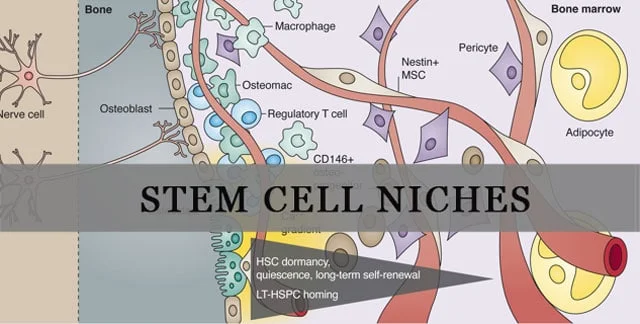
A Stem cell niche pertains to the particular tissue area where stem cells exist. The actual word ‘niche’ means the medium was “live” in vivo or in a lab or in-vitro microenvironment. [1] Recent journals and clinical studies on Mesenchymal cells from diverse systems have shown that stem cell function is controlled by extracellular cues from the niche and by intrinsic genetic programs within the cell polar body.[2]
The concept of the “stem cell niche” often refers to the specific microenvironment in which stem cells are found, and where they interact with various other cell types and extracellular factors to maintain their undifferentiated state or initiate differentiation. The niche provides the necessary biochemical and biophysical cues for stem cell self-renewal, differentiation, and proliferation. Understanding the stem cell niche is crucial for both basic biology and therapeutic applications involving stem cells.
The stem cell niche is a complex and dynamic environment made up of various components:
Understanding the mechanisms that govern stem cell niches can have profound implications for regenerative medicine and cancer therapy:
Despite its importance, the stem cell niche is not fully understood. One of the challenges is the difficulty in precisely mimicking the natural niche in the laboratory setting for studying stem cell behavior. Advanced techniques like 3D cell culture systems, organoids, and in vivo imaging are helping researchers get closer to understanding the complexities of the stem cell niche.
Other types of niches include bone marrow niches, intestine stem cell niche, brain cell niche or Haematopoietic stem cell (HSC) niches.[3]
GSC or Germline stem cells are a type of niche that can generates,sperms, haploid gametes or oocytes. Oocytes are primarily responsible for transmitting of a humans genetic information from one generation to the next generation.
The stem cell niche is a critical factor in the regulation of stem cell function, offering promising avenues for therapeutic applications but also posing challenges that require further research. Understanding and manipulating these specialized microenvironments could revolutionize stem cell therapies and offer new strategies for combating diseases, including cancer.
[1] ^ Li, Linheng, and Ting Xie. 2005. Stem cell niche: structure and function. Annual review of cell and developmental biology. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16212509
[2] ^ Ovadia, Jeremy, and Qing Nie. 2013. Stem cell niche structure as an inherent cause of undulating epithelial morphologies. Biophysical journal, no. 1 (January 8). doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.3807. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23332076
[3] ^ Yang, Sheng-An, Wen-Der Wang, Ciao-Ting Chen, Chen-Yuan Tseng, Yi-Ning Chen, and Hwei-Jan Hsu. 2013. FOXO/Fringe is necessary for maintenance of the germline stem cell niche in response to insulin insufficiency. Developmental biology, no. 1 (July 27). doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.07.018. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23895933
If you've seen people take ice baths or cold showers and wondered if they're onto… Read More
Immunomodulation stands at the forefront of biomedical research, steering the immune system's ability to fight… Read More
Stem cell research leads the charge in medical innovation, heralding revolutionary advances in regenerative medicine.… Read More
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a crucial shield for the brain, regulating the entry of… Read More
While peptide bonds are fundamental to protein structure, their direct relationship with stem cells lies… Read More
When discussing cutting-edge cancer treatments, NK cell therapy stands out due to its unique approach… Read More