Pheresis refers to the process of stem cell extraction from blood. It involves the passing of donor blood through an extraction machine and the eventual isolation of the stem cells (PDF Link) found within prior to pumping of the blood back into the heart and vascular system. The term “pheresis” (or “apheresis” from the Greek “to take away”) refers to a medical procedure in which the blood of a patient or donor is passed through an apparatus that separates out one particular component and returns the remainder to the circulation. This process allows for the selective removal or collection of specific blood components, such as platelets, plasma, or white blood cells.
In recent years, more and more people have been turning to apheresis, plasmapheresis, and plasma exchange as medical treatments. But what are these procedures, and how do they work? In this article, we’ll explore the basics of apheresis, plasmapheresis, and plasma exchange, and take a closer look at how they can help patients.
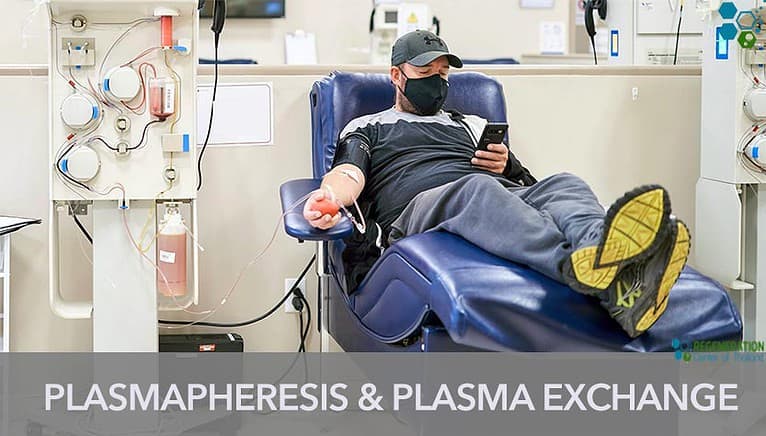
Apheresis is a medical procedure that involves removing blood from a patient, separating the blood into its individual components, and then returning the desired components to the patient. The word “apheresis” comes from the Greek word “aphairesis,” which means “a taking away.” Apheresis can be used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including autoimmune disorders, blood disorders, and neurological disorders. It can also be used to collect blood components for transfusions.
During the procedure, the patient’s blood is removed through a needle or catheter and passed through a machine called an apheresis machine. This machine separates the blood into its components, such as red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma, and platelets. The desired component is then collected, and the rest of the blood is returned to the patient.
Plasmapheresis is a type of apheresis that specifically targets the patient’s plasma. Plasma is the liquid portion of the blood that contains proteins, hormones, and other substances. Plasmapheresis is used to treat conditions that are caused by a problem with the patient’s plasma, such as autoimmune disorders. During plasmapheresis, the patient’s blood is removed, and the plasma is separated from the rest of the blood using an apheresis machine. The plasma is then discarded, and the other components of the blood are returned to the patient.
Plasma exchange is another type of apheresis that involves removing the patient’s plasma and replacing it with donor plasma or a plasma substitute. This procedure is used to treat a variety of medical conditions, including autoimmune disorders, blood disorders, and neurological disorders. During plasma exchange, the patient’s blood is removed, and the plasma is separated from the rest of the blood using an apheresis machine. The patient then receives donor plasma or a plasma substitute, and the rest of the patient’s blood is returned to them.
Apheresis, plasmapheresis, and plasma exchange can be used to treat a wide range of medical conditions. Some of the conditions that can be treated with these procedures include:
Like any medical procedure, apheresis, plasmapheresis, and plasma exchange come with some risks and side effects. Some of the potential risks and side effects can include:
It’s important to note that these risks and side effects are rare, and most patients tolerate the procedures well.
Apheresis, plasmapheresis, and plasma exchange are important medical procedures that can provide significant benefits to patients with certain medical conditions. While they do come with some risks and side effects, these are generally rare and most patients tolerate the procedures well. If you or a loved one is facing a medical condition that may be treated with apheresis, plasmapheresis, or plasma exchange, be sure to speak with your healthcare provider to determine if these procedures are right for you.
Several types of pheresis procedures exist, based on the component of blood being separated or collected:
Pheresis is a versatile medical procedure with applications in both treatment and donation, allowing for the targeted removal or collection of specific blood components.
If you've seen people take ice baths or cold showers and wondered if they're onto… Read More
Immunomodulation stands at the forefront of biomedical research, steering the immune system's ability to fight… Read More
Stem cell research leads the charge in medical innovation, heralding revolutionary advances in regenerative medicine.… Read More
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a crucial shield for the brain, regulating the entry of… Read More
While peptide bonds are fundamental to protein structure, their direct relationship with stem cells lies… Read More
When discussing cutting-edge cancer treatments, NK cell therapy stands out due to its unique approach… Read More