The human body contains two primary types of cells:
- Haploid cells
- Diploid cells
Haploid Vs Diploid
Haploid cells pertains to the number of chromosomes found in a gamete or represents half of the normal chromosome count in a particular somatic cells. The primary difference between haploid and diploid cells are the total number of chromosomes they consist of.[1]
The haploids are also called gametes. During the process of meiosis, the homologous chromosomal pairs separate to produce 2 haploid daughter cells.[2]
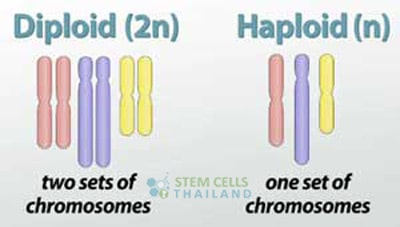

When sex cells such as egg and sperm meet, the combined genetic material creates a full 46 chromosomes becoming diploid.Thus human Sexual reproduction is designed as a natural method of producing genetically diverse offspring.[3]
To learn more or if you have any other questions please contact us today.
Published Clinical Citations
[1] ^ Mahasup, Namfon, Paskorn Sritipsukho, Raweewan Lekskulchai, and Tippawan Hansakunachai. 2012. Effects of mirror neurons stimulation on motor skill rehabilitation in children with cerebral palsy: a clinical trial. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand = Chotmaihet thangphaet. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23964461
[2] ^ Easley, Charles A, Bart T Phillips, Megan M McGuire, Jennifer M Barringer, Hanna Valli, Brian P Hermann, Calvin R Simerly, et al. 2012. Direct differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells into haploid spermatogenic cells. Cell reports, no. 3 (August 23). doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2012.07.015. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22921399
[3] ^ Matangkasombut, Oranart, Roongtiwa Wattanawaraporn, Keiko Tsuruda, Masaru Ohara, Motoyuki Sugai, and Skorn Mongkolsuk. 2009. Cytolethal distending toxin from Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans induces DNA damage, S/G2 cell cycle arrest, and caspase- independent death in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae model. Infection and immunity, no. 2 (December 7). doi:10.1128/IAI.00857-09. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19995894