization: To deliver materials that can block off blood vessels feeding tumors or to stop bleeding.
- Coronary Angiography: To inject contrast dye into the blood vessels, making them visible on CT Scans or other imaging techniques, helping to diagnose conditions like blockages, tumors, or aneurysms.
- Aneurysm repair: Endovascular stent grafts are placed to reinforce weakened areas of an artery (aneurysms) and prevent rupture.
- Stent placement: To deploy stents (small, mesh-like tubes) to open up narrowed or blocked blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Thrombectomy: To remove blood clots from the blood vessels.
For more information please contact us.

