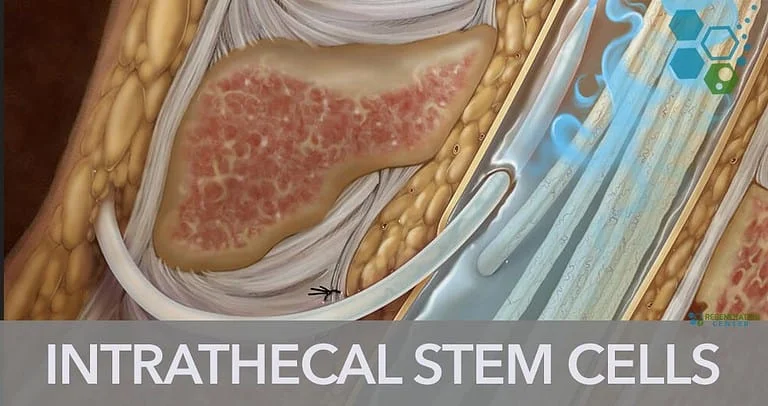
Stem cell therapy has emerged as a revolutionary new treatment approach for neurological and spinal disorders. One up-and-coming method of administering stem cells is an intrathecal application, which involves injecting the cells directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). This technique allows the stem cells to travel throughout the CSF and reach the brain and spinal cord, making it ideal for treating central nervous system conditions.
During intrathecal stem cell transplantation, a small sample of stem cells is extracted from the patient’s body or a donor. These stem cells are then cultured and multiplied in a lab before being suspended in a solution to prepare them for administration.
The stem cell solution is injected using a lumbar puncture between the lower back vertebrae directly into the CSF. This allows the cells to circulate with the natural ebb and flow of the CSF, bringing them into contact with the spinal cord and brain.
Once administered via the cerebrospinal fluid, the stem cells have the potential to:
This combination of regenerative and protective mechanisms is what makes intrathecal stem cell therapy so promising for neurological disorders.
Researchers are actively investigating intrathecal stem cell transplantation for a wide array of central nervous system conditions, including:
Injecting various stem cell types (e.g., neural stem cells, MSCs) intrathecally soon after spinal injury can help modify the lesion environment, preserve existing tissue, and support regenerative processes.
Early clinical research found intrathecal umbilical cord MSCs improved motor function in children with cerebral palsy with no severe adverse effects.
Clinical research suggests intrathecal MSCs introduced after ischemic stroke can significantly improve neurobehavioral function. The Regeneration Center has investigated safety and efficacy of Intrathecal stem cells for stroke patients.
With promising preclinical data across such a wide range of conditions, intrathecal stem cell therapy may have far-reaching therapeutic potential as long as safety and efficacy trials continue generating positive results.
Most investigational stem cell therapies for neurological disorders have relied on intravenous infusion. However, intravenously injected cells become widely dispersed throughout the body, and only a tiny fraction reaches the brain or spinal cord due to the blood brain barrier.
Intrathecal administration allows for:
These advantages make cells from iliac crest and intrathecal delivery an extremely promising avenue for administering stem cell therapies for neurological diseases. Ongoing research aims to fully elucidate the benefits of intravenous and fully establish proper cell dosing and safety parameters.
While an intrathecal approach shows tremendous potential, there are still important factors current trials aim to address:
Over the last 16 years the Regeneration Center last developed foundational protocols that deliver positive results. As our research continues, we constantly consider cost, scalability, and commercialization hurdles to translate intrathecal stem cell therapy into practical treatment applications in Regenerative healthcare.
In the coming decades, advancing stem cell culturing techniques and more selective MSC cell types will make intrathecal delivery even more targeted and effective. Stem cell activations via gene editing may also enhance their therapeutic properties.
With so many neurodegenerative diseases lacking adequate treatment options, unlocking the full potential of intrathecal stem cell therapy could transform how we treat debilitating conditions like ALS, MS, Alzheimer’s and spinal cord injuries. While more rigorous clinical trials are still needed, this innovative delivery strategy demonstrates immense promise for healing the injured and diseased central nervous system.
Intrathecal stem cell injection into the CSF allows widespread delivery to the spinal cord and brain to target neurological diseases. Direct CSF injection enables better stem cell engraftment compared to intravenous infusion. Proper cell dosing, safety parameters, and functional impacts are still being optimized. Advancing cell types and activation methods may further enhance intrathecal therapy potential.
The Regeneration Center aims to translate this innovative delivery approach into safe, effective new cell based interventions. To learn more please contact us.
If you've seen people take ice baths or cold showers and wondered if they're onto… Read More
Immunomodulation stands at the forefront of biomedical research, steering the immune system's ability to fight… Read More
Stem cell research leads the charge in medical innovation, heralding revolutionary advances in regenerative medicine.… Read More
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a crucial shield for the brain, regulating the entry of… Read More
While peptide bonds are fundamental to protein structure, their direct relationship with stem cells lies… Read More
When discussing cutting-edge cancer treatments, NK cell therapy stands out due to its unique approach… Read More